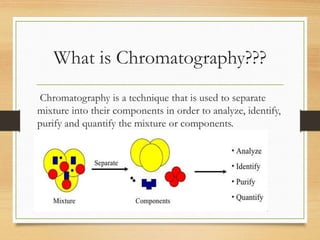
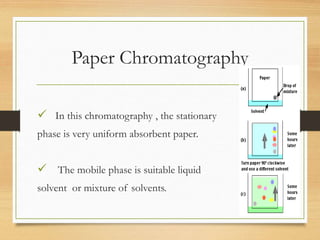
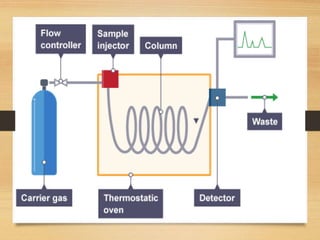
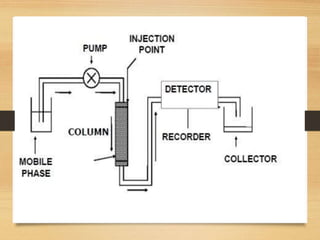
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures into individual components through differences in how they interact with mobile and stationary phases. It was invented in 1901 by Mikhail Tswett and has since been improved. There are several types including paper, gas, thin-layer, and liquid chromatography, each using different stationary and mobile phases to separate substances like plant pigments, pharmaceuticals, environmental pollutants, and more.