The document is a presentation on the choice of programming languages for web development, covering key topics such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, and PHP. It provides an overview of web programming, including client-side and server-side scripting, along with examples and basic syntax for each language. The presentation emphasizes the importance of these technologies in building dynamic and interactive web pages.


























![I n t e r n e t
Client requests page
Completed HTML sent to client
Web Server
Client Machine
With Web
Browser
• The script, written by the website developer, generates the HTML code of the page requested.
• The HTML code is not actually a file. The code is actually held in the server’s memory until it is
sent directly to the client.
Script builds
HTML code
HTML ready to send
Server runs script
[ ASP / PHP / Ruby ]
Script
HTML Code
How Scripting Languages Work30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/choiceofprogramminglanguageforwebdeveloping-161106112257/85/Choice-of-programming-language-for-web-developing-30-320.jpg)







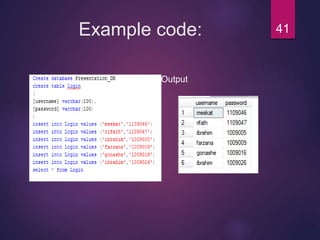
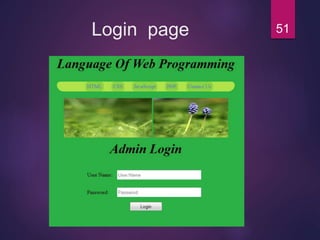
![How to Insert values& Delete
Table?
INSERT
Used to enter data into table
Syntax:
INSERT INTO column_name
VALUES (value1, value2, … , value_N);
DELETE
Deletes a table row
Syntax:
DELETE FROM tablename
[WHERE conditionlist ];
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/choiceofprogramminglanguageforwebdeveloping-161106112257/85/Choice-of-programming-language-for-web-developing-39-320.jpg)
![Select & update
operation
SELECT
Used to list contents of table
Syntax:
SELECT columnlist
FROM tablename;
UPDATE
Modify data in a table
Syntax:
UPDATE tablename
SET columnname = expression [, columnname =
expression]
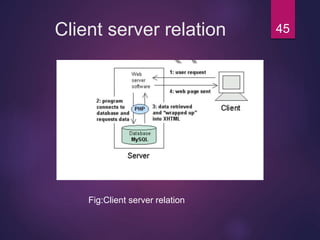
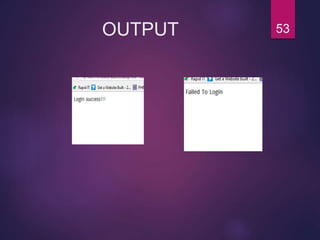
[WHERE conditionlist];
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/choiceofprogramminglanguageforwebdeveloping-161106112257/85/Choice-of-programming-language-for-web-developing-40-320.jpg)