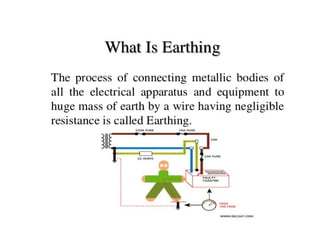
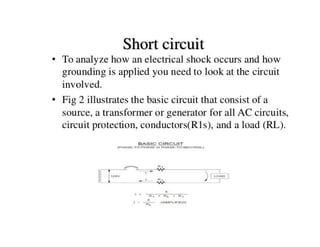
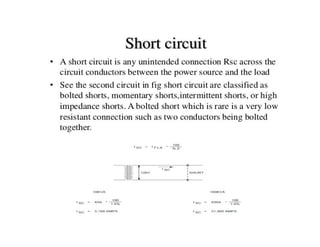
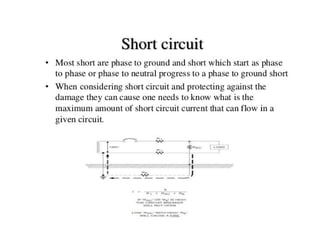
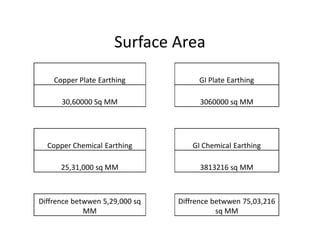
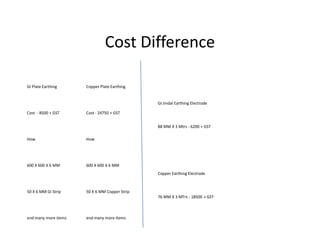
This document discusses earthing systems and their importance for safety. It defines earthing as protecting people from electric shock by providing an alternative path for fault currents. The objectives of earthing are to ensure safe voltages and prevent overcurrent. Good earthing has low impedance to quickly disconnect faulty circuits. Chemical earthing uses graphite and aluminum silicate for higher heat dissipation and longer lifespan than conventional earthing using charcoal and salt. Chemical earthing also has a larger surface area and is easier to install and maintain. In conclusion, chemical earthing provides better corrosion resistance and performance at a lower cost compared to copper or GI plate earthing systems.