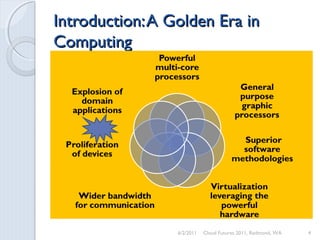
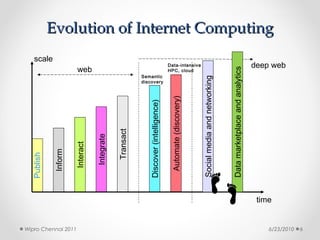
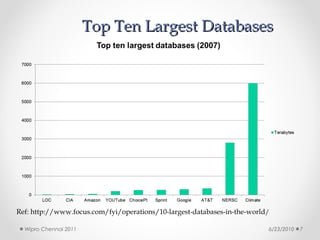
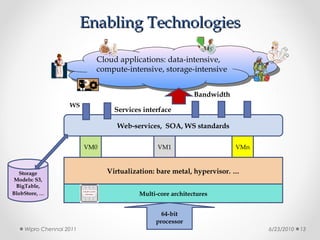
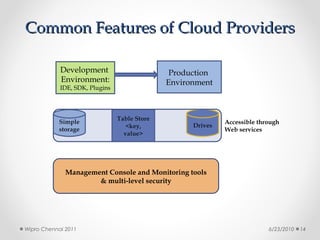
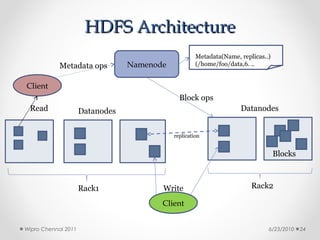
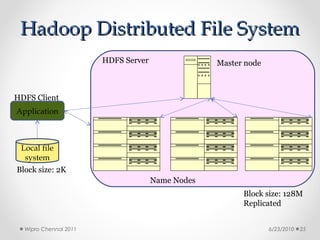
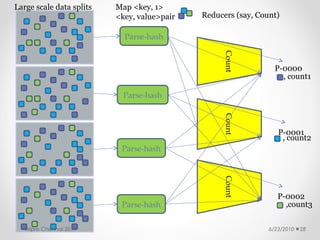
This document discusses cloud computing concepts, technologies, and business implications. It provides an introduction to cloud models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It also demonstrates cloud capabilities through examples of cloud models, data and computing models using MapReduce, and graph processing using Amazon Elastic MapReduce. The document discusses enabling cloud technologies including virtualization, multi-core architectures, and web services interfaces.