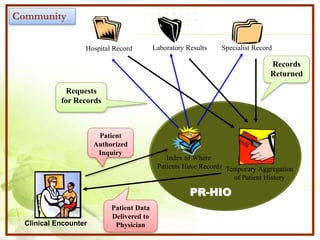
This document discusses health information technologies and their direction in Puerto Rico. It notes the deterioration of public health on the island and rising healthcare costs. It introduces concepts like health information exchange (HIE), meaningful use of electronic health records, and telehealth/m-health. Nurses are emphasized as important players in selecting and using new technologies. Charts show growing cell phone and internet usage, demonstrating Puerto Rico's increasing digital society. While the future remains uncertain, new technologies offer potential for improved health outcomes and more efficient, coordinated care.