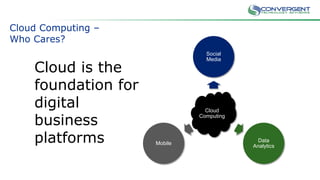
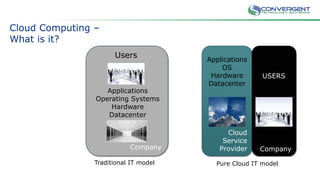
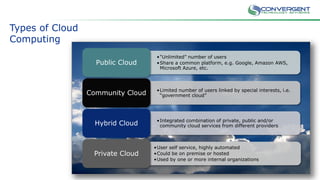
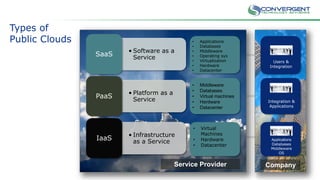
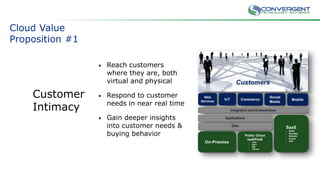
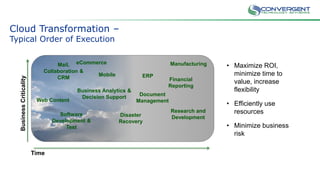
The document is a primer on cloud computing aimed at executives, emphasizing its role in enabling new business models, enhancing efficiency, and fostering agility. It outlines different types of cloud computing, such as public, private, and hybrid clouds, and discusses their value propositions, including customer intimacy and business velocity. Additionally, it highlights when to avoid cloud adoption, stressing that not all systems should migrate to the cloud due to potential risks and costs.