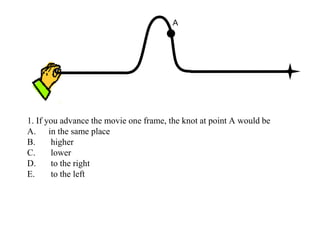
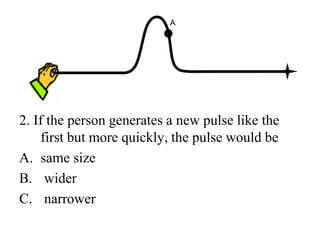
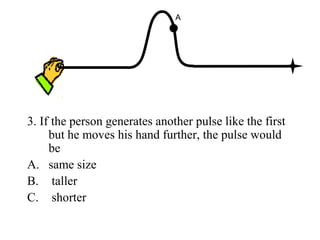
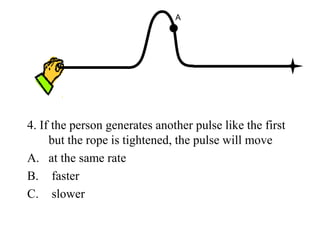
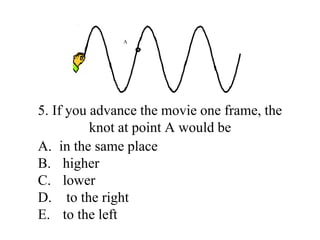
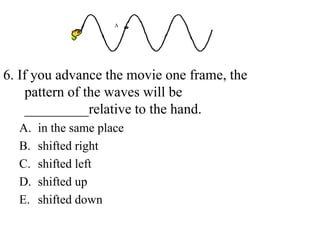
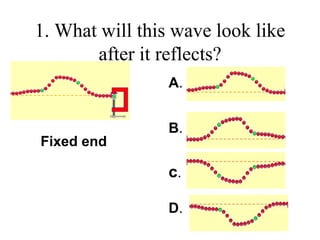
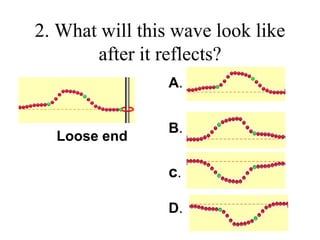
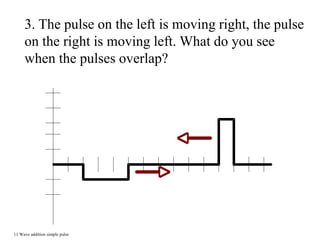
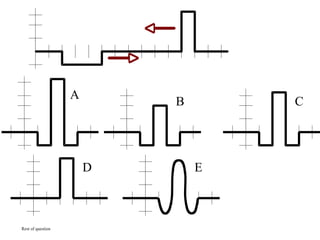
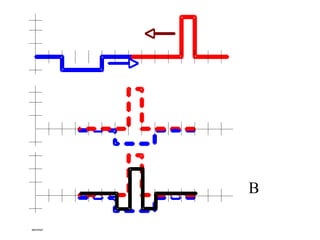
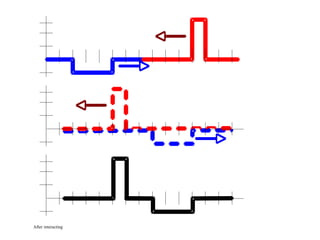
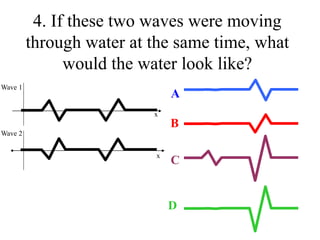
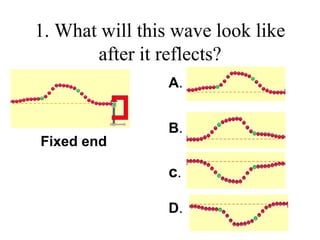
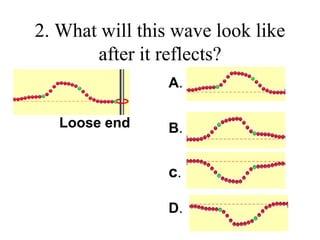
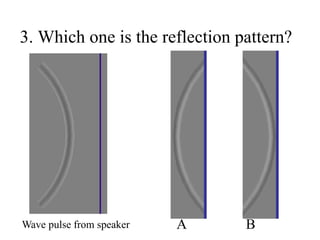
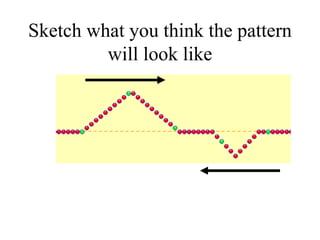
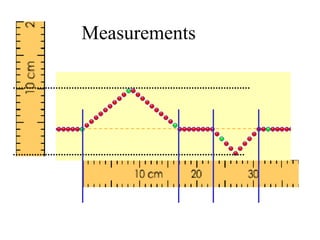
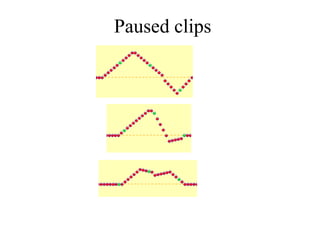
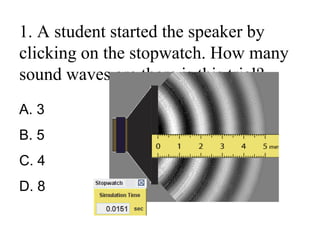
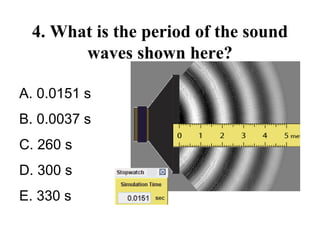
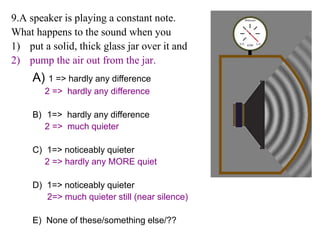
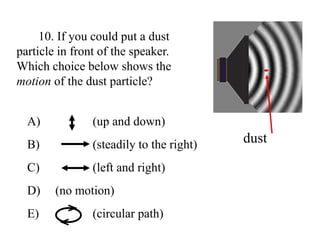
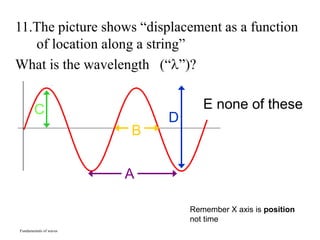
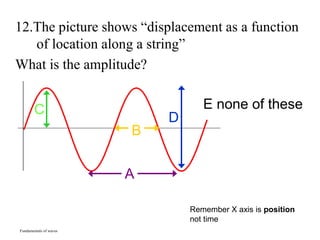
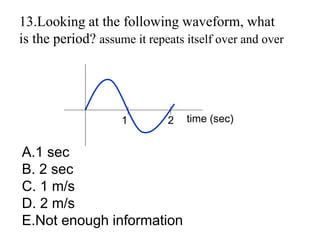
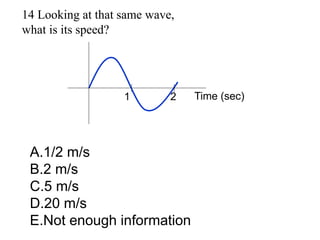
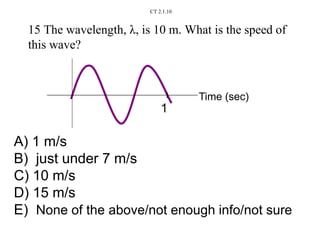
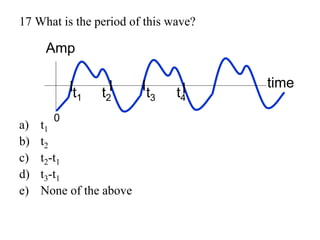
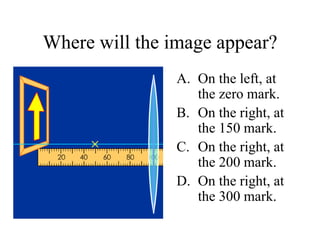
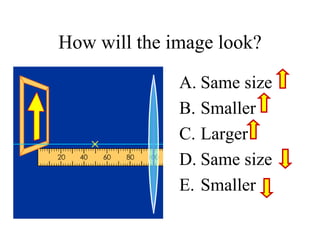
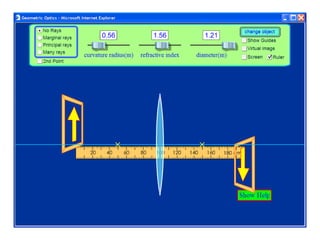
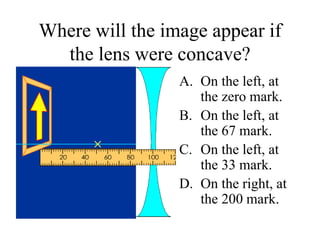
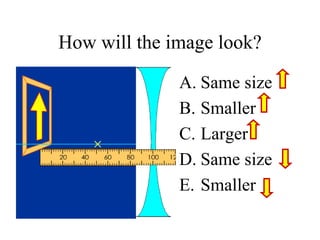
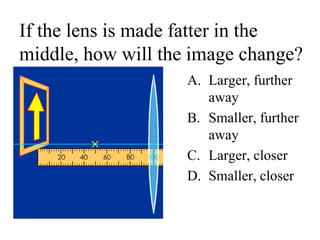
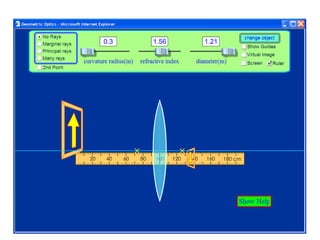
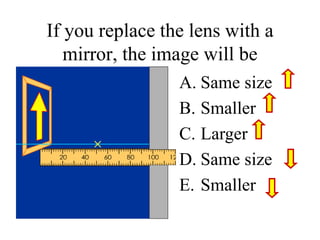
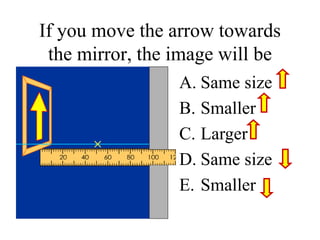
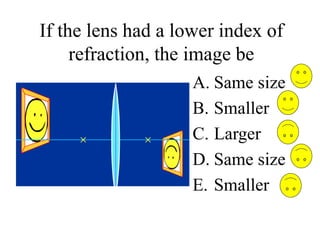
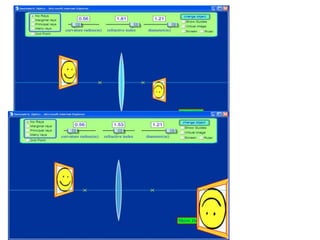
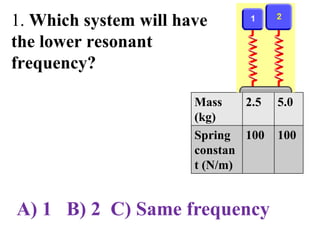
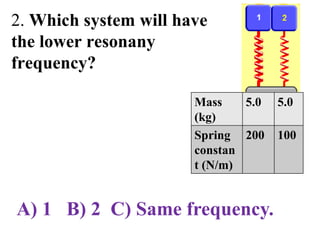
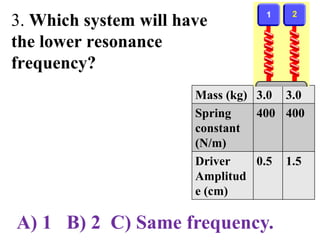
The document outlines a series of clicker questions designed for teaching wave concepts, including wave behaviors, sound waves, resonance, and reflection in various systems. It contains questions on topics such as pulse generation, wave frequencies, sound wave properties, and how different factors affect wave behavior. The questions are intended to facilitate student engagement and assess understanding of wave-related phenomena in a classroom setting.