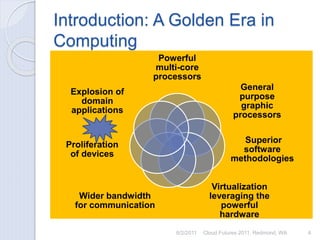
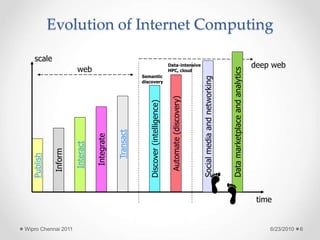
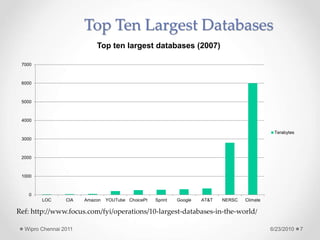
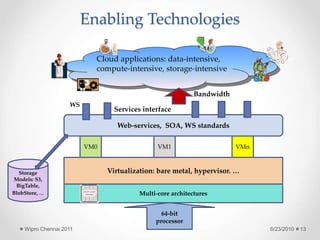
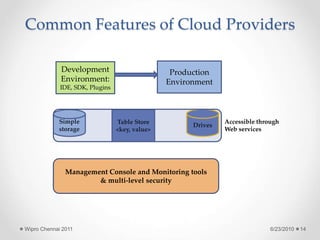
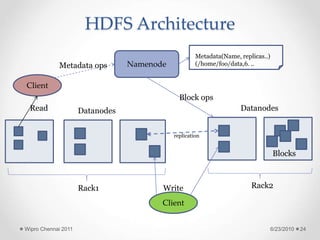
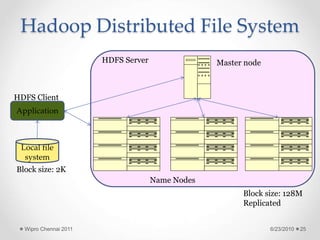
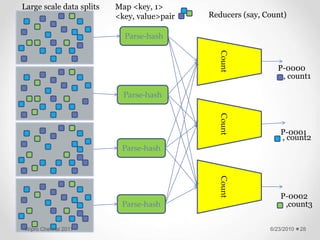
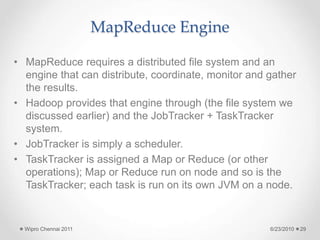
The document discusses cloud computing concepts and technologies. It provides an introduction to cloud models like IaaS, PaaS and SaaS and demonstrates cloud capabilities through examples on Amazon AWS, Google App Engine and Windows Azure. It also discusses the Hadoop distributed file system and MapReduce programming model for large scale data processing in the cloud.