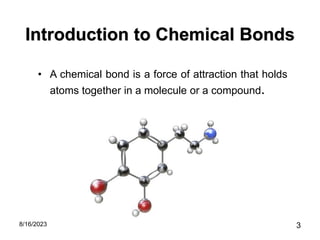
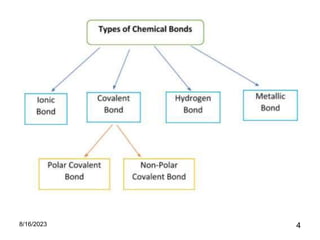
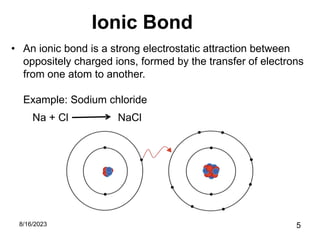
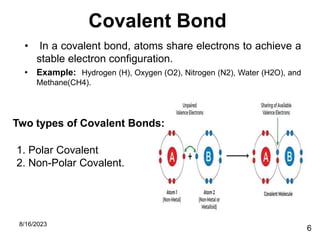
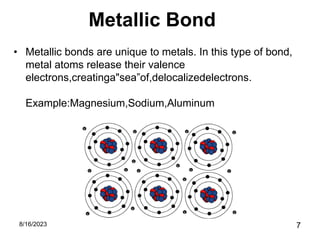
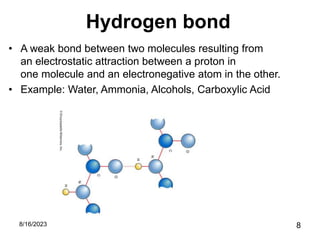
The presentation focuses on chemical bonds, which are the forces keeping atoms together in molecules and compounds. It covers various types of bonds including ionic, covalent, metallic, and hydrogen bonds, highlighting their importance in stability, compound formation, and real-world applications such as pharmaceuticals, electrochemistry, agriculture, and nanotechnology. The discussion emphasizes that understanding chemical bonds is essential for advancements in multiple fields.