Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times





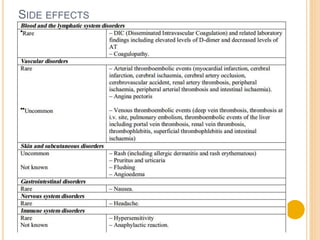
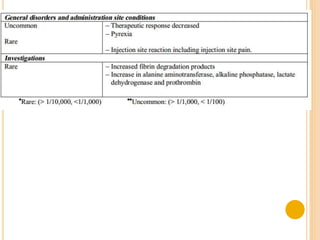


Factor VII is a protein involved in the coagulation cascade that causes blood to clot. It is encoded by a gene on chromosome 13. Factor VII deficiency is a rare, recessive bleeding disorder. Factor VII is used medically to treat and prevent bleeding episodes in patients undergoing surgery or invasive procedures, including those with hemophilia, congenital Factor VII deficiency, and Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. It is administered intravenously under physician supervision and can cause side effects.







