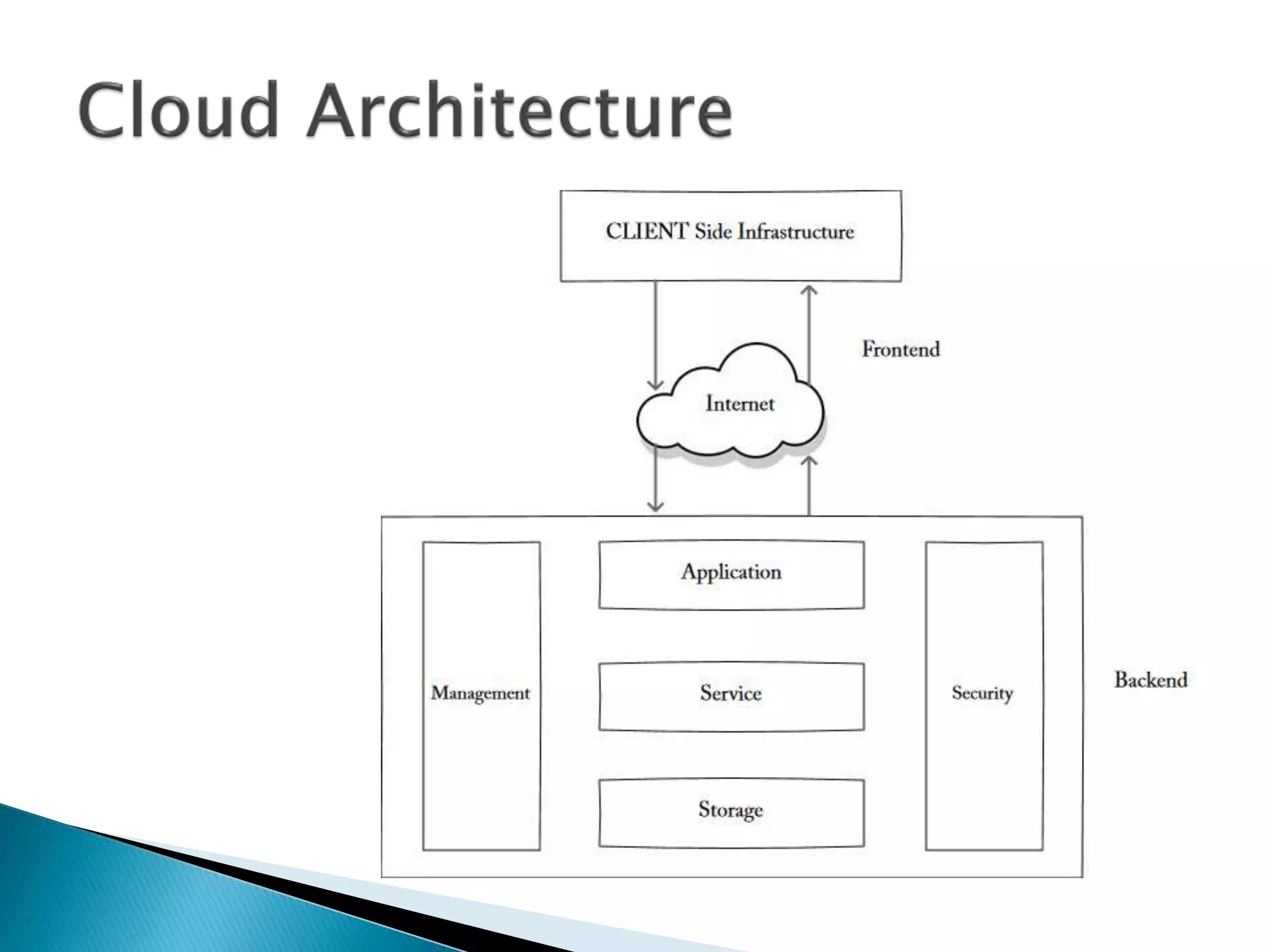
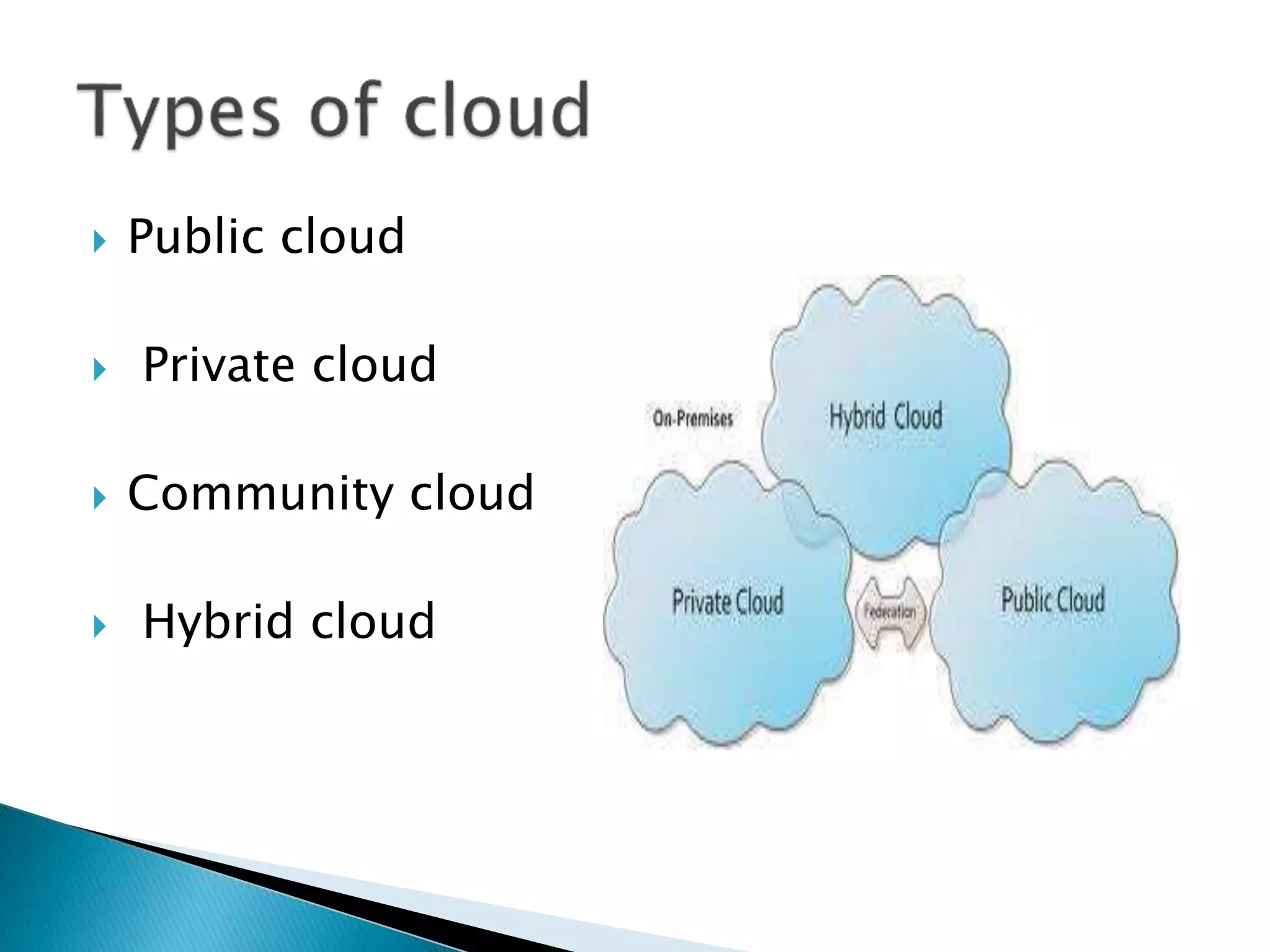
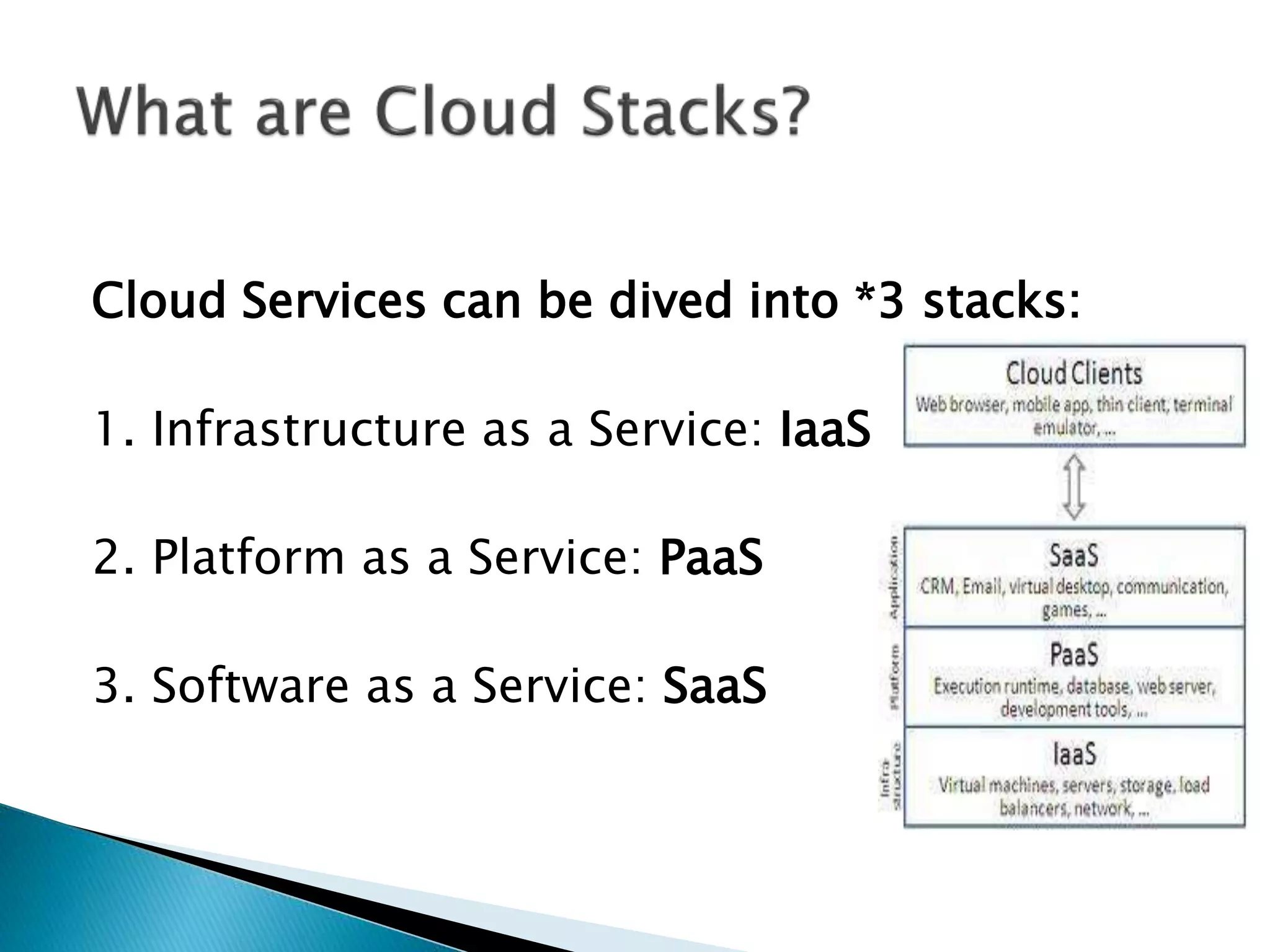
Cloud computing uses central remote servers and the internet to maintain data and applications. It consists of three service models - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides basic storage and networking services, PaaS provides development platforms, and SaaS provides end-user applications. Cloud computing offers benefits like reduced costs, flexibility, scalability, and accessibility but also raises security and privacy concerns that need to be addressed.