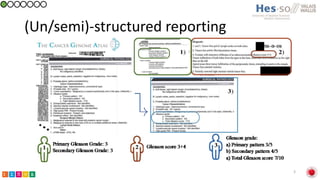
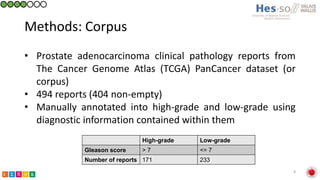
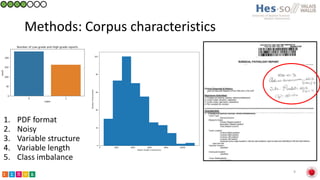
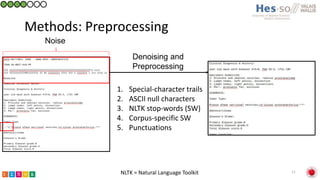
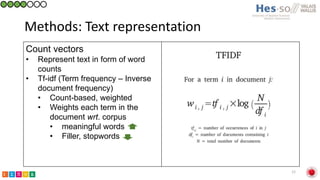
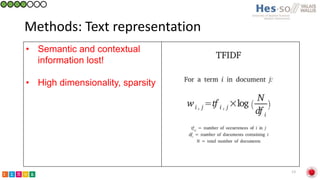
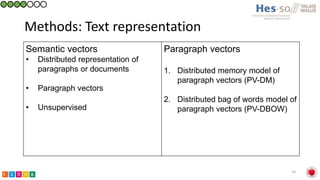
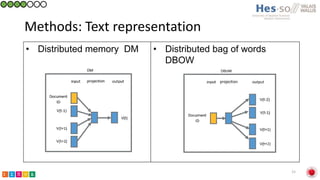
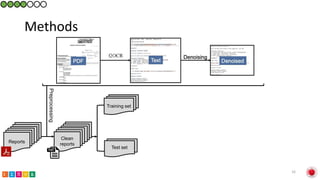
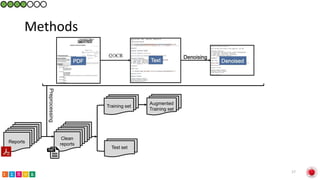
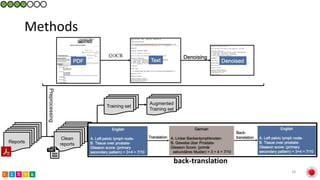
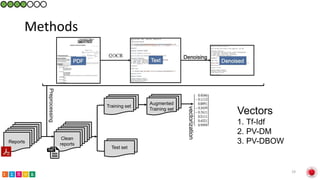
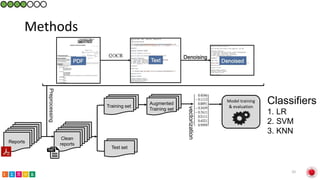
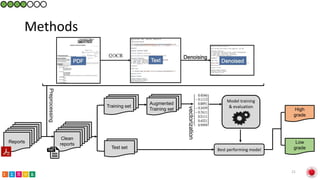
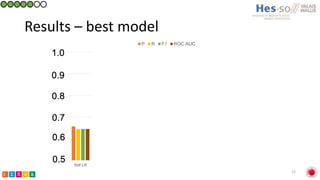
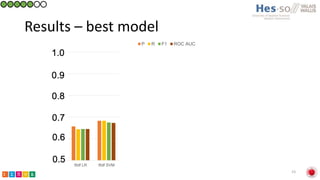
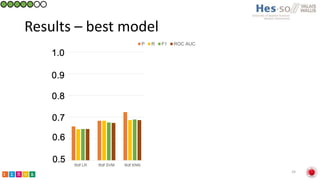
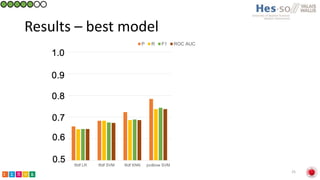
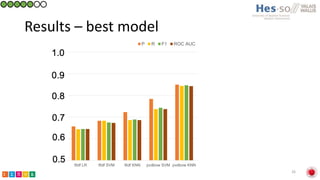
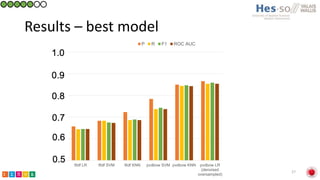
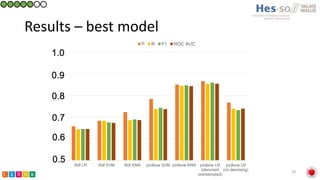
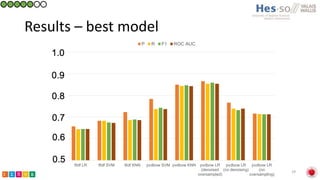
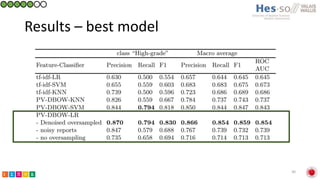
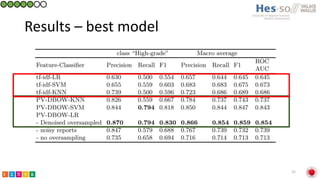
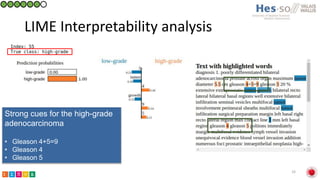
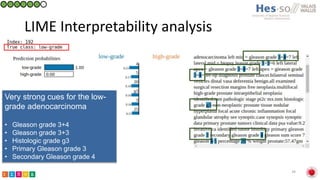
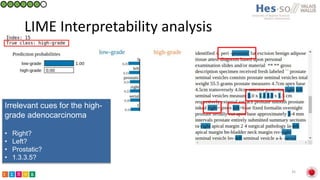
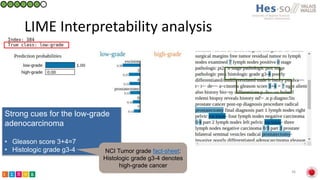
This document summarizes research on classifying prostate cancer pathology reports into high-grade and low-grade categories using natural language processing. The best performing model was a logistic regression model trained on paragraph vector representations of reports, achieving an ROC AUC score of 0.91. An analysis of the model's interpretations found that it strongly associated terms like "Gleason 4+5=9" with high-grade cancer and "Gleason grade 3+3" with low-grade cancer. Future work will aim to extract additional clinical information like tumor staging from the reports.