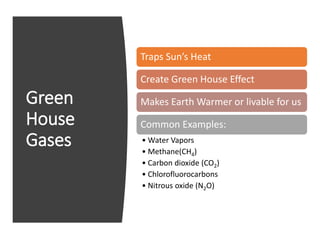
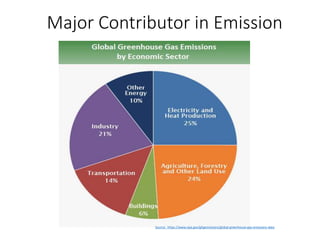
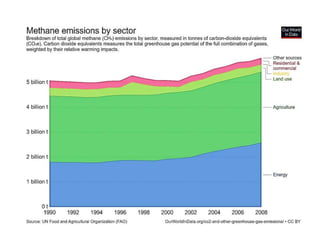
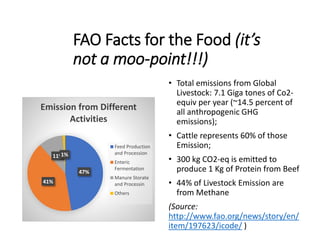
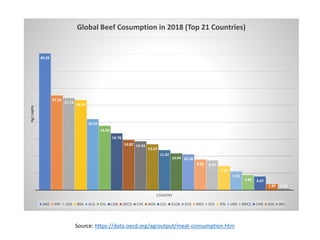
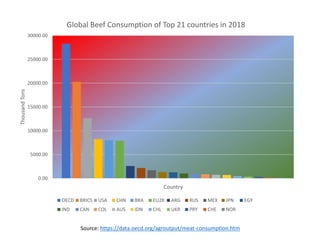
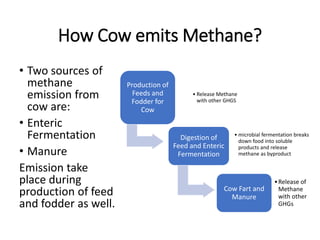
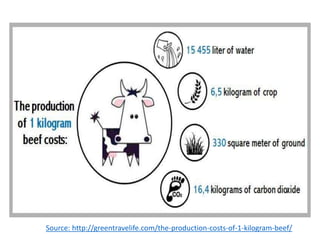
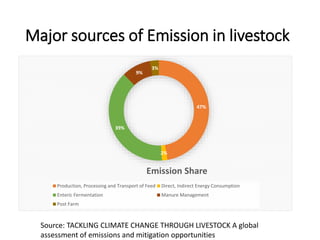
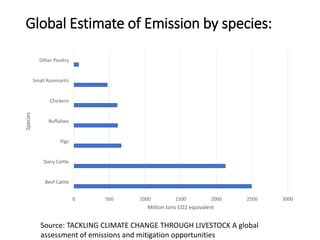
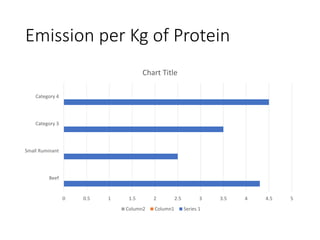
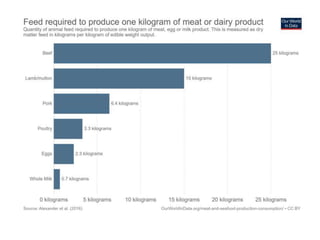
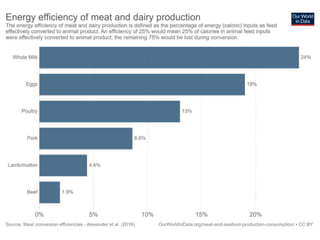
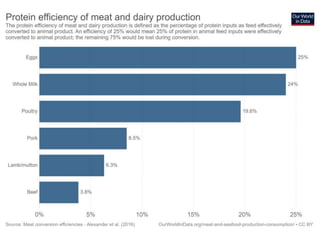
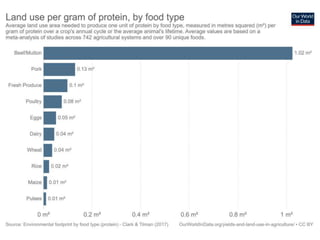
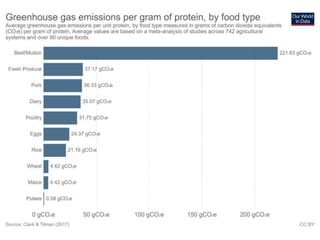
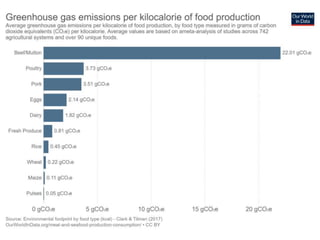
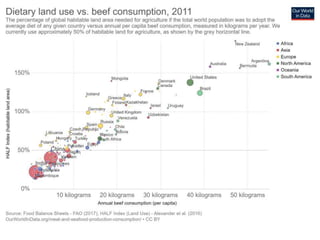
The document discusses the significant impact of beef production on climate change, highlighting that global livestock contributes 14.5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, with cattle being the predominant emitter. It illustrates the processes by which cattle produce methane and the role of feed production in greenhouse gas emissions. The author calls for a reduction in beef consumption and better management practices to mitigate environmental impacts.