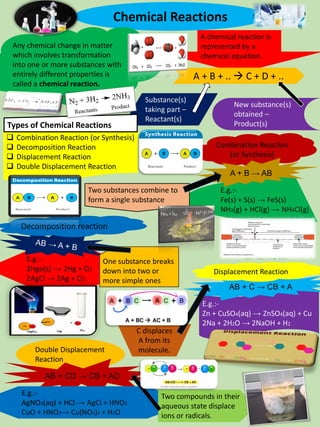
This document defines chemical reactions and describes the main types: combination, decomposition, displacement, and double displacement. It provides examples of each type of reaction and explains that a chemical reaction is represented by a chemical equation showing the reactants and products. The document also discusses exothermic and endothermic reactions, neutralization reactions between acids and bases, and the different properties of metallic, non-metallic, basic, acidic, amphoteric, and neutral oxides in chemical reactions.