The document discusses a service operator-aware trust scheme (SOTS) for resource matchmaking across multiple clouds, aiming to enhance user trust and system dependability by modeling trust evaluation through multi-attribute decision-making. It develops an adaptive trust evaluation approach based on information entropy theory, overcoming limitations of traditional trust methods. The proposed scheme is designed to accurately identify trusted resources and improve resource dependability in cloud environments.

![ABSTRACT
Service Operator-aware Trust Scheme (SOTS)[multi-dimentional
resource service operator]
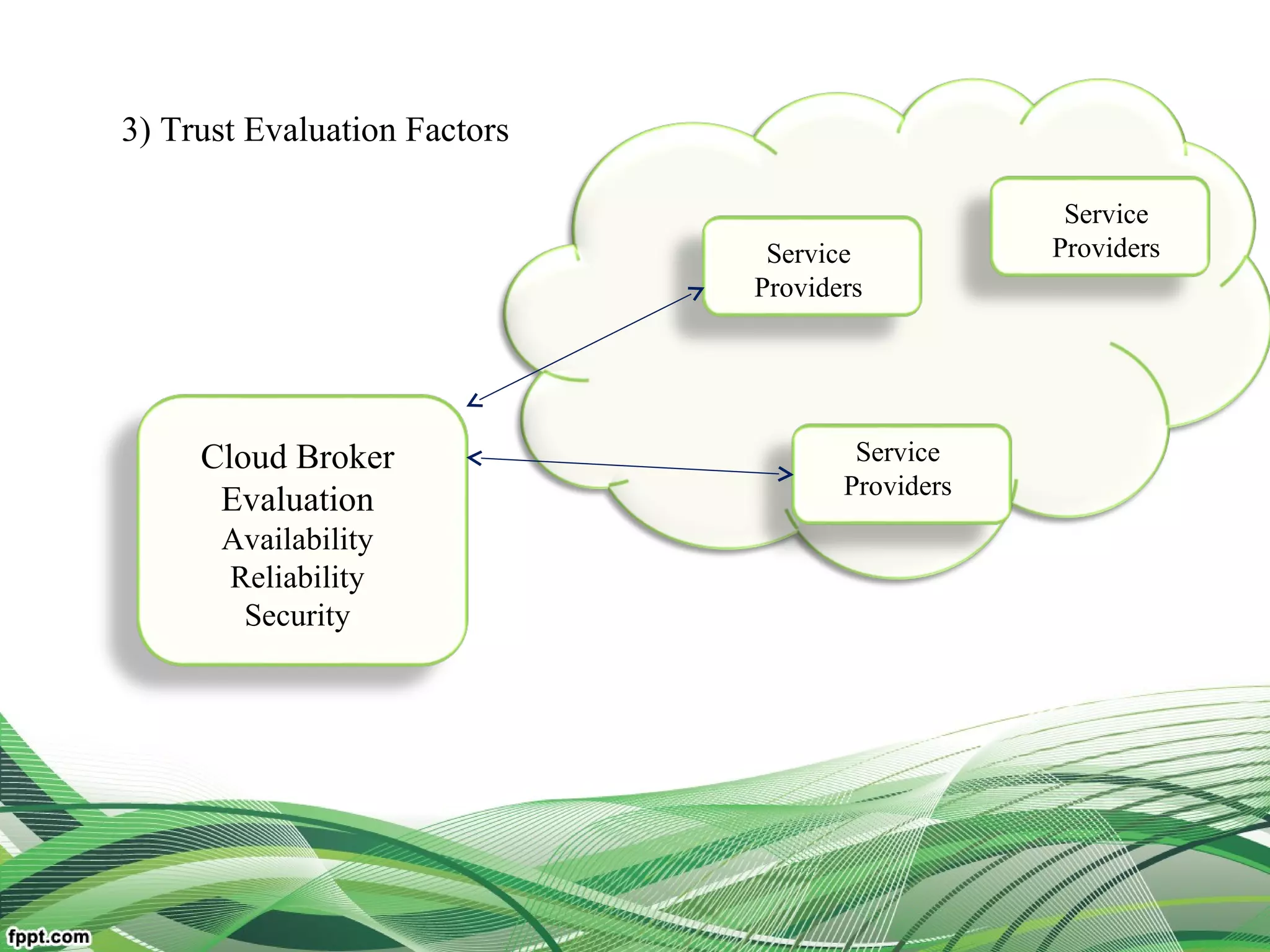
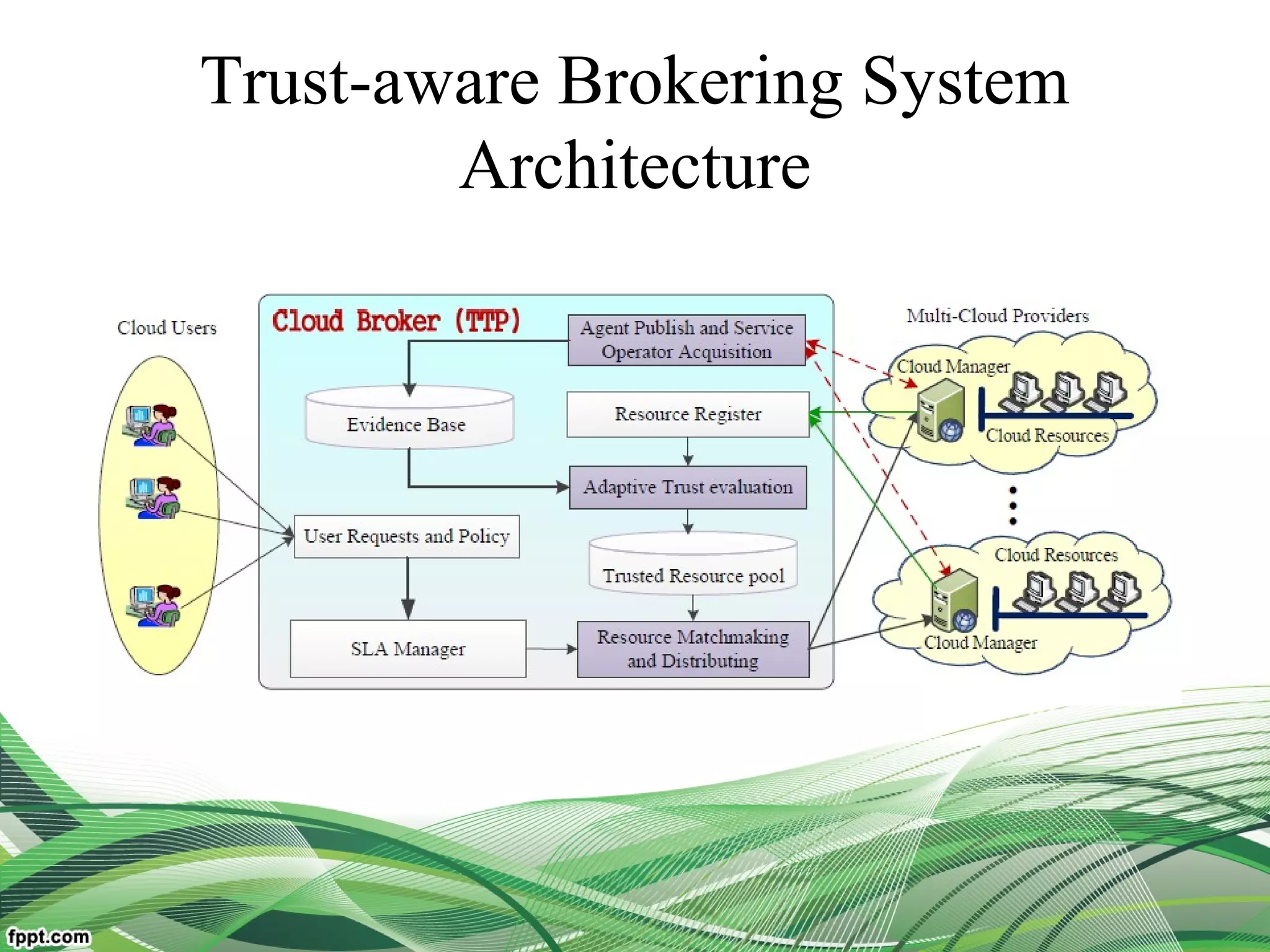
For resource matchmaking across multiple clouds
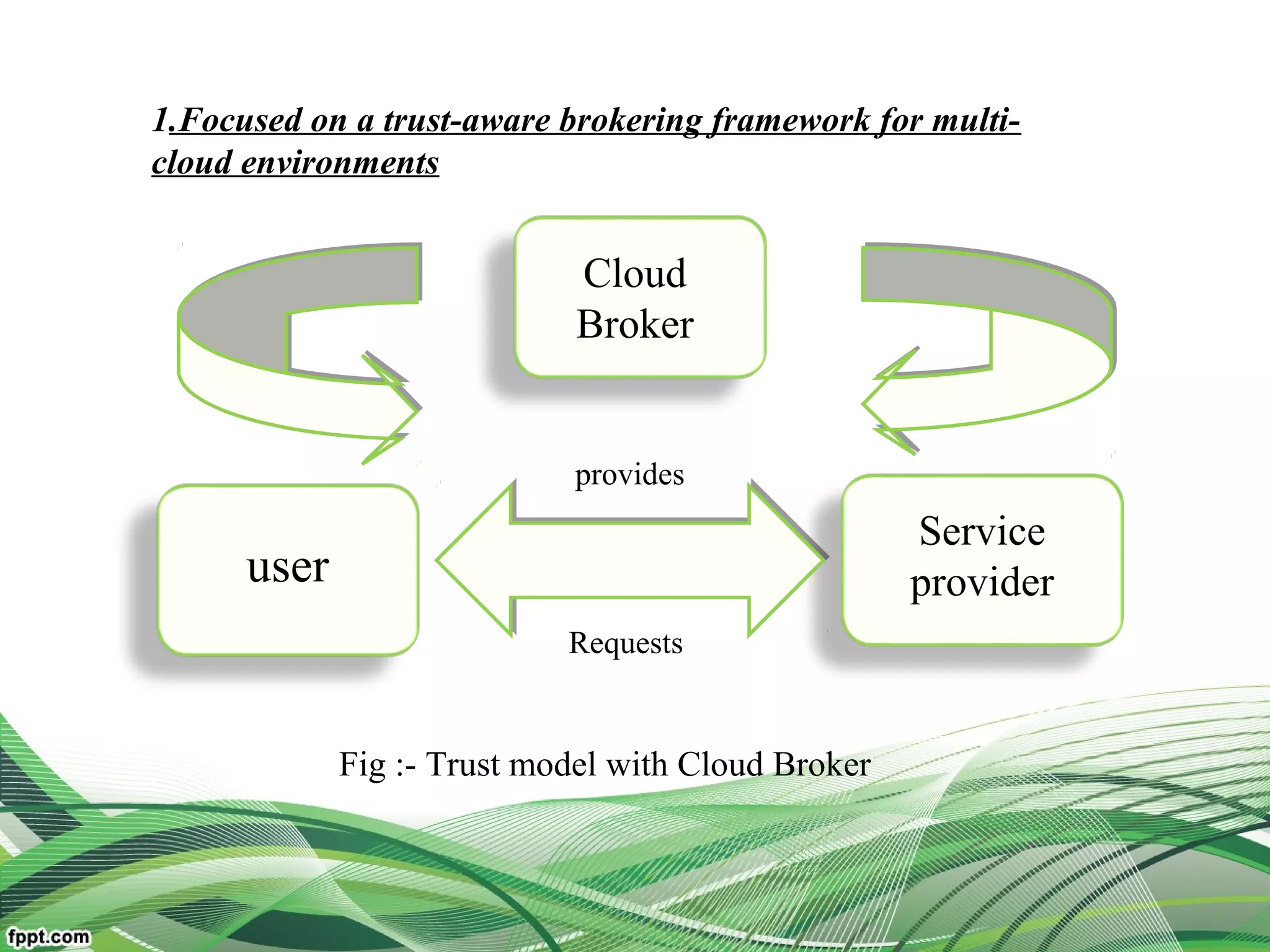
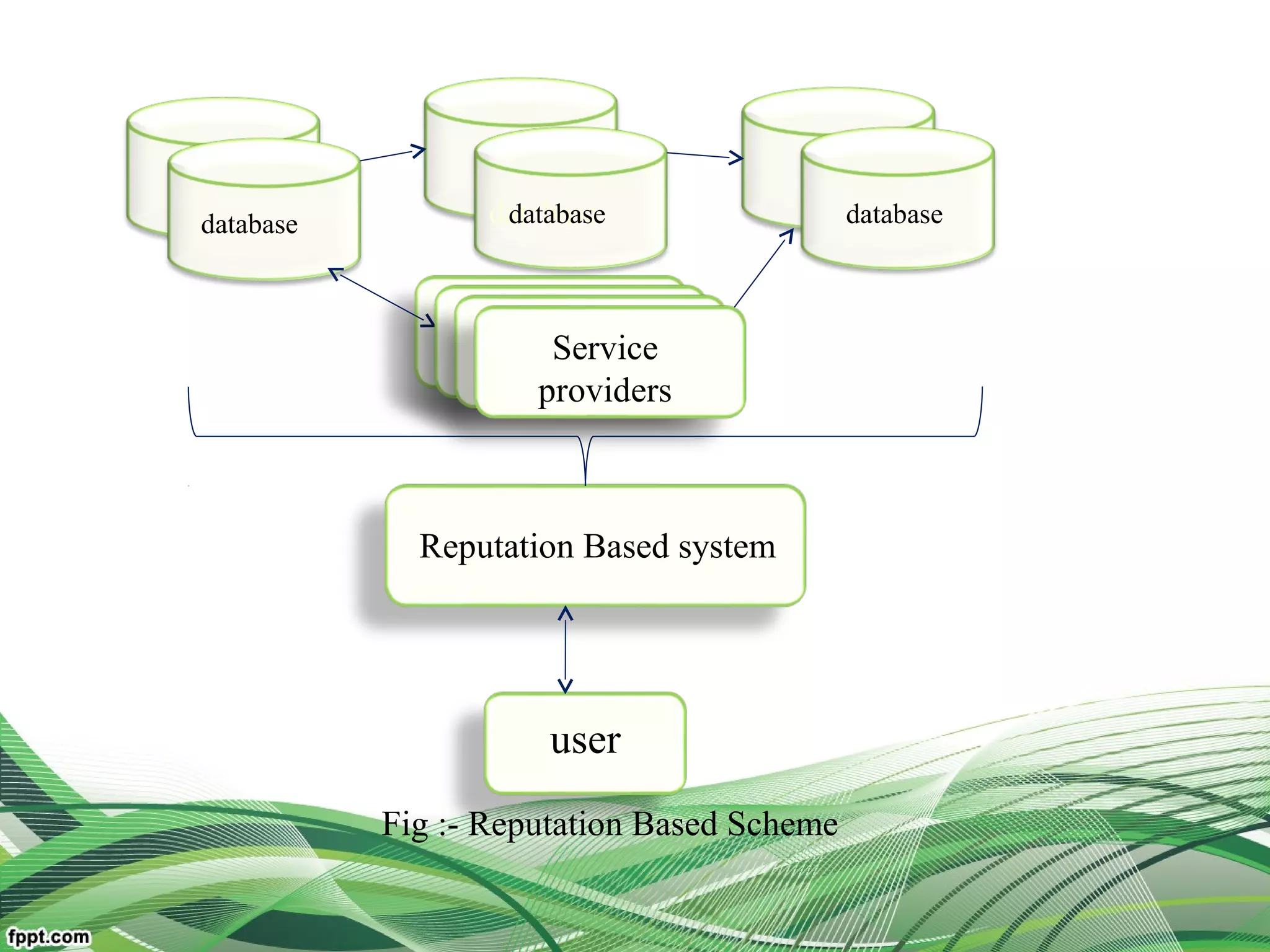
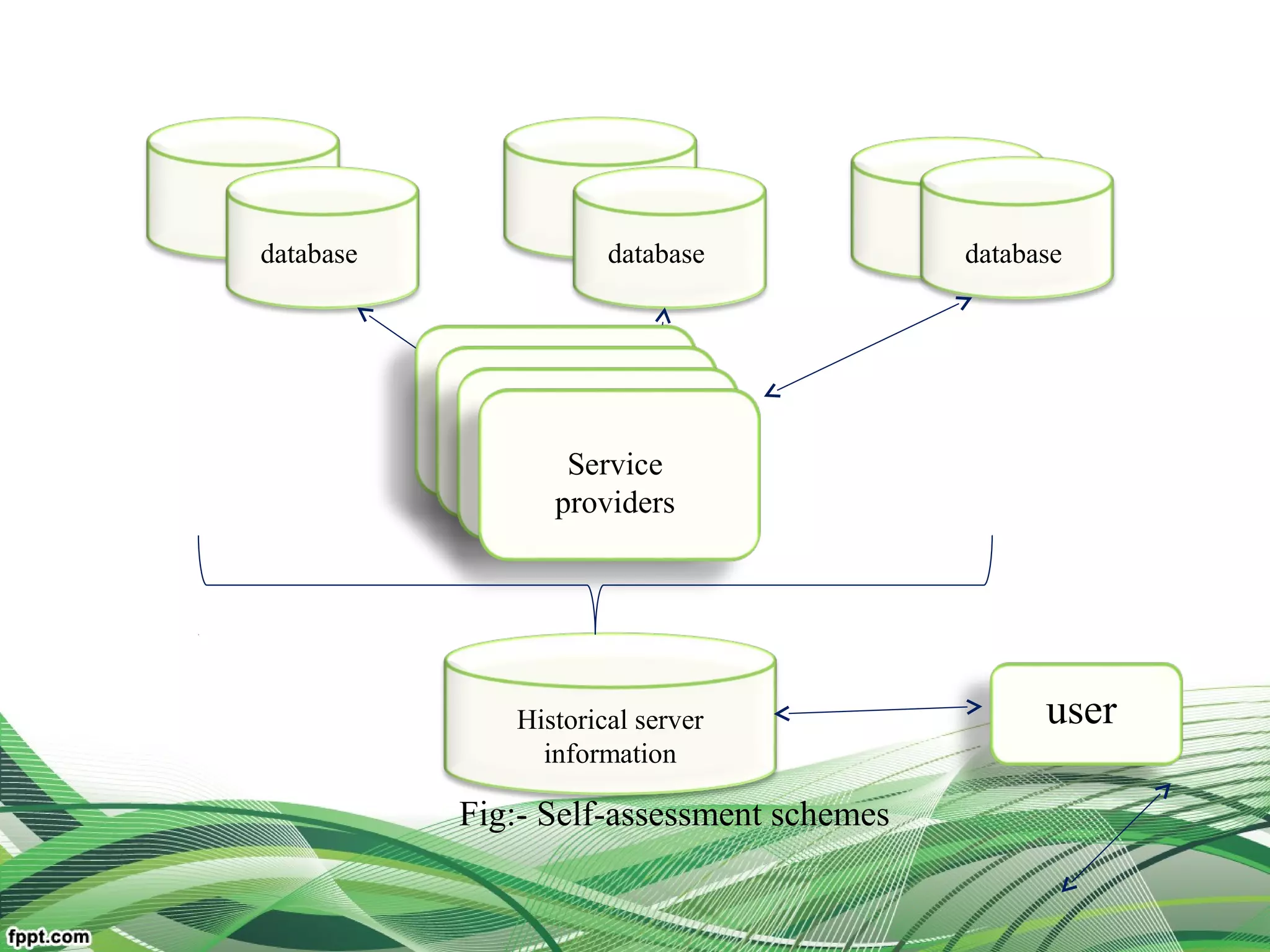
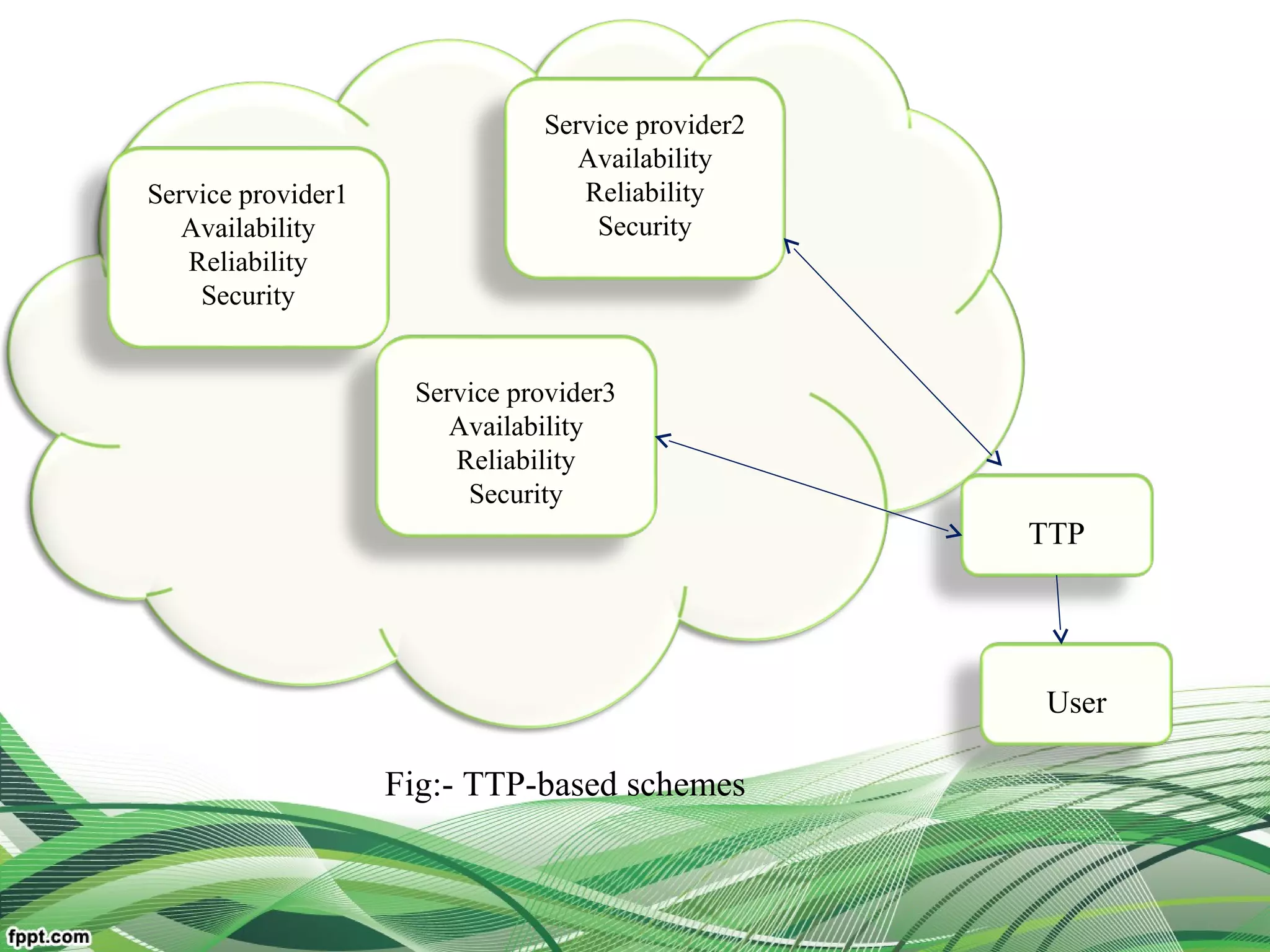
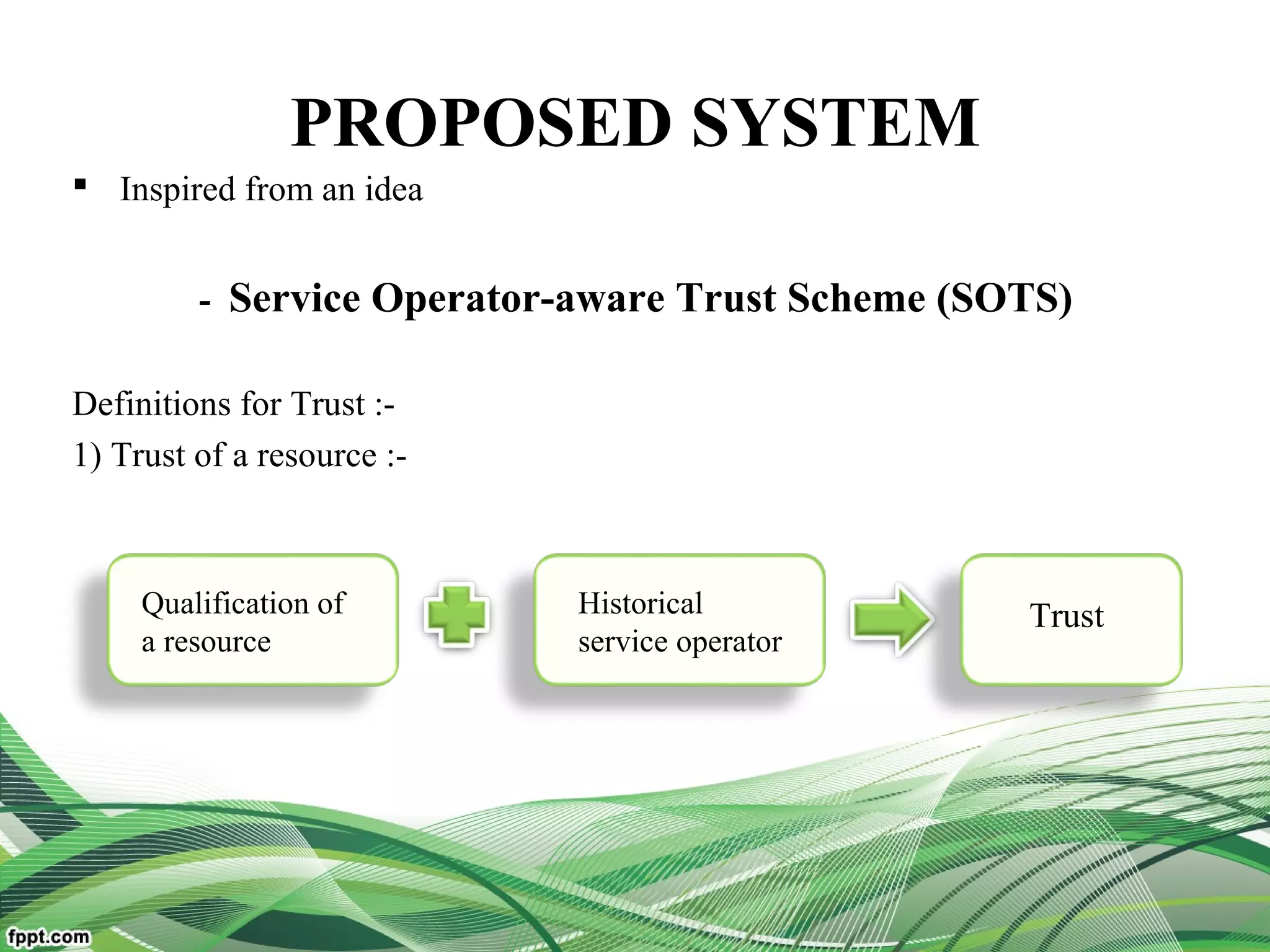
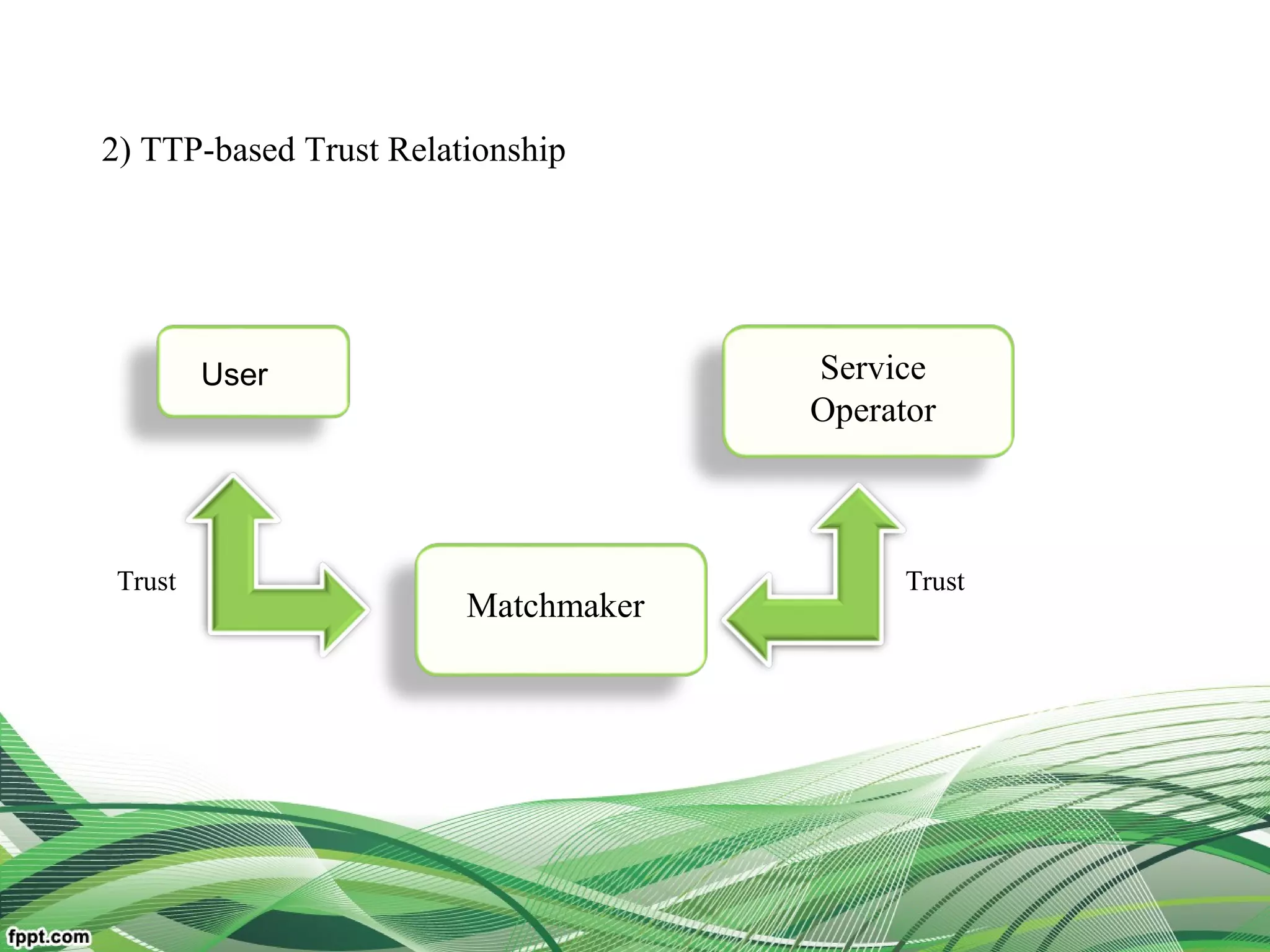
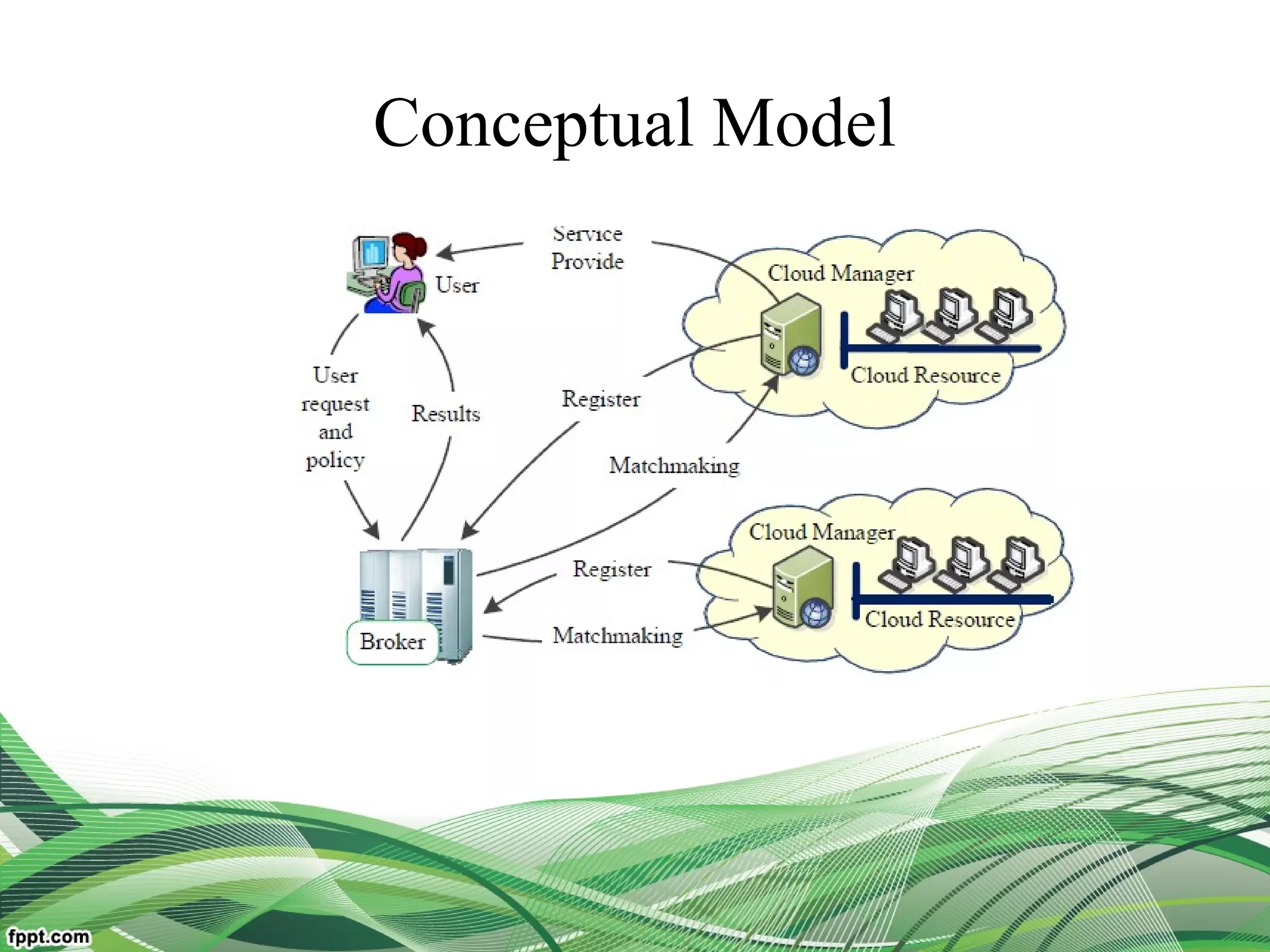
Explain relationship between the users, broker, the service
resources(middleware framework of trust)
Reduce user burden and improve system dependability
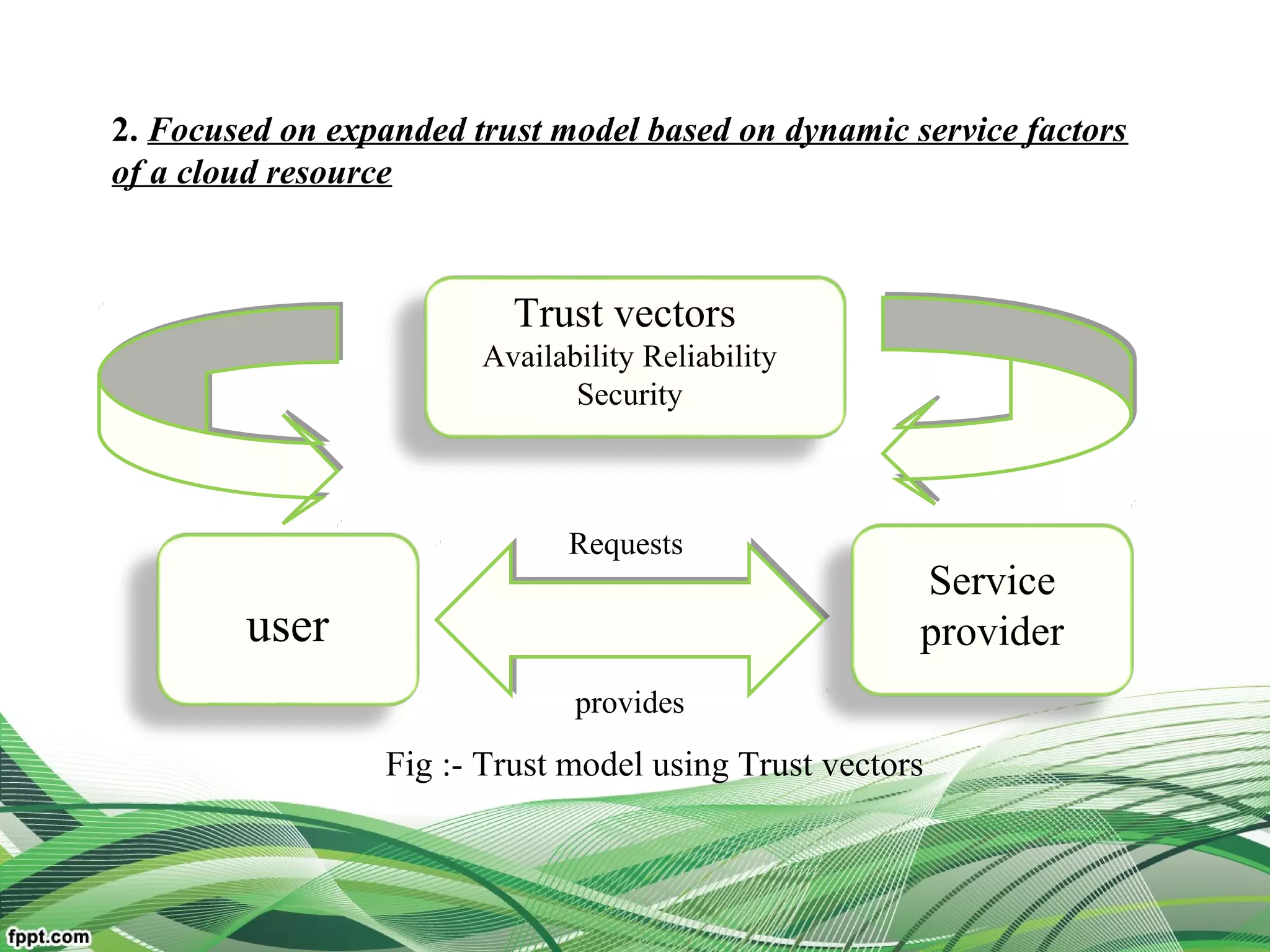
Model the problem of trust evaluation by multi-attribute decision-making
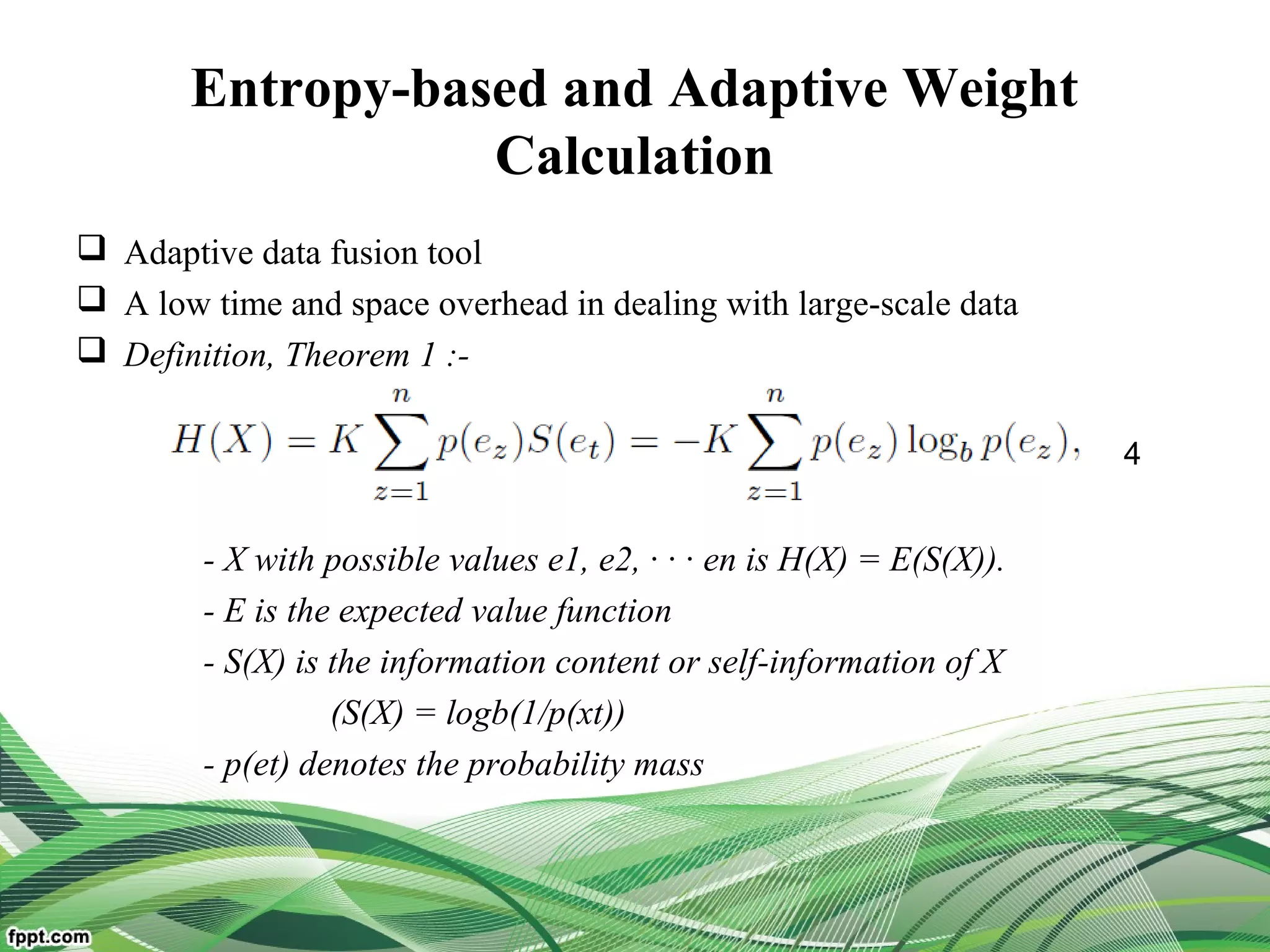
Develop an adaptive trust evaluation approach on information entropy
theory
To overcome the limitations of traditional trust schemes
the broker can efficiently and accurately prepare the most trusted resources
provide more dependable resources to users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160308064034/75/cloud-computing-service-operator-aware-trust-scheme-2-2048.jpg)










![Real-trust Trust Degree (RTD)
Evaluate recent cloud resource service operators
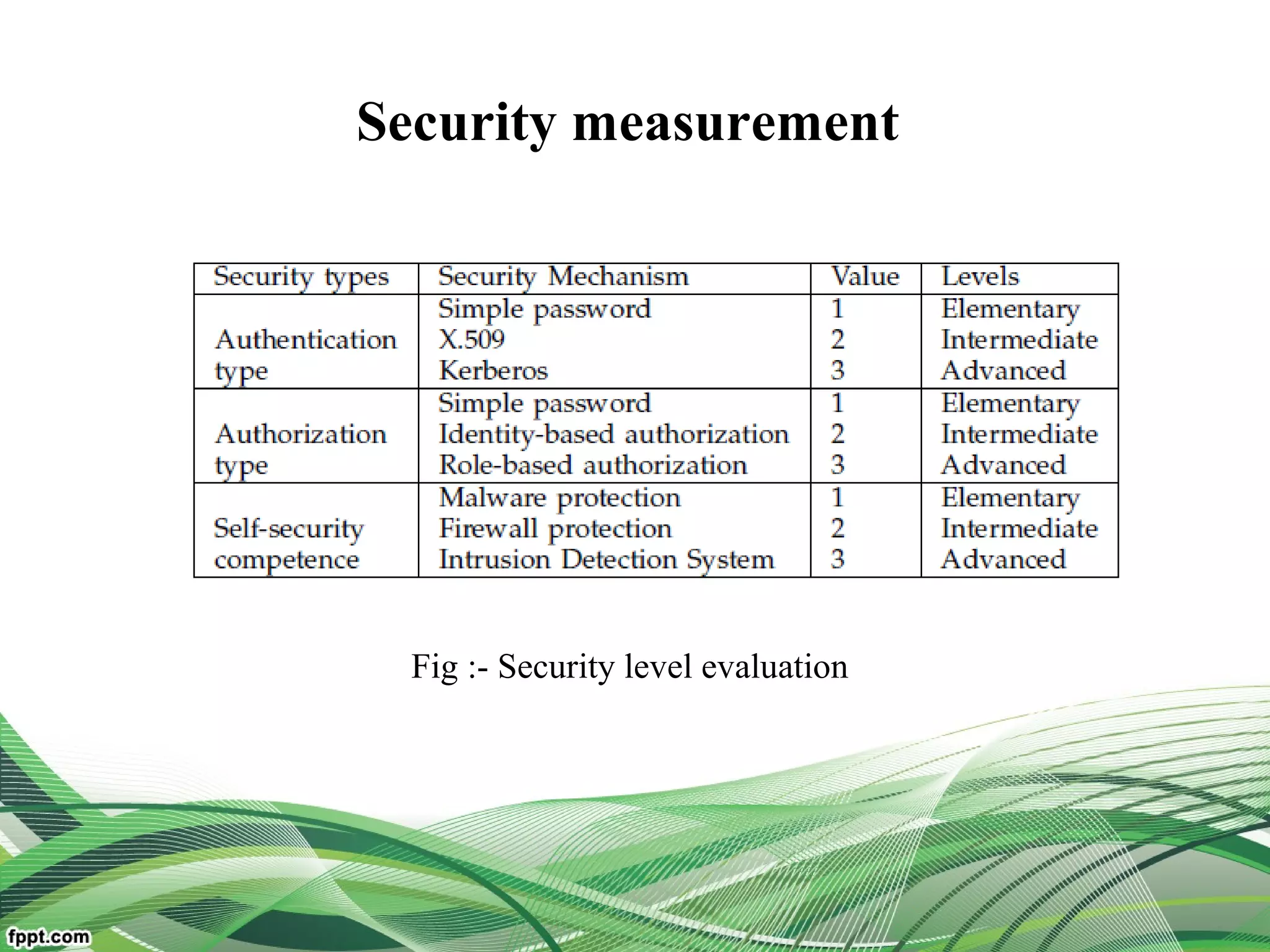
Evaluated by resource’s quality of service
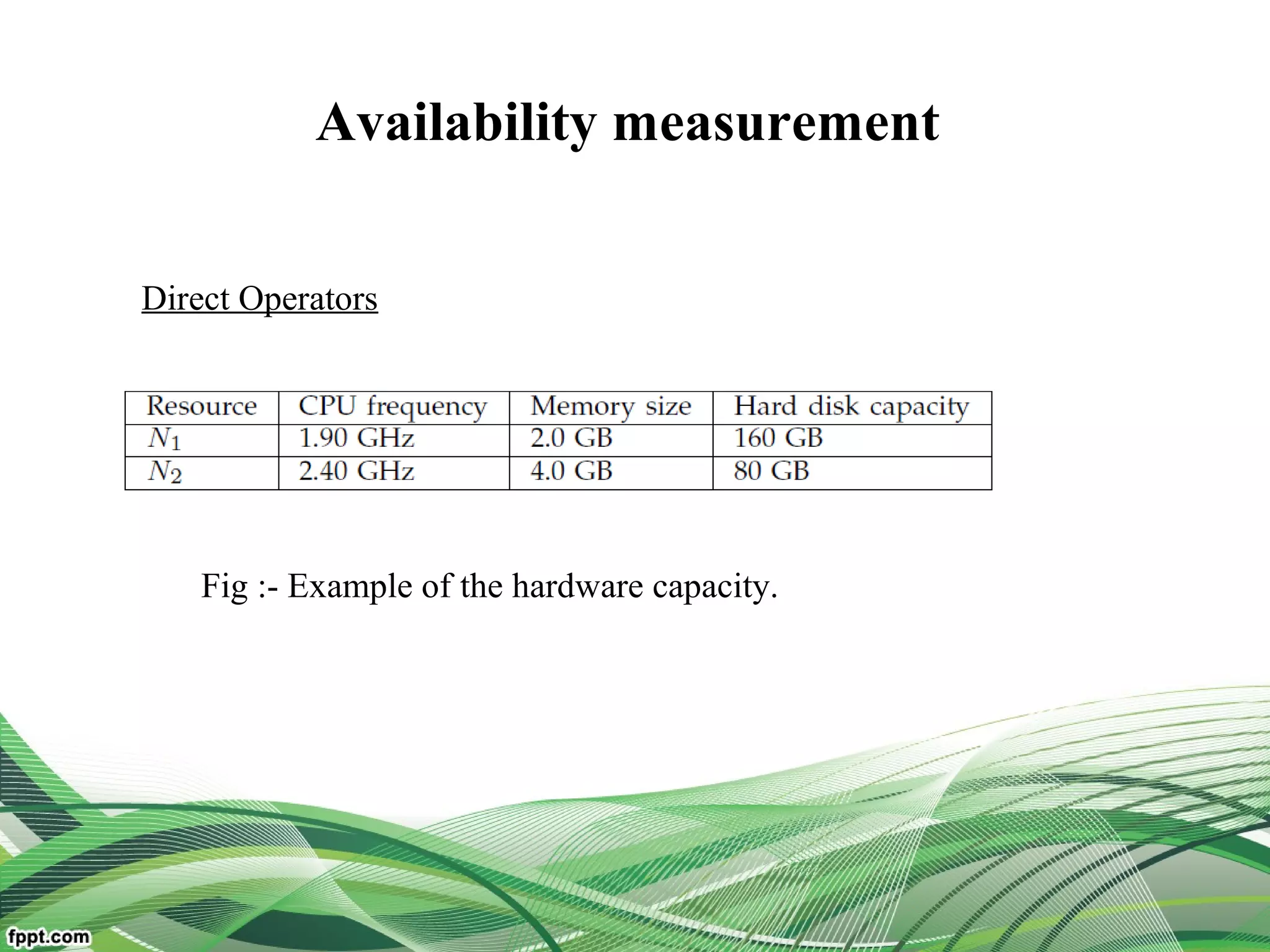
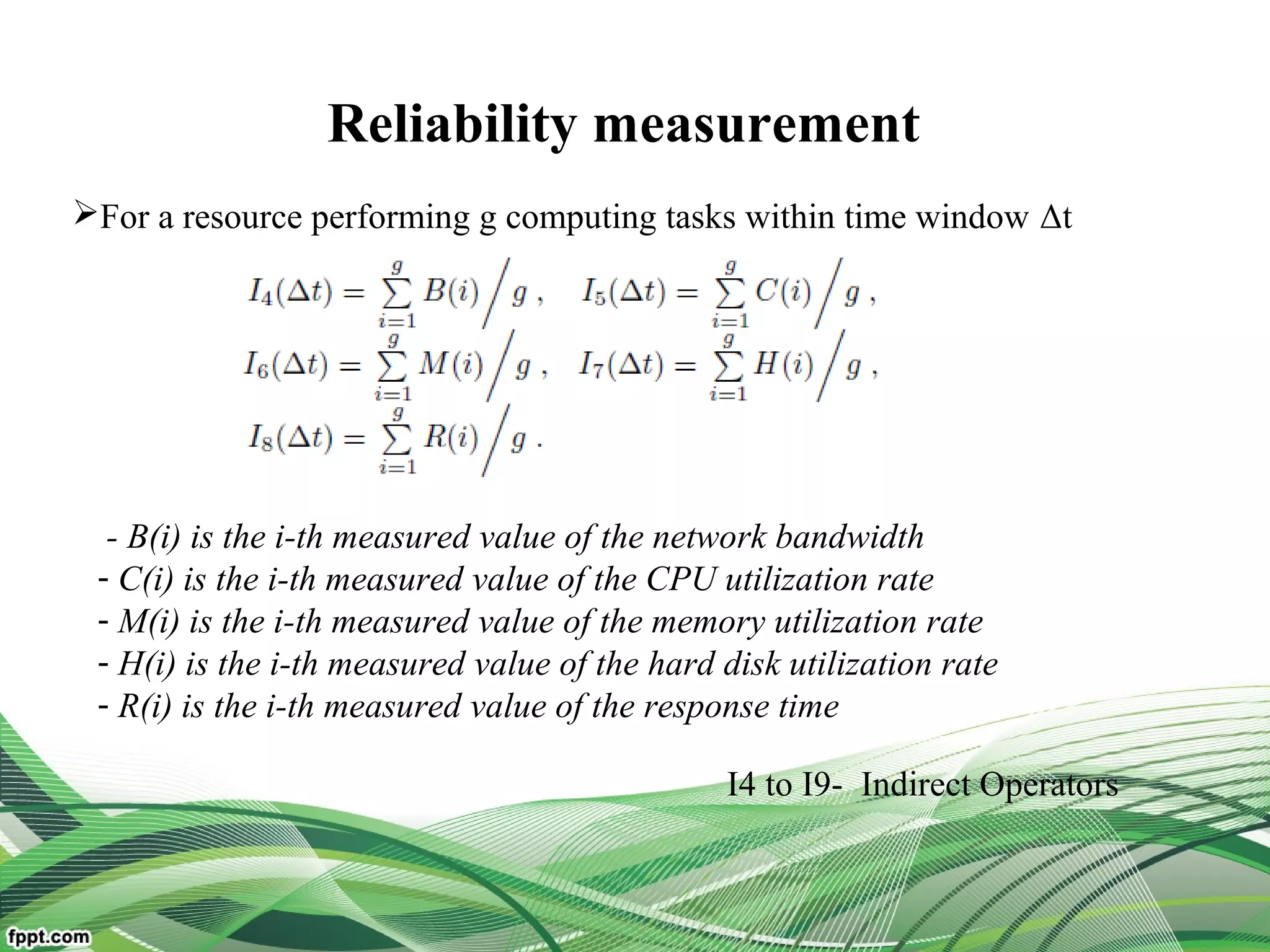
- time window-based trusted indicator for service operators
- more sensitive to new operators
- generates time window interaction takes place b/w user and
resource
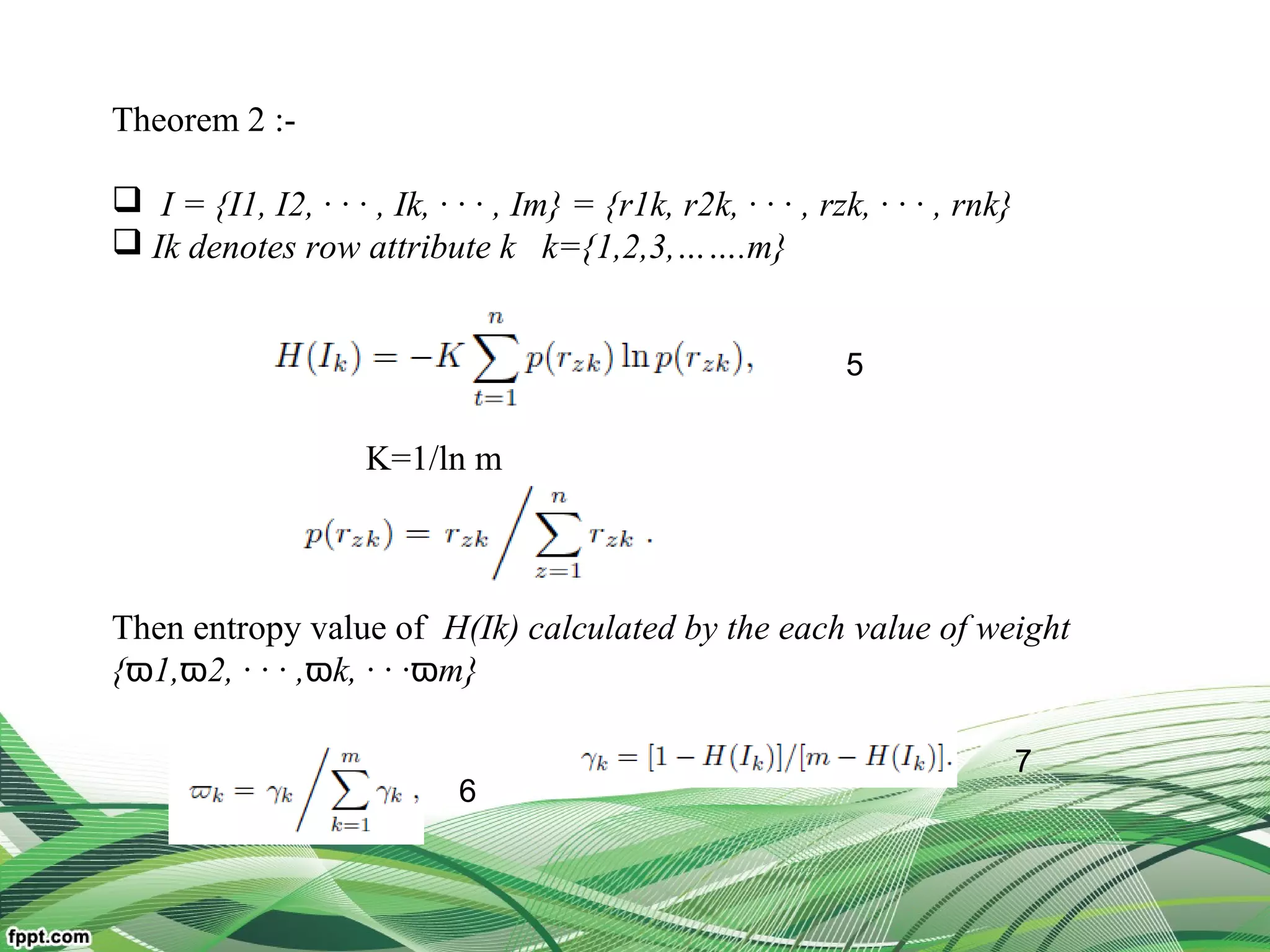
Definition :-
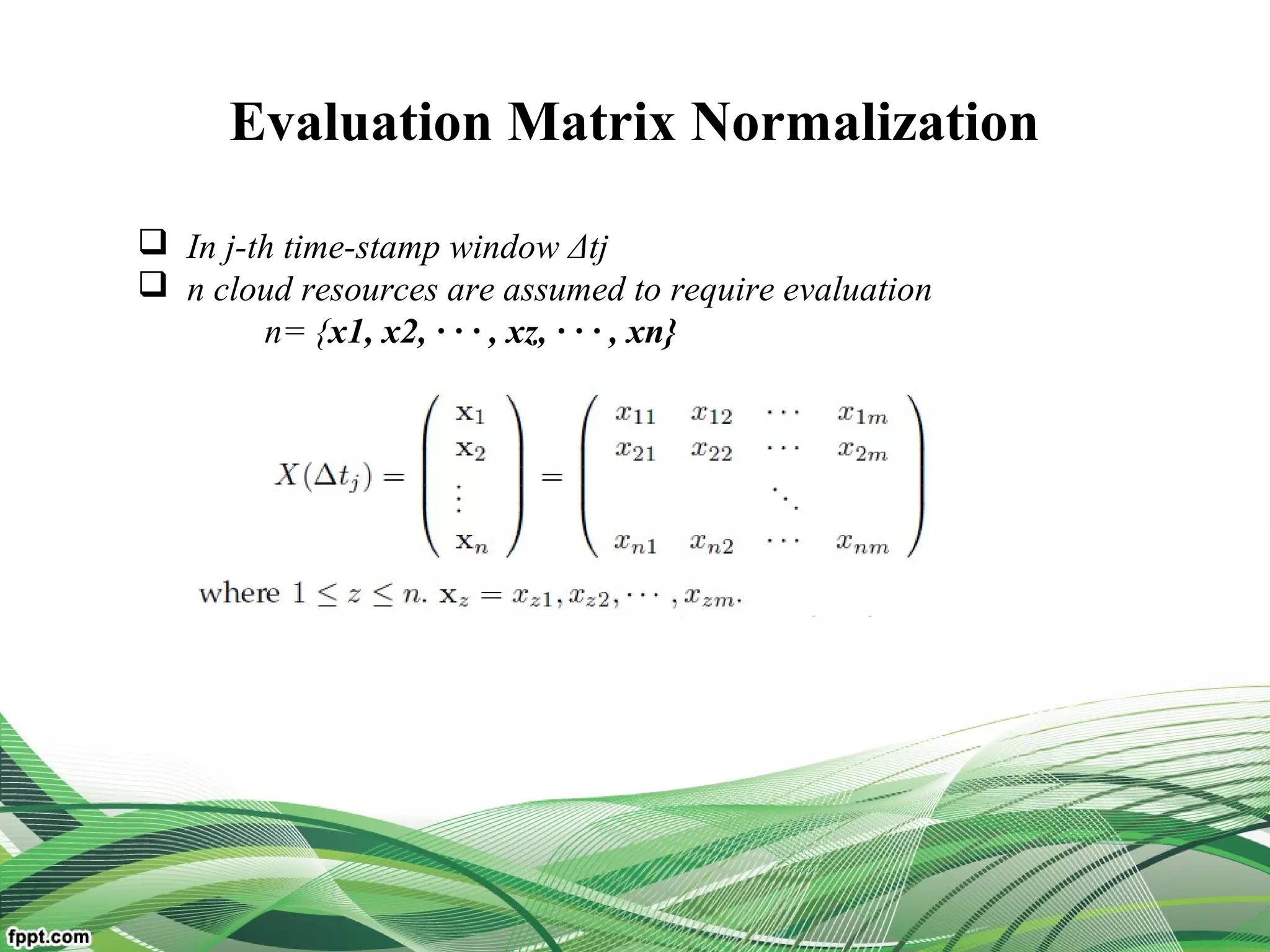
Ω = {N1,N2, · · · ,Nn} denotes n registered resources in the broker
TNz(Δtj) denote the RTD of resource Nn
TNz(Δtj) = rz × W
rz=(rz1, rz2, · · · , rzk, · · · , rzm),
W = { 1, 2, · · · ,ϖ ϖ ϖk, · · ·ϖm} ϖk [0, 1],∈](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160308064034/75/cloud-computing-service-operator-aware-trust-scheme-30-2048.jpg)
![Global Trust Degree (GTD)
Time window v = (Δt1,Δt2, · · · ,Δtn)
Time series D = {TNi(Δt1), TNi(Δt2), · · · , TNi(Δtn)}
A = {a(Δt1), a(Δt2), · · · , a(Δtj), · · · , a(Δtn)}
a(Δtj) [0, 1] is the weights assigned∈ to each RTD TNi(Δtj)
λ [0, 1]∈
8
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-160308064034/75/cloud-computing-service-operator-aware-trust-scheme-33-2048.jpg)







