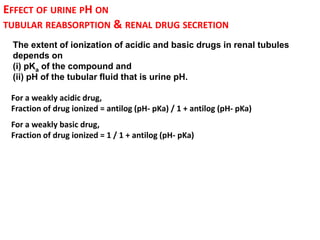
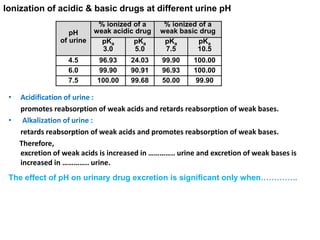
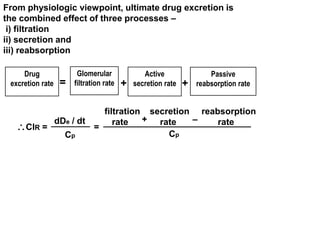
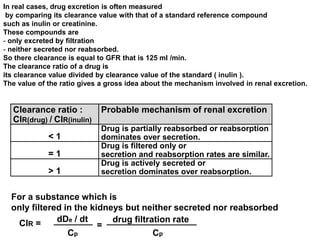
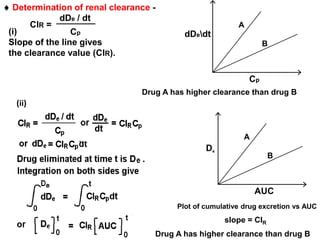
The document discusses how urine pH affects the tubular reabsorption and renal excretion of weak acids and bases. It states that acidification of urine promotes reabsorption of weak acids and retards reabsorption of weak bases, while alkalization of urine has the opposite effects. The extent of ionization of drugs depends on the drug's pKa value and urine pH. It also discusses how urine flow rate and drug clearance influence renal drug excretion. Clearance is defined as the volume of fluid cleared of drug per unit of time and can be used to determine the mechanism of renal drug excretion.