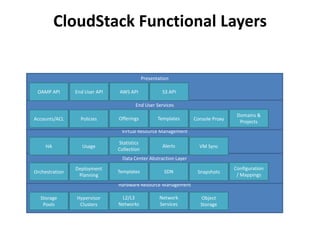
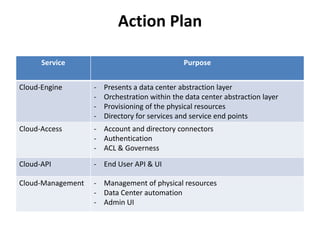
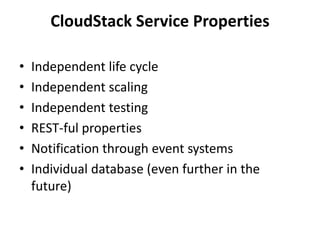
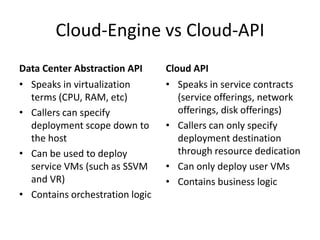
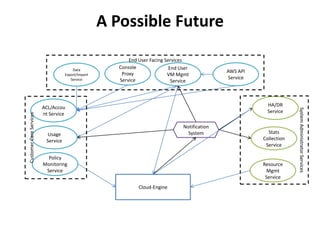
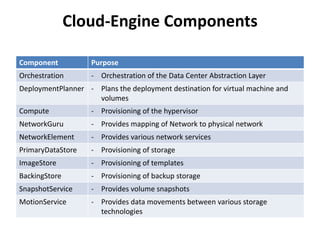
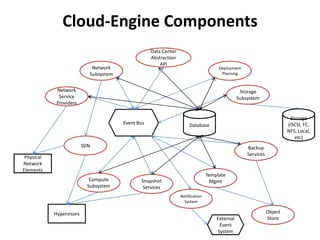
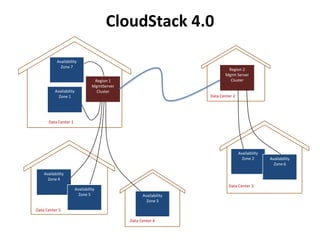
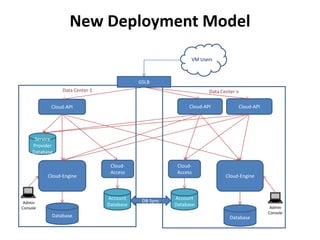
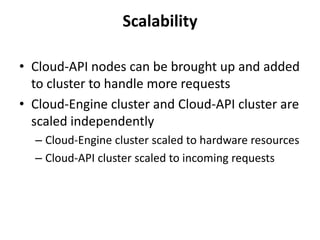
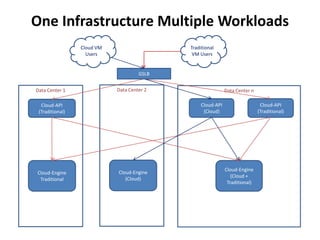
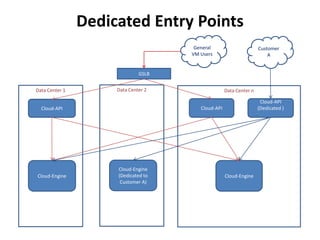
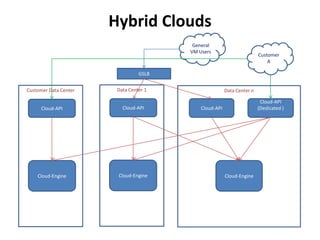
The document outlines a proposal by Alex Huang for the evolution of Apache CloudStack, aiming to enhance developer experience, deployment flexibility, and system maintainability through service disaggregation and improved orchestration. Key action items include redefining cloud architecture, independent scaling of components, and employing well-known frameworks, which will facilitate easier integration and reduced interdependencies. Challenges such as ensuring reliability and adapting developer skill sets are acknowledged, along with a roadmap for implementation milestones.