Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for clinical psychologisits
- 1. Introduction to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Dr Nastaran Otared
- 2. Scenario 1: Job Interview Rejection Alex, a recent graduate, feels nervous and excited about their first job interview. Despite preparing thoroughly, they worry about making a good impression and competing against more experienced candidates. Alex hopes this job will be the start of a successful career. Negative Automatic Thoughts: 1."I'm not good enough for any job." 2."Everyone else is better than me." 3."I'll never succeed in my career." 4."I'm a failure." 5."No one will ever hire me." 6."I messed up and it's all my fault." 7."There's something wrong with me." 8."This rejection proves I'm not capable."
- 3. Scenario 2: Receiving Criticism from a Friend Description of Someone: Jamie, who values their close friendships deeply, feels sensitive about maintaining these relationships. After a misunderstanding leads to criticism from a friend, Jamie starts to doubt their self-worth and fears the impact this incident may have on their friendship. Negative Automatic Thoughts: 1."My friend hates me." 2."I'm a bad friend." 3."I always say the wrong thing." 4."No one likes spending time with me." 5."I'm unworthy of love or friendship." 6."I can never do anything right." 7."This criticism means I'm a terrible person." 8."Everyone must be talking about how awful I am."
- 4. Think about the last time you felt depressed or anxious and write your negative thoughts.
- 5. WHAT IS COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY? CognitiveTherapy+BehavioralTherapy=CognitiveBehavioralTherapy Cognitive Model: The cognitive model focuses on thinkingand how our thoughts are connected to our mood, physiological responses, and behaviors Cognitivetherapy will teach you to change your thoughts, beliefs,and attitudes that contributeto yourproblems. Two people can be faced with similar situations, but because they think about those situations in different ways,theyhave different reactions to them.
- 7. Example 1 Situation: You send a message to a friend and they don't reply for several hours. Automatic Thought: "They're ignoring me because they don't like me anymore." Reaction: •Emotional: You feel sad, rejected, and anxious. •Behavioral: You might avoid contacting other friends for fear of being ignored again, or you might obsessively check your phone for a reply. •Physical: You could experience stomach aches or headaches due to the stress and anxiety from these thoughts.
- 8. Example 2 Situation: You receive a lower grade than expected on a project at work. Automatic Thought: "I'm incompetent and I'm going to lose my job." Reaction: •Emotional: You feel embarrassed, disappointed in yourself, and fearful about your job security. •Behavioral: You might work late hours to compensate, avoid taking on new projects for fear of failure, or not ask for feedback to avoid further criticism. •Physical: You may have trouble sleeping, lose appetite, or experience increased stress levels.
- 9. BEHAVIORAL MODEL “Depressedindividualsdo not get enough positive reinforcementfrom interactionswith their environment to maintain happy,adaptive behavior. Two behavioral patterns associated with depression: Low levelof positive feelings from engagingin life activities No longer participating in enjoyableactivities Not getting as much enjoyment in activities as in the past No longer enjoying socializing with others High rate of negative consequences Frequently noticing things are not working out Feeling a lack of support and understanding from others
- 10. History of CBT
- 11. COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL MODEL Wenzel, A., Brown, G. K., & Karlin, B. E. (2011). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Depression in Veterans and Military Servicemembers: Therapy Manual. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs.
- 12. CBT is evidence based. CBT has been well tested in research studies and has been provento be effectiveintreating mental health problems. CBT is structured. You should expect to have a good idea of where you’re going and how to get there. So, we will set clear goals to create a roadmap that will help us find the best way to improve your symptoms. During each session we will set an agenda for what we want to discuss, we will discuss last week’s practice assignment, discuss agenda items, and then assignnewhomework. CBT is psychoeducational. The entire program is skill based and involves you enhancing your skill set. You will learn different “tools” to help cope with your current problems that you will be able to take with you when treatment is over. CBT is goal oriented. We will work together to identify and achieve specific treatmentgoals. We will trackyourprogresson yourgoals and problemsolveways to reach them. CBTis time limited. Treatment is usually 8-20weeks.
- 13. CBT requires you to attend weekly sessions. Regular attendance is essential to recovery. Sessions areapproximately 50 minutes long. CBT requires active participation. What you get out of treatment is a direct result of the effort you put into it. Just showing up is not enough. We need you to be anactivepartner in yourtreatment process. CBT has a home practice requirement. Treatment is challenging and takes daily commitment from you to be successful. CBT is not a one time therapy. It is not an instant change that you will immediately notice after one session. Practice assignments help put your new skills to use. CBT focuses on the here and now. Treatment emphasizes how depression is maintained in yourpresent life. CBT is collaborative. Although the therapist is the expert on CBT, you are the experton yourself. We will worktogetherto tailoryourtreatment to yourneeds.
- 14. What is Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)? A PROBLEM- ORIENTED THERAPY FOCUS ON PRESENTAND FUTURE SHORT-TERM FORMAT SESSIONSARE STRUCTURED INVOLVESA STRONG WORKING ALLIANCE HOMEWORK IS A CENTRAL FEATURE BASED ON COGNITIVE THEORY REQUIRES COLLABORATIVE EMPIRICISM
- 17. Core beliefs are like the big ideas we have about ourselves, other people, and life. They're the main thoughts that we believe really deep down, even if we don't always talk about them. Core beliefs are formed through a variety of experiences, including our upbringing, cultural background, significant life events, and relationships.
- 18. We can split core beliefs into three kinds: 1.About Ourselves: These are thoughts like "I'm good at making friends" or "I'm bad at sports." They're what we think about who we are. 2.About Others: These beliefs might be like "People are mostly kind" or "You can't trust anyone." They're our ideas about what other people are like. 3.About the World: These are big ideas like "The world is a beautiful place" or "Life is hard." They're what we think life in general is like. So, if someone grows up being told they're smart and does well in school, they might believe "I am smart." If they see people helping each other, they might think "People are helpful." And if they find fun things to do, they might believe "The world is an exciting place." These are examples of core beliefs.
- 19. Intermediate beliefs are the beliefs that lie between core beliefs and automatic thoughts. Core beliefs are deeply ingrained beliefs about ourselves, others, and the world, while automatic thoughts are the immediate thoughts that pop into our minds in response to situations. Intermediate beliefs, are more specific than core beliefs but more general than automatic thoughts. They often reflect our attitudes, rules, expectations, and assumptions about various aspects of life. Intermediate beliefs can be either helpful or unhelpful, and they play a significant role in shaping our interpretations of events and our emotional reactions to them
- 20. 1.Rules: These are rigid guidelines or principles that individuals feel they must adhere to in order to feel safe, worthy, or in control. For example, someone might have a rule that says, "I must always please others," or "I should never make mistakes.“ 2.Assumptions: Assumptions are underlying beliefs about how the world works or how people should behave. They are often taken for granted and can influence interpretations of events. An example of an assumption might be, "If I fail at something, it means I'm incompetent," or "People will always disappoint me.“ 3.Attitudes: Attitudes are general evaluations or feelings toward certain people, objects, or situations. They can be positive, negative, or neutral and influence how individuals approach various aspects of life. For instance, someone might have a negative attitude toward authority figures, believing that they are always trying to control others.
- 21. Automatic thoughts are rapid, reflexive streams of thought that occur in response to situations. They are often influenced by underlying beliefs and past experiences, and can intensify or alleviate emotions. These thoughts are characterized by their speed, emotional impact, and tendency to follow certain patterns or themes. In cognitive-behavioral therapy, individuals learn to identify and challenge automatic thoughts to promote more balanced thinking and reduce distress.
- 22. Situation: Giving a presentation at work. Automatic thought: "Everyone is going to think I'm incompetent because I stumbled over my words." Situation: Receiving a text message from a friend inviting you to a social event. Automatic thought: "They only invited me out of pity; they probably don't really want me there."
- 23. Scenario: Sarah is preparing for a job interview at a prestigious company. As she reviews her qualifications and prepares answers to potential interview questions, she begins to feel increasingly anxious about the upcoming interview. Core beliefs? Intermediate beliefs? Automatic beliefs?
- 24. Core Belief: Sarah's core belief might be "I am not good enough." This deep-seated belief stems from past experiences of feeling inadequate and unworthy, such as receiving criticism from a former boss or comparing herself unfavorably to others. Intermediate Beliefs: she might hold the rule "I must always excel in everything I do" or the assumption "If I make a mistake, it means I am a failure." These beliefs shape her expectations and standards for herself, leading to heightened anxiety about the interview. Automatic Thoughts: She thinks, "They're going to see right through me," "I'll never get this job," and "I'm going to embarrass myself."
- 25. 1.Downward Arrow Technique 2.Thought Records 3.Socratic Questioning 4.Imagery-Based Techniques 5.Life History Timeline 6.Behavioral Experiments 7.Values Clarification 8.Core Belief Worksheet 9.Belief Driven Formulation 10.Dysfunctional Thought Record 11.ABC Model (Activating Event, Belief, Consequence) 12.Role-Playing 13.Chair Work 14.Pie Chart Technique 15.Continuum Techniques 16.Historical Test of Beliefs 17.Identifying Cognitive Distortions 18.The Two-Column Technique 19.Cost-Benefit Analysis (Decisional Balancing) 20.Perspective-Taking Exercises
- 26. Downward Arrow Technique The Downward Arrow Technique is a cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) tool used to uncover deeper, underlying core beliefs from surface-level automatic thoughts. The process involves repeatedly asking the client to consider what their automatic thought says about them, leading to a deeper exploration of their beliefs about themselves, others, and the world. This technique helps reveal the core beliefs that fuel emotional distress and dysfunctional behavior.
- 27. Situation: A client is upset because they were not selected for a project at work. Automatic Thought: "I was not chosen for the project because I'm not good enough.“ Using the Downward Arrow Technique: 1.Therapist: "What does it mean about you that you weren't chosen for the project?“ 2.Client: "It means I'm not skilled enough.“ 3.Therapist: "And if you're not skilled enough, what does that say about you?“ 4.Client: "That I'm incompetent."
- 28. 1.Therapist: "What does being incompetent mean to you on a deeper level?“ 2.Client: "That I'll never succeed in my career.“ 3.Therapist: "And what would it mean about you if you never succeed in your career?“ 4.Client: "That I'm a failure.“ 5.Therapist: "And if you're a failure, how does that make you feel about yourself?“ 6.Client: "That I'm worthless."
- 29. Situation: A client is extremely anxious about an upcoming public speaking engagement. Automatic Thought: "I'm going to embarrass myself in front of everyone.“ 1.Therapist: "What does it mean about you if you embarrass yourself?“ 2.Client: "It means I'm not capable of speaking in public.“ 3.Therapist: "And if you're not capable of speaking in public, what does that say about you?“ 4.Client: "That I'm inadequate."
- 30. 1.Therapist: "What does being inadequate mean to you on a deeper level?“ 2.Client: "That I'm not as good as others.“ 3.Therapist: "And what would it mean about you if you're not as good as others?“ 4.Client: "That I'm worthless."
- 31. Situation: A client feels anxious and insecure in their romantic relationship. Automatic Thought: "My partner is going to leave me." 1.Therapist: "What does it mean about you if your partner leaves you?" 2.Client: "It means I'm not lovable." 3.Therapist: "And if you're not lovable, what does that say about you?" 4.Client: "That there's something fundamentally wrong with me." 5.Therapist: "What does having something fundamentally wrong with you mean on a deeper level?" 6.Client: "That I'm flawed and undeserving of love." 7.Therapist: "And if you're flawed and undeserving of love, how does that make you feel about yourself?" 8.Client: "That I'm alone and always will be."
Editor's Notes
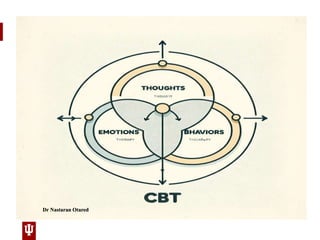
- There is a bidirectional arrow between Situation and Thought, indicating that situations influence thoughts and vice versa. Thoughts influence Emotions, as shown by the arrow pointing from Thought to Emotion. Emotions influence Behaviors, with an arrow pointing from Emotion to Behavior. Behaviors also influence Situations, shown by the arrow pointing from Behavior back to Situation. There's a dotted line from Behavior to Emotion, suggesting that behaviors can have a direct effect on emotions as well.
- Analogical model between tree and cognitive model
- For example, consistent positive reinforcement from parents might lead to the development of the core belief that "I am lovable," whereas persistent criticism might foster a belief such as "I am not good enough."