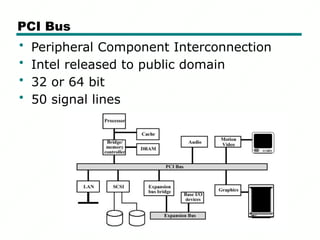
The document outlines the organization and architecture of computers, focusing on the interconnection of various units such as memory, CPU, and input/output components. It discusses the types of buses used for communication, including data, address, and control buses, as well as the differences between dedicated and multiplexed buses. Additionally, it covers bus arbitration methods, emphasizing centralized versus distributed approaches.