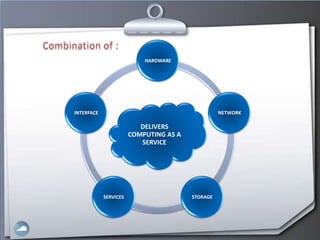
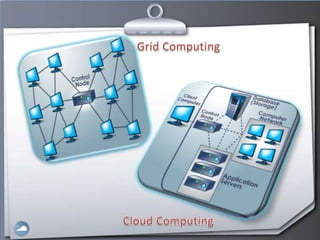
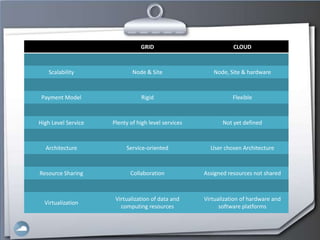
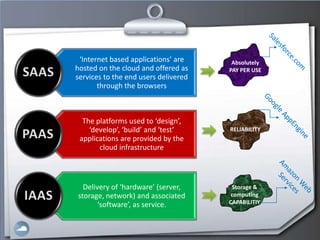
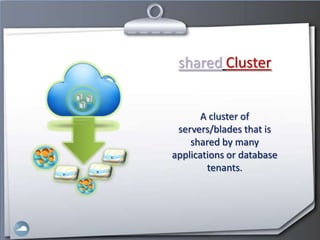
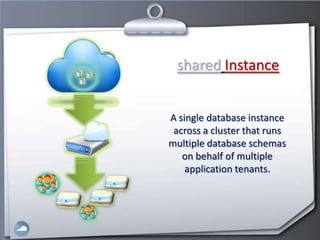
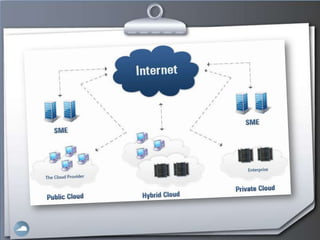
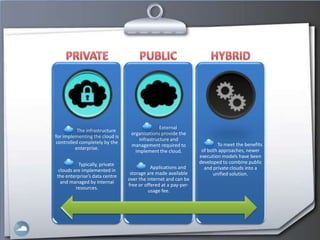
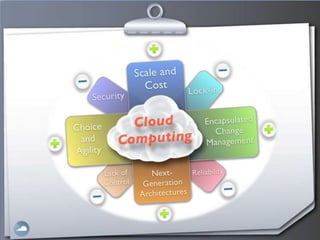
1. The document discusses cloud computing and compares it to grid computing. Cloud computing delivers computing as a service using virtualized hardware and software platforms.
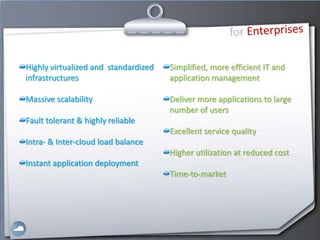
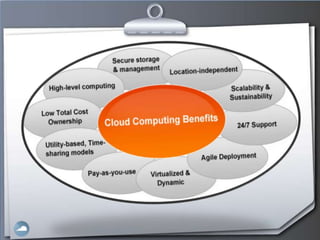
2. Cloud computing provides massive scalability, fault tolerance, and reliable service quality through virtualization and load balancing across infrastructure.
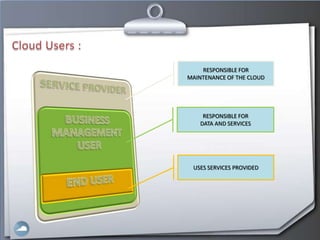
3. Users can access cloud applications and services from any internet-connected device without installing or managing software/hardware themselves.