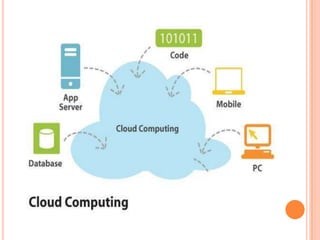
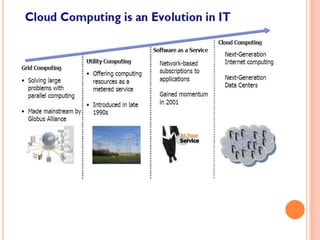
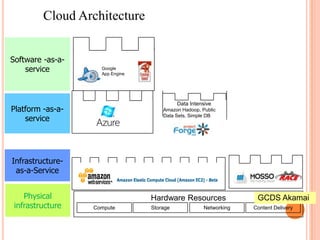
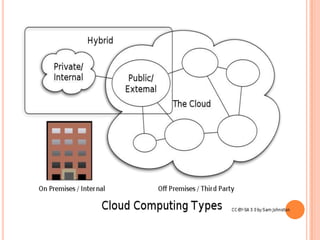
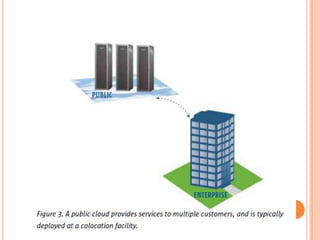
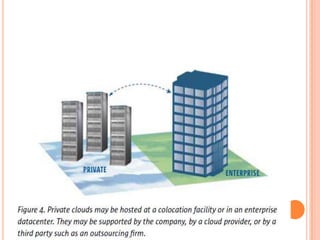
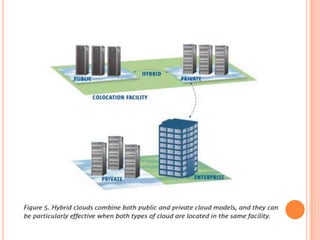
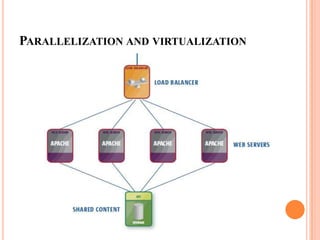
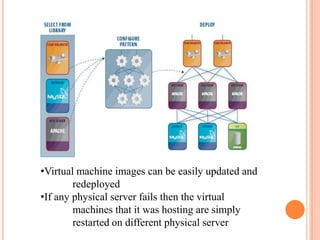
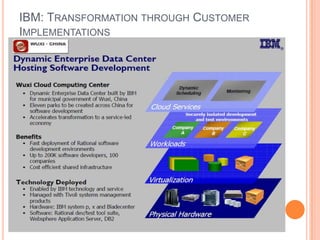
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing, including its components, architecture, types of clouds, and virtualization. It discusses how cloud computing provides scalable and on-demand computing resources through virtual machines. The key components of cloud computing are clients, services, and the cloud infrastructure, which includes compute, storage, and networking resources. There are three main types of cloud services: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Virtualization allows for server consolidation and improved efficiency. Related works from Microsoft, IBM, and Cisco are also summarized.