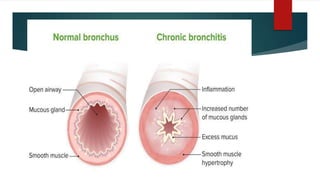
Chronic bronchitis is defined as a persistent cough with sputum production for at least 3 months in two consecutive years. The most common cause is cigarette smoking. Clinical features include persistent cough, sputum production, wheezing, and breathlessness. In later stages, patients develop hypercapnia, hypoxemia, and mild cyanosis known as "blue boaters." Assessment of a patient with chronic bronchitis involves collecting demographic information, medical history, subjective reports of symptoms like cough and breathlessness, and objective measures including reduced lung function, increased pCO2, and chest x-ray abnormalities in later stages.






![PT assessment
[A] General assessment
demographic data:
Name-
Age-
Gender-
BMI-
Occupation-
Provisional diagnosis-chronic bronchitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicbronchitis-230130054022-33e3b4cd/85/Chronic-bronchitis-Physio-assessment-pptx-8-320.jpg)

![[C] subjective assessment
1.breathlessness
o Progressive exertional dyspnea
o Duration:
o Severity (assessed by NYHA scale)
o Pattern: orthopnea
o Precipitating factors: on exertion,exposure with pollutants
o Relieving factors:rest,bronchodilators](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicbronchitis-230130054022-33e3b4cd/85/Chronic-bronchitis-Physio-assessment-pptx-10-320.jpg)


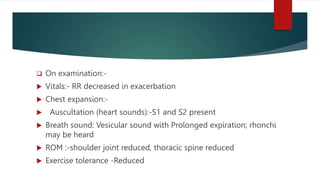
![[D]objective assessment
On observation:
1.General observation:-
o Level of consciousness-alert
o General health and body built:-obese in blue boaters.
o cyanosis-present
o Peripheral cyanosis
2.observation of chest:
o Shape-barrel shaped chest
o Breathing pattern-abnormal apical breathing
o Use of accessory muscles-present](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicbronchitis-230130054022-33e3b4cd/85/Chronic-bronchitis-Physio-assessment-pptx-14-320.jpg)