Chem_Enzymes.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•4 views
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of biochemical reactions by lowering the energy of activation. They are typically proteins that bind specifically to substrates and induce a shape change that facilitates the chemical reaction. This induced fit allows the enzyme to reduce the energy needed for the reaction to occur and be used repeatedly without being consumed in the process. Changing conditions like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, or adding inhibitors can impact the reaction rate by altering how well the enzyme and substrate interact.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Chapter 4 enzymes

- Amylase, lipase, proteases added to laundry detergents
- Papain, bromelain added to meat tenderizers
- Lysozyme added to wound dressings
Diagnostic:
- Measuring enzyme levels in blood/urine to detect organ damage
- Measuring enzyme levels in blood to diagnose genetic disorders
Therapeutic:
- Enzyme replacement therapy for genetic disorders
- Enzymes as digestive aids or supplements
Research:
- Enzymes used as reagents in clinical assays and diagnostic kits
So in summary, enzymes play important roles in diagnostics, research, and therapeutics in medicine. Their catalytic properties are exploited for various applications.
ENZYME BIOCHEMISTRY

Dr. Naresh Panigrahi discusses enzymes and biochemistry. Some key points:
- Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in cells without being used up in the process. They have high specificity for their substrate.
- Enzyme structure includes an apoenzyme protein portion and often a cofactor like a coenzyme, prosthetic group, or metal ion that is required for catalytic activity.
- Factors like pH, temperature, and inhibitors can impact enzyme activity by altering its structure-function relationship.
- Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze and have unique names and EC numbers in enzyme nomenclature systems
ENZYMES.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that regulate chemical reactions in living organisms. They catalyze reactions involved in metabolism, digestion, and energy production and conversion. All enzymes are proteins except for some ribozymes, which are made of RNA. Enzymes greatly increase the rates of biochemical reactions by lowering activation energy. They are highly specific and efficient catalysts. Enzyme activity is influenced by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration. The Michaelis-Menten model describes enzyme-catalyzed reactions and defines terms like Km, which indicates an enzyme's affinity for its substrate.
ENZYMES

It covers enzyme kinetics, classification of enzymes, catalysis, types of catalysis, nomenclature of enzymes, apoenzymes, cofactors, isoenzymes, holoenzyme, factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction, clinical importance of enzymes. It is useful for the students of life sciences and biochemistry as well. The slides help even the teachers teaching basics of enzyme kinetics at the UG and PG levels.
Enzyme Catalysis.pptx

• Enzyme catalysis is the process by which there is an increase in the rate of a reaction through a biological molecule called an enzyme.
• For a reaction to be successful, the molecules of the reactants should contain sufficient energy to cross the energy barrier, i.e., the activation energy.
Enzymes

This powerpoint presentation talks about enzymes, specifically its functions, the different types according to its function, and the definition of enzyme activator and inhibitor. A picture diagram is also included to show the process of enzyme activity and as well as a table differentiating apoenzyme and coenzyme. The different factors that affects the enzyme activity are also explained and lastly, the other uses of enzyme in medicine, food and etc.The content of the powerpoint presentation has undergone a research through internet and the best answers has been selected for better understanding. The resources of all the research made that was in this presentation are acknowledged as shown in the Reference part of the slide.
Enzymology ii factors affecting enzyme activity

what makes your enzyme work better?
temperature, pH, concentrations of substrate, enzyme and end product.
*factors that affect the enzyme activity#
Lec 4 level 3-nu (enzymes)

1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They do this via an active site that binds to specific substrates.
2. Each enzyme has both a short recommended name as well as a more detailed systematic name that identifies the reaction it catalyzes.
3. Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze, such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, etc.
4. Enzyme activity can be regulated by factors like substrate and product concentration, temperature, and pH level. Inhibitors also diminish enzyme activity through competitive or noncompetitive inhibition.
Recommended
Chapter 4 enzymes

- Amylase, lipase, proteases added to laundry detergents
- Papain, bromelain added to meat tenderizers
- Lysozyme added to wound dressings
Diagnostic:
- Measuring enzyme levels in blood/urine to detect organ damage
- Measuring enzyme levels in blood to diagnose genetic disorders
Therapeutic:
- Enzyme replacement therapy for genetic disorders
- Enzymes as digestive aids or supplements
Research:
- Enzymes used as reagents in clinical assays and diagnostic kits
So in summary, enzymes play important roles in diagnostics, research, and therapeutics in medicine. Their catalytic properties are exploited for various applications.
ENZYME BIOCHEMISTRY

Dr. Naresh Panigrahi discusses enzymes and biochemistry. Some key points:
- Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in cells without being used up in the process. They have high specificity for their substrate.
- Enzyme structure includes an apoenzyme protein portion and often a cofactor like a coenzyme, prosthetic group, or metal ion that is required for catalytic activity.
- Factors like pH, temperature, and inhibitors can impact enzyme activity by altering its structure-function relationship.
- Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze and have unique names and EC numbers in enzyme nomenclature systems
ENZYMES.pptx

Enzymes are protein catalysts that regulate chemical reactions in living organisms. They catalyze reactions involved in metabolism, digestion, and energy production and conversion. All enzymes are proteins except for some ribozymes, which are made of RNA. Enzymes greatly increase the rates of biochemical reactions by lowering activation energy. They are highly specific and efficient catalysts. Enzyme activity is influenced by factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration. The Michaelis-Menten model describes enzyme-catalyzed reactions and defines terms like Km, which indicates an enzyme's affinity for its substrate.
ENZYMES

It covers enzyme kinetics, classification of enzymes, catalysis, types of catalysis, nomenclature of enzymes, apoenzymes, cofactors, isoenzymes, holoenzyme, factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction, clinical importance of enzymes. It is useful for the students of life sciences and biochemistry as well. The slides help even the teachers teaching basics of enzyme kinetics at the UG and PG levels.
Enzyme Catalysis.pptx

• Enzyme catalysis is the process by which there is an increase in the rate of a reaction through a biological molecule called an enzyme.
• For a reaction to be successful, the molecules of the reactants should contain sufficient energy to cross the energy barrier, i.e., the activation energy.
Enzymes

This powerpoint presentation talks about enzymes, specifically its functions, the different types according to its function, and the definition of enzyme activator and inhibitor. A picture diagram is also included to show the process of enzyme activity and as well as a table differentiating apoenzyme and coenzyme. The different factors that affects the enzyme activity are also explained and lastly, the other uses of enzyme in medicine, food and etc.The content of the powerpoint presentation has undergone a research through internet and the best answers has been selected for better understanding. The resources of all the research made that was in this presentation are acknowledged as shown in the Reference part of the slide.
Enzymology ii factors affecting enzyme activity

what makes your enzyme work better?
temperature, pH, concentrations of substrate, enzyme and end product.
*factors that affect the enzyme activity#
Lec 4 level 3-nu (enzymes)

1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They do this via an active site that binds to specific substrates.
2. Each enzyme has both a short recommended name as well as a more detailed systematic name that identifies the reaction it catalyzes.
3. Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze, such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, etc.
4. Enzyme activity can be regulated by factors like substrate and product concentration, temperature, and pH level. Inhibitors also diminish enzyme activity through competitive or noncompetitive inhibition.
Enzymes

A comprehensive coverage of Enzymes including basics, mechanisms of enzyme catalysis, enzyme inhibition and clinical applications, mostly based on Stryer- Biochemistry. The slides were intended for MBBS teaching, but should benefit the students of Biochemistry and allied sciences.
Prepared in Sept 2015
Enzyme

Catalysts are something that speeds up the chemical reaction. Almost all biochemical reactions require catalysts.
Enzymes are biocatalysts. Biochemical catalysts speed up the biochemical reactions.
In presence of an enzyme, less energy is required for the reaction to take place.
A catalyst may be defined as a substance that increases the velocity or rate of chemical reactions without itself undergoing any change in the overall process.
2 updated prsentation 2 ch8 enzymes lecture presentation manal 2018 no regulaion

This document provides an overview of key concepts in metabolism and enzyme function:
1) Metabolism consists of thousands of chemical reactions in living cells catalyzed by enzymes. Metabolic pathways are organized with specific enzymes catalyzing each step.
2) Catabolic pathways break down molecules and release energy while anabolic pathways use energy to build molecules. Spontaneous reactions require no energy input but enzymes greatly accelerate reactions by lowering their activation energy.
3) Enzymes are highly specific catalytic proteins that use their active sites to orient and strain substrate bonds, lowering the activation energy needed for chemical reactions. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on substrate concentration.
enzymes.ppt

1. Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower the activation energy of reactions and increase reaction rates. They are often proteins that contain cofactors.
2. Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze, such as oxidation-reduction, hydrolysis, or transfer of chemical groups. Common enzyme names end in "-ase".
3. The lock and key model describes how enzymes bind specifically to substrates in their active sites to form enzyme-substrate complexes. In the induced fit model, the enzyme structure changes to better fit the substrate.
Enzymes-.pdf

Metabolism involves the breakdown (catabolism) and building (anabolism) of molecules in the body. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze metabolic reactions and are made up of amino acids folded into shapes with active sites. Enzymes require cofactors like vitamins and minerals to function as holoenzymes in reactions. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, substrate concentration, and pH - with each enzyme having optimal conditions for maximum reaction rates.
Ezyme-Honors5.ppt

Enzymes are biological catalysts that are mainly made of proteins. They speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. Enzymes have several key characteristics - they lower the activation energy of reactions, interact specifically with substrates, and work best at an optimum temperature and pH. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be affected by limiting factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations. Enzymes are classified based on the type of chemical reaction they catalyze, such as hydrolases and oxidation-reduction enzymes.
Enzyme And Metabolism

This document provides an overview of enzymes and metabolism. It defines enzymes as proteins that catalyze chemical reactions and discusses the lock-and-key and induced-fit models of enzyme action. It also explains factors that influence enzyme activity such as pH and temperature, and describes the roles of coenzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
CHAPTER 6.pptx

- Enzymes are protein biocatalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed. They are specific in their action and composed of apoenzyme and coenzyme.
- The active site of an enzyme binds specifically to substrates and contains residues that help hold the substrate. Changes to the active site shape affect enzyme function.
- Factors like temperature, pH, substrate/product concentration, and presence of activators or inhibitors can regulate an enzyme's activity rate. Studying an enzyme's kinetics reveals its catalytic mechanism.
- Regulation allows cells to control metabolic pathways by modulating enzyme activity. Competitive inhibitors bind the active site while non-competitive inhibitors cause conformational changes. I
Enzyme’s activity

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and have many applications in industry. In the human body, enzymes are involved in essential processes like DNA replication and protein synthesis. Industrially, enzymes are used in detergents, textiles, and food processing. This document discusses the importance and mechanisms of enzyme activity, including how enzymes lower activation energy and use specific active sites. It also covers measuring enzyme activity, factors that affect it like temperature and pH, and examples of their use in industries like cheese and wine production.
Enzyme

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing substrates to be converted to products more easily. Enzymes are specific in their action and only catalyze certain reactions. They work by binding substrates in their active sites and facilitating the biochemical transformations. The structure and conditions of the active site, as well as factors like temperature and pH, influence an enzyme's activity level and specificity.
Enzymes

The document discusses several key points about enzymes:
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions. Almost all enzymes are proteins, but some nucleic acids called ribozymes can also act as enzymes.
- Enzyme catalysts only work efficiently at temperatures below 40°C, while inorganic catalysts can work at higher temperatures and pressures.
- The enzyme carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction of H2CO3 to CO2 and H2O by about 10 million times.
- Cofactors like prosthetic groups, coenzymes, and metal ions are required for enzymatic activity. Prosthetic groups are tightly bound organic compounds, while coenzymes associate
Enzymology-BSc-Biotechnology-SEM-II-PPT.pptx

1. The document provides an overview of the history and key concepts of enzymology including the discovery of enzymes and pioneering scientists in the field.
2. It discusses the definition of enzymes as biological catalysts and their properties such as substrate specificity, cofactors, inhibition, and factors affecting enzymatic activity like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration.
3. Examples are given of different types of enzymes and several enzyme-catalyzed reactions are described to illustrate concepts like the enzyme-substrate interaction and use of coenzymes.
Enzymes

1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They achieve specificity by inducing conformational changes that tightly bind substrates in the active site.
2. The induced fit model proposes that weak initial interactions between the enzyme and substrate induce structural changes that strengthen binding.
3. Key factors that affect enzyme activity include temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and substrate concentration. Activity is optimized within narrow ranges for each factor.
Enzymes

- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions.
- Enzymes have an active site that binds specifically to substrates. This binding forms an enzyme-substrate complex that lowers the energy needed for chemical reactions to occur.
- Enzyme activity can be affected by temperature and pH levels, with most enzymes functioning optimally around body temperature and neutral pH. Extreme temperatures and acidity/alkalinity can cause an enzyme to denature.
Enzymes

Definition, Classification, Models of enzyme activity, Enzyme specificity, Factors affecting enzyme activity, Enzyme inhibition, Isoenzyme, Allosteric enzyme, Application, etc.
Overview of enzyme

This slideshow is about overview of enzyme. It describes important properties of enzymes, classification, functions and mode of action.
Enzymes 

Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. They have a globular structure and an active site that binds specifically to substrates. Some enzymes require cofactors to function. The lock and key and induced fit hypotheses explain how enzymes bind substrates specifically. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like substrate concentration, pH, temperature, and inhibitors. Inhibitors bind to enzymes and reduce reaction rates, and are used in areas like medicine and biochemistry.
BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 4 - CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE CELL PART 2

1. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in cells by lowering the activation energy needed, allowing reactions to occur more quickly.
2. They are highly specific and each enzyme catalyzes only one reaction. Enzymes have an active site that allows only specific substrates to bind.
3. Many factors can affect enzyme activity, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration, and presence of cofactors or inhibitors. Enzymes function best within a limited range of conditions.
Enzymes

- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions.
- Enzymes have an active site where substrates bind specifically. The enzyme-substrate complex leads to products. Enzyme activity is affected by temperature and pH. They are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels.
- Enzymes catalyze both the breaking down of large molecules and building up of complex molecules from simpler ones. They are required in small amounts and can catalyze reversible reactions.
Enzymes bph

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions and stabilizing transition states. Enzymes require cofactors like metal ions or organic coenzymes to function. The active site of an enzyme binds specifically to substrates to catalyze reactions. Many factors influence enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, substrate and product concentration.
3.3 P-P NETWORKS.pptx

This document discusses protein-protein interaction networks. It begins by explaining that proteins interact physically with each other to form complexes, without exchanging subunits like chemical reactions. The network of all protein-protein interactions in an organism is called an interactome. Experimental techniques to detect interactions include co-immunoprecipitation of individual protein complexes and high-throughput methods like the yeast two-hybrid system to comprehensively map the interactome. However, two-hybrid results can be unreliable with high false positive and negative rates. More accurate affinity purification methods tag a protein of interest to purify its interacting complexes.
2.1RANDOM NETWORKS.pptx

Random graphs are mathematical models that use probability distributions to represent complex networks. They lie at the intersection of graph theory and probability theory. The most commonly studied random graph model is the Erdős–Rényi model, also known as G(n,p), where n is the number of vertices and p is the probability of an edge between any two vertices. In G(n,p), each possible edge occurs independently with probability p, allowing for analysis of average properties like the diameter as the graph size increases.
More Related Content
Similar to Chem_Enzymes.pptx
Enzymes

A comprehensive coverage of Enzymes including basics, mechanisms of enzyme catalysis, enzyme inhibition and clinical applications, mostly based on Stryer- Biochemistry. The slides were intended for MBBS teaching, but should benefit the students of Biochemistry and allied sciences.
Prepared in Sept 2015
Enzyme

Catalysts are something that speeds up the chemical reaction. Almost all biochemical reactions require catalysts.
Enzymes are biocatalysts. Biochemical catalysts speed up the biochemical reactions.
In presence of an enzyme, less energy is required for the reaction to take place.
A catalyst may be defined as a substance that increases the velocity or rate of chemical reactions without itself undergoing any change in the overall process.
2 updated prsentation 2 ch8 enzymes lecture presentation manal 2018 no regulaion

This document provides an overview of key concepts in metabolism and enzyme function:
1) Metabolism consists of thousands of chemical reactions in living cells catalyzed by enzymes. Metabolic pathways are organized with specific enzymes catalyzing each step.
2) Catabolic pathways break down molecules and release energy while anabolic pathways use energy to build molecules. Spontaneous reactions require no energy input but enzymes greatly accelerate reactions by lowering their activation energy.
3) Enzymes are highly specific catalytic proteins that use their active sites to orient and strain substrate bonds, lowering the activation energy needed for chemical reactions. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions depends on substrate concentration.
enzymes.ppt

1. Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower the activation energy of reactions and increase reaction rates. They are often proteins that contain cofactors.
2. Enzymes are classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze, such as oxidation-reduction, hydrolysis, or transfer of chemical groups. Common enzyme names end in "-ase".
3. The lock and key model describes how enzymes bind specifically to substrates in their active sites to form enzyme-substrate complexes. In the induced fit model, the enzyme structure changes to better fit the substrate.
Enzymes-.pdf

Metabolism involves the breakdown (catabolism) and building (anabolism) of molecules in the body. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze metabolic reactions and are made up of amino acids folded into shapes with active sites. Enzymes require cofactors like vitamins and minerals to function as holoenzymes in reactions. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, substrate concentration, and pH - with each enzyme having optimal conditions for maximum reaction rates.
Ezyme-Honors5.ppt

Enzymes are biological catalysts that are mainly made of proteins. They speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. Enzymes have several key characteristics - they lower the activation energy of reactions, interact specifically with substrates, and work best at an optimum temperature and pH. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be affected by limiting factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations. Enzymes are classified based on the type of chemical reaction they catalyze, such as hydrolases and oxidation-reduction enzymes.
Enzyme And Metabolism

This document provides an overview of enzymes and metabolism. It defines enzymes as proteins that catalyze chemical reactions and discusses the lock-and-key and induced-fit models of enzyme action. It also explains factors that influence enzyme activity such as pH and temperature, and describes the roles of coenzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
CHAPTER 6.pptx

- Enzymes are protein biocatalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed. They are specific in their action and composed of apoenzyme and coenzyme.
- The active site of an enzyme binds specifically to substrates and contains residues that help hold the substrate. Changes to the active site shape affect enzyme function.
- Factors like temperature, pH, substrate/product concentration, and presence of activators or inhibitors can regulate an enzyme's activity rate. Studying an enzyme's kinetics reveals its catalytic mechanism.
- Regulation allows cells to control metabolic pathways by modulating enzyme activity. Competitive inhibitors bind the active site while non-competitive inhibitors cause conformational changes. I
Enzyme’s activity

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and have many applications in industry. In the human body, enzymes are involved in essential processes like DNA replication and protein synthesis. Industrially, enzymes are used in detergents, textiles, and food processing. This document discusses the importance and mechanisms of enzyme activity, including how enzymes lower activation energy and use specific active sites. It also covers measuring enzyme activity, factors that affect it like temperature and pH, and examples of their use in industries like cheese and wine production.
Enzyme

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing substrates to be converted to products more easily. Enzymes are specific in their action and only catalyze certain reactions. They work by binding substrates in their active sites and facilitating the biochemical transformations. The structure and conditions of the active site, as well as factors like temperature and pH, influence an enzyme's activity level and specificity.
Enzymes

The document discusses several key points about enzymes:
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions. Almost all enzymes are proteins, but some nucleic acids called ribozymes can also act as enzymes.
- Enzyme catalysts only work efficiently at temperatures below 40°C, while inorganic catalysts can work at higher temperatures and pressures.
- The enzyme carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction of H2CO3 to CO2 and H2O by about 10 million times.
- Cofactors like prosthetic groups, coenzymes, and metal ions are required for enzymatic activity. Prosthetic groups are tightly bound organic compounds, while coenzymes associate
Enzymology-BSc-Biotechnology-SEM-II-PPT.pptx

1. The document provides an overview of the history and key concepts of enzymology including the discovery of enzymes and pioneering scientists in the field.
2. It discusses the definition of enzymes as biological catalysts and their properties such as substrate specificity, cofactors, inhibition, and factors affecting enzymatic activity like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration.
3. Examples are given of different types of enzymes and several enzyme-catalyzed reactions are described to illustrate concepts like the enzyme-substrate interaction and use of coenzymes.
Enzymes

1. Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They achieve specificity by inducing conformational changes that tightly bind substrates in the active site.
2. The induced fit model proposes that weak initial interactions between the enzyme and substrate induce structural changes that strengthen binding.
3. Key factors that affect enzyme activity include temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and substrate concentration. Activity is optimized within narrow ranges for each factor.
Enzymes

- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions.
- Enzymes have an active site that binds specifically to substrates. This binding forms an enzyme-substrate complex that lowers the energy needed for chemical reactions to occur.
- Enzyme activity can be affected by temperature and pH levels, with most enzymes functioning optimally around body temperature and neutral pH. Extreme temperatures and acidity/alkalinity can cause an enzyme to denature.
Enzymes

Definition, Classification, Models of enzyme activity, Enzyme specificity, Factors affecting enzyme activity, Enzyme inhibition, Isoenzyme, Allosteric enzyme, Application, etc.
Overview of enzyme

This slideshow is about overview of enzyme. It describes important properties of enzymes, classification, functions and mode of action.
Enzymes 

Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed. They have a globular structure and an active site that binds specifically to substrates. Some enzymes require cofactors to function. The lock and key and induced fit hypotheses explain how enzymes bind substrates specifically. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like substrate concentration, pH, temperature, and inhibitors. Inhibitors bind to enzymes and reduce reaction rates, and are used in areas like medicine and biochemistry.
BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 4 - CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE CELL PART 2

1. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in cells by lowering the activation energy needed, allowing reactions to occur more quickly.
2. They are highly specific and each enzyme catalyzes only one reaction. Enzymes have an active site that allows only specific substrates to bind.
3. Many factors can affect enzyme activity, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration, and presence of cofactors or inhibitors. Enzymes function best within a limited range of conditions.
Enzymes

- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions.
- Enzymes have an active site where substrates bind specifically. The enzyme-substrate complex leads to products. Enzyme activity is affected by temperature and pH. They are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels.
- Enzymes catalyze both the breaking down of large molecules and building up of complex molecules from simpler ones. They are required in small amounts and can catalyze reversible reactions.
Enzymes bph

Enzymes are protein catalysts that accelerate biochemical reactions without being consumed. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions and stabilizing transition states. Enzymes require cofactors like metal ions or organic coenzymes to function. The active site of an enzyme binds specifically to substrates to catalyze reactions. Many factors influence enzyme activity, such as temperature, pH, substrate and product concentration.
Similar to Chem_Enzymes.pptx (20)
2 updated prsentation 2 ch8 enzymes lecture presentation manal 2018 no regulaion

2 updated prsentation 2 ch8 enzymes lecture presentation manal 2018 no regulaion
BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 4 - CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE CELL PART 2

BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 4 - CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE CELL PART 2
More from AnandKumar459862
3.3 P-P NETWORKS.pptx

This document discusses protein-protein interaction networks. It begins by explaining that proteins interact physically with each other to form complexes, without exchanging subunits like chemical reactions. The network of all protein-protein interactions in an organism is called an interactome. Experimental techniques to detect interactions include co-immunoprecipitation of individual protein complexes and high-throughput methods like the yeast two-hybrid system to comprehensively map the interactome. However, two-hybrid results can be unreliable with high false positive and negative rates. More accurate affinity purification methods tag a protein of interest to purify its interacting complexes.
2.1RANDOM NETWORKS.pptx

Random graphs are mathematical models that use probability distributions to represent complex networks. They lie at the intersection of graph theory and probability theory. The most commonly studied random graph model is the Erdős–Rényi model, also known as G(n,p), where n is the number of vertices and p is the probability of an edge between any two vertices. In G(n,p), each possible edge occurs independently with probability p, allowing for analysis of average properties like the diameter as the graph size increases.
2.4 RANDOM NETWORKS - Copy.pptx

A scale-free network is characterized by a power-law degree distribution, meaning a few nodes have many connections while most nodes have few. This gives scale-free networks a long-tailed degree distribution with hubs that are orders of magnitude higher than average. One way to generate scale-free networks is through preferential attachment, where new nodes connect preferentially to higher degree nodes, allowing hubs to grow in size over time. Plotting the degree distribution on a log-log scale will show it follows a linear power law.
McFaddenSymposium-04182016.pptx

This document discusses challenges and opportunities for wheat breeding in the 21st century. It outlines the need to address nutritional security threats through transformative plant breeding using new technologies like genomics, phenomics, and genome editing. It emphasizes taking an interdisciplinary systems approach that integrates social sciences to develop crops with improved productivity, efficiency, nutrition, and resilience in a changing environment.
PlantBreedingandGenetics.ppt

This document outlines the course objectives, learning outcomes, schedule, and content for a plant breeding and genetics course. The course aims to teach students about both classical breeding methods and modern molecular breeding techniques. It will cover the history of plant breeding, basics of genetics, classical breeding schemes, molecular genetics applications like PCR and marker-assisted selection, and examine examples from crops and ornamental plants. The schedule lists topics like Mendelian genetics, applied plant breeding, and molecular breeding that will help students understand the developments and current practices in plant breeding.
6_2019_10_12!09_16_04_AM.pptx

This document discusses various methods used in virology, including:
1. Cultivating viruses in animal, plant, and bacterial cells to allow for replication.
2. Isolating viruses using techniques like plaque assays which form discrete zones of cell death.
3. Purifying viruses through centrifugation techniques like differential and density gradient centrifugation to separate viruses from cell debris.
4. Investigating viral and cell structures using microscopes, X-ray crystallography, and other methods to analyze physical properties.
year-5-lesson-4-animal-life-cycles.pptx

This document provides information for parents to support their child's learning about comparing the life cycles of different animals. It includes key learning points about animal reproduction and metamorphosis. The activities involve students researching and comparing the life cycles of frogs, butterflies, and other animals through video clips and fact files. They are asked to describe similarities and differences between two animal life cycles using a Venn diagram. Review materials provide examples of learning outcomes describing stages in frog and butterfly development.
powerpoint poresentation.ppt

This document summarizes the use of bacteriophages to treat fecal coliform bacteria in sewage. It notes that sewage treatment plants in India are overloaded and unable to fully treat sewage. While treatment reduces biochemical oxygen demand and suspended solids, it does not specifically target fecal coliform bacteria. The document proposes using bacteriophages targeted against fecal coliform bacteria as a natural, biological means to reduce levels and make water safer for uses like bathing. It outlines a 18 month pilot project to culture and apply bacteriophages to sewage treatment plants and drains in 5 states and monitor their ability to reduce fecal coliform bacteria.
Michael Hucka.ppt

This document discusses SBML (Systems Biology Markup Language), SBGN (Systems Biology Graphical Notation), and BioModels.net. SBML is a standard format for representing computational models of biochemical networks that allows models to be exchanged between software tools and researchers. Over 100 software tools now support SBML. SBGN is a project to develop a standard notation for diagrams of cellular networks. BioModels.net is a database of models encoded in SBML that has been made possible by the adoption of SBML as a common exchange format.
Slides_SB3.ppt

This document provides an overview of a course on systems biology. It defines systems biology as examining biological systems as a whole through the interactions of all components, rather than in isolation. The course covers basic analysis tools for large datasets, such as examining distributions, correlations, and clustering. It also discusses more advanced modular analysis tools like biclustering that decompose data into transcription modules. An example iterative algorithm called the Signature Algorithm is described for finding related genes based on expression profiles and score thresholds.
BIOMED_presentation.ppt

The document summarizes several biomedical applications that utilize the EGEE grid computing infrastructure:
- There are 3 pilot applications that have been running since 2004: CDSS for clinical decision support, GATE for radiation therapy planning, and GPS@ for protein structure analysis.
- CDSS classifies medical cases from distributed databases accessed through the grid. GATE uses grid resources to parallelize Monte Carlo simulations for radiation therapy planning. GPS@ provides bioinformaticians access to international databases and algorithms.
- Additional applications described include co-registration of medical images for contrast agent diffusion analysis, and SiMRI3D for magnetic resonance image simulation. These applications utilize the grid's parallel computing resources to process large medical datasets.
lect_2_fox_study_populations.pptx

This document discusses selecting study populations for clinical trials. It begins by outlining the process of defining the target, accessible, and study populations. Important considerations for selecting the study population include practicality, accessibility, and relevance to the study objectives. Random sampling methods are described that can help ensure a study sample is representative of the target population. The document then discusses minimizing biases in clinical trials through randomization, allocation concealment, and blinding. Finally, it provides an example sample size calculation for a hypothetical clinical trial on treating latent tuberculosis infection.
QuickStart.ppt

The document provides an outline of the steps involved in getting a clinical research project started at UT-Houston Medical School. It begins with developing a research idea and question, then performing a literature review and developing a detailed study protocol. Approval must then be obtained from physicians, the institutional review board (IRB), and the hospital before project implementation. Funding may also be needed. The document recommends textbooks on clinical research design and lists training courses available to learn clinical research methodology. It provides guidance on developing different types of clinical research questions and the ideal study designs to answer each type of question.
slideset-Navigating-NIH-Programs-Nov2021.pptx

This document provides information to help navigate career development opportunities at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It describes the various NIH Institutes and Centers and their funding priorities. It also outlines the different types of grants, fellowships, and awards available at different career stages, from training programs to independent research awards. Key resources covered include the NIH RePORTER database to find funded projects, program officers to discuss ideas, and the NIH Research Training website for more details on specific opportunities. The document aims to guide scientists seeking NIH support in identifying the right Institute and program to fit their research area and career stage.
BIOMEDICAL .ppt

BioMed Central is an independent publisher of peer-reviewed open access research journals. It launched its first journals in 2000 and now publishes over 150 open access journals across biology and medicine. All research articles published in BioMed Central journals are universally and freely accessible online. Authors retain copyright and grant anyone the right to use, reproduce or disseminate their work. Journal costs are covered by article processing charges typically paid by the author's funder or institution. BioMed Central has experienced rapid growth in submissions and readership, and many of its journals have received impact factors. It aims to make peer-reviewed scientific research available to all.
fouad_kharroubi_PhD_Defense_05_06_2014.ppt

1) The document summarizes the PhD thesis of Fouad KHARROUBI, which investigates random search algorithms for solving the routing and wavelength assignment problem in WDM networks.
2) The thesis proposes a new mathematical formulation of the maximum routing and wavelength assignment problem and investigates four random search algorithms (ROA, GA, TSA, EP) to solve the problem.
3) Extensive experiments running the four algorithms on different network topologies show that the Tabu Search Algorithm performs best in terms of accepting the most connection requests, followed by the Random Optimization Algorithm.
s15-miller-chap-6b-lecture.ppt

This document discusses the enzyme chymotrypsin (CT) as a model for understanding enzyme mechanisms. It describes the structure of CT and its catalytic triad. The reaction proceeds through an acylation phase where a covalent bond forms between the enzyme and substrate, and a deacylation phase where this bond is hydrolyzed. Figures depict each step of the reaction mechanism. The document also discusses enzyme kinetics, regulatory enzymes, and examples of allosteric and covalent regulation including phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase.
enzyme_class2.ppt

Enzymes are globular proteins that function as biological catalysts, lowering the activation energy of chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They speed up reactions via an active site where substrates bind. Enzyme activity depends on structure and is highly specific. Factors like temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentration can affect reaction rate. Enzymes use various mechanisms like lock-and-key and induced fit to catalyze reactions. Inhibition studies help understand metabolic pathways and develop drugs. There are three main types of reversible inhibition - competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive - which are distinguished by their effects on Km and Vmax values.
More from AnandKumar459862 (18)
Recently uploaded
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx

• Pitfalls and pivots needed to use AI effectively in public health
• Evidence-based strategies to address health misinformation effectively
• Building trust with communities online and offline
• Equipping health professionals to address questions, concerns and health misinformation
• Assessing risk and mitigating harm from adverse health narratives in communities, health workforce and health system
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler, Verified Chapters 1 - 33, Complete Newest Version Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by Stamler Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition TEST BANK by Stamler Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Study Guide Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Test Bank For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Pdf Download Course Hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Answers Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Ebook Download Course hero Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Chapters Download Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Pdf Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Study Guide Questions and Answers Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Ebook Download Stuvia Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Questions Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Studocu Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Quizlet Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition Test Bank Stuvia
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
NVBDCP.pptx Nation vector borne disease control program

NVBDCP was launched in 2003-2004 . Vector-Borne Disease: Disease that results from an infection transmitted to humans and other animals by blood-feeding arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas. Examples of vector-borne diseases include Dengue fever, West Nile Virus, Lyme disease, and malaria.
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidadeProf. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
Recomendações da OMS sobre cuidados maternos e neonatais para uma experiência pós-natal positiva.
Em consonância com os ODS – Objetivos do Desenvolvimento Sustentável e a Estratégia Global para a Saúde das Mulheres, Crianças e Adolescentes, e aplicando uma abordagem baseada nos direitos humanos, os esforços de cuidados pós-natais devem expandir-se para além da cobertura e da simples sobrevivência, de modo a incluir cuidados de qualidade.
Estas diretrizes visam melhorar a qualidade dos cuidados pós-natais essenciais e de rotina prestados às mulheres e aos recém-nascidos, com o objetivo final de melhorar a saúde e o bem-estar materno e neonatal.
Uma “experiência pós-natal positiva” é um resultado importante para todas as mulheres que dão à luz e para os seus recém-nascidos, estabelecendo as bases para a melhoria da saúde e do bem-estar a curto e longo prazo. Uma experiência pós-natal positiva é definida como aquela em que as mulheres, pessoas que gestam, os recém-nascidos, os casais, os pais, os cuidadores e as famílias recebem informação consistente, garantia e apoio de profissionais de saúde motivados; e onde um sistema de saúde flexível e com recursos reconheça as necessidades das mulheres e dos bebês e respeite o seu contexto cultural.
Estas diretrizes consolidadas apresentam algumas recomendações novas e já bem fundamentadas sobre cuidados pós-natais de rotina para mulheres e neonatos que recebem cuidados no pós-parto em unidades de saúde ou na comunidade, independentemente dos recursos disponíveis.
É fornecido um conjunto abrangente de recomendações para cuidados durante o período puerperal, com ênfase nos cuidados essenciais que todas as mulheres e recém-nascidos devem receber, e com a devida atenção à qualidade dos cuidados; isto é, a entrega e a experiência do cuidado recebido. Estas diretrizes atualizam e ampliam as recomendações da OMS de 2014 sobre cuidados pós-natais da mãe e do recém-nascido e complementam as atuais diretrizes da OMS sobre a gestão de complicações pós-natais.
O estabelecimento da amamentação e o manejo das principais intercorrências é contemplada.
Recomendamos muito.
Vamos discutir essas recomendações no nosso curso de pós-graduação em Aleitamento no Instituto Ciclos.
Esta publicação só está disponível em inglês até o momento.
Prof. Marcus Renato de Carvalho
www.agostodourado.com
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis is an increasing cause of morbidity among the elderly.
In this document , a brief outline of osteoporosis is given , including the risk factors of osteoporosis fractures , the indications for testing bone mineral density and the management of osteoporosis
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
Top 10 Best Ayurvedic Kidney Stone Syrups in India

we have mentioned the best 10 ayurvedic Kidney Stone Syrups. You can check all these products and choose the best one for yourself.
Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh

Basavarajeeyam is an important text for ayurvedic physician belonging to andhra pradehs. It is a popular compendium in various parts of our country as well as in andhra pradesh. The content of the text was presented in sanskrit and telugu language (Bilingual). One of the most famous book in ayurvedic pharmaceutics and therapeutics. This book contains 25 chapters called as prakaranas. Many rasaoushadis were explained, pioneer of dhatu druti, nadi pareeksha, mutra pareeksha etc. Belongs to the period of 15-16 century. New diseases like upadamsha, phiranga rogas are explained.
A Classical Text Review on Basavarajeeyam

Basavarajeeyam is a Sreshta Sangraha grantha (Compiled book ), written by Neelkanta kotturu Basavaraja Virachita. It contains 25 Prakaranas, First 24 Chapters related to Rogas& 25th to Rasadravyas.
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

There is increasing confidence that cell therapies will soon play a role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders, but the extent of this impact remains to be seen. Early readouts on autologous CAR-Ts in lupus are encouraging, but manufacturing and cost limitations are likely to restrict access to highly refractory patients. Allogeneic CAR-Ts have the potential to broaden access to earlier lines of treatment due to their inherent cost benefits, however they will need to demonstrate comparable or improved efficacy to established modalities.
In addition to infrastructure and capacity constraints, CAR-Ts face a very different risk-benefit dynamic in autoimmune compared to oncology, highlighting the need for tolerable therapies with low adverse event risk. CAR-NK and Treg-based therapies are also being developed in certain autoimmune disorders and may demonstrate favorable safety profiles. Several novel non-cell therapies such as bispecific antibodies, nanobodies, and RNAi drugs, may also offer future alternative competitive solutions with variable value propositions.
Widespread adoption of cell therapies will not only require strong efficacy and safety data, but also adapted pricing and access strategies. At oncology-based price points, CAR-Ts are unlikely to achieve broad market access in autoimmune disorders, with eligible patient populations that are potentially orders of magnitude greater than the number of currently addressable cancer patients. Developers have made strides towards reducing cell therapy COGS while improving manufacturing efficiency, but payors will inevitably restrict access until more sustainable pricing is achieved.
Despite these headwinds, industry leaders and investors remain confident that cell therapies are poised to address significant unmet need in patients suffering from autoimmune disorders. However, the extent of this impact on the treatment landscape remains to be seen, as the industry rapidly approaches an inflection point.
Recently uploaded (20)
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx

share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx
TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...

TEST BANK For Community Health Nursing A Canadian Perspective, 5th Edition by...
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
NVBDCP.pptx Nation vector borne disease control program

NVBDCP.pptx Nation vector borne disease control program
Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade

Novas diretrizes da OMS para os cuidados perinatais de mais qualidade
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf
Top 10 Best Ayurvedic Kidney Stone Syrups in India

Top 10 Best Ayurvedic Kidney Stone Syrups in India
Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh

Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh
Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Vestibulocochlear Nerve by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease

Cell Therapy Expansion and Challenges in Autoimmune Disease
Chem_Enzymes.pptx
- 2. Energy of Activation • If you mix two moles of hydrogen gas H2 with one mole of oxygen gas-nothing happens. • If you add a spark to the container, the following reaction occurs. KABOOM • 2H2 + O2 2 H2O G= -58 kcal/mole 2 In order for water to be produced H2 must become 2H and the O2 must become 2O as this frees up the electrons tied up in covalent bonds, to form chemical bonds forming water, H2O.
- 3. Energy of Activation • The energy used to break the bonds in the reactants so they can be reformed in the products is called the energy of activation. 3
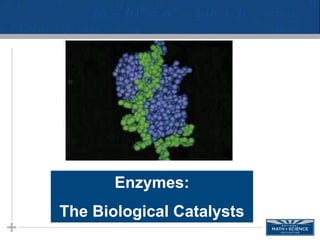
- 4. Enzymes • Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the reaction rate of biochemical reactions. 4 Characteristics of enzymes A. Made of proteins (or RNA). B.They are very specific and only work with a certain set of reactants or substrates that fit on their active site. The enzyme shown is lysozyme
- 5. Induced Fit C. Enzymes can be used over and over again. D. When an enzyme binds with the substrate, the substrate interacts with the enzyme causing it to change shape. This change in shape facilitates the chemical reaction to occur. This is called the induced fit. 5
- 6. Enzyme Example Ribonuclease • Ribonuclease decomposes RNA, and the nucleotides can be recycled. • The purple part is the enzyme; the green part is the substrate (RNA). 6
- 7. Enzymes Work by Lowering the Energy of Activation E. Enzymes increase the reaction rate by lowering the energy of activation. They do NOT change Gibbs free energy or G. 7
- 8. The Enzyme Sucrase Decomposing Sucrose 8
- 10. Initial Velocity • The reaction rate of an enzymatic reaction is always fastest at the beginning of the reaction when there is the greatest concentration of substrate. Why? 10
- 11. Effect of Increasing Substrate Concentration 11
- 12. Effect of Increasing Temperature and Reaction Rates 12
- 13. Effect of Varying pH and Enzymatic Reaction Rates 13
- 14. Effect of Competitive Inhibitors and Enzymatic Reaction Rates 14
- 15. Effect of Noncompetitive Inhibitors and Enzymatic Reaction Rates 15
- 16. Effect of Allosteric Regulation 16
- 18. Cooperativity 18
Editor's Notes
- As the hydrogen gas and oxygen gas bonds are broken and new ones are formed the system has a net loss of free energy. In a system, such as the Hindenburg, that energy is released as heat and light. However, unlike the Hindenburg, where a spark provided the energy of activation, the combining of hydrogen and oxygen to make water during cellular respiration cannot rely on heat for the energy of activation. Heat energy would cause molecules such as proteins to decompose. Cells must rely on catalysts, which are molecules that speed up a chemical reaction without being consumed in the chemical reaction. Most inorganic catalysts provide a surface on which the chemical reaction can take place and thereby lower the amount of activation energy required to a more cell friendly quantity. Organic catalysts come in the form of proteins (or RNA molecules).
- Most enzymes are proteins, but recently it had been discovered that certain molecules of RNA can also have enzymatic properties. Terms Substrate- These are reactants that interact with the enzyme during a biochemical reaction. Active site- This is the part of the enzyme actually involved in the chemical reaction.
- Note that names of molecules ending in the suffix –ase are enzymes.
- The graph represents the amount of product formed. At first, the amount of product formed increases, then the rate slows down as the concentration of substrate decreases. The fastest rate of product formation is at the beginning and is called the initial velocity. Ask students to explain why, logically, this has to be true. (i.e. more likely to get an effective collision between enzyme and substrate molecules if there are more substrate molecules present; as in the beginning of the reaction.) If the enzyme is kept constant and there is an increase in the amount of substrate, there will be an increase in the initial velocity until a saturation point is reached.
- The previous experiment is repeated with the same amount of enzyme but increasing amount of substrate. The initial velocities increase because there is more substrate to attach the enzyme ,but eventually there is no increase in initial velocity because all of the enzymes have become saturated with substrate. If the enzyme is kept constant and there is an increase in the amount of substrate, there will be an increase in the initial velocity until a saturation point is reached.
- There are many factors that can affect the reaction rates of enzymes. Temperature- at first an increase in temperature will increase the reaction rate because of the kinetics of the reaction, but after a certain temperature is reached, the hydrogen bonds fall apart and the enzyme will denature. Notice that with thermophiles natural selection has favored enzymes that can tolerate higher temperatures. For these bacteria, the optimum temperature is 70o C for most of their enzymatic reactions.
- 2. pH can also affect the reaction rates. Most enzymes work best at a range of 6 to 8, but there are some exceptions, such as pepsin. If the environment changes much from the optimum pH, again hydrogen bonds are affected, denaturing the enzyme. Notice that this is more of a bell shaped curve because both an increase and a decrease in pH from the optimum can denature the enzyme. Sometimes the hydrogen bonds that are affected are not at the active site and therefore the enzyme will still work. As the pH moves further from the optimum pH, it increases the likelihood that the active site is disrupted.
- Enzyme inhibitors- Some chemicals inhibit the action of an enzyme. A competitive inhibitor is a molecule that resembles the substrate enough that it can bind to the active site in place of the substrate. This will slow down the reaction rate as a certain percentage of the enzyme will combine with the inhibitor.
- A noncompetitive inhibitor is one that does not bind to the receptor site but to some other place on the molecule causing a conformational change in the enzyme (protein). This causes the active site to change shape so that substrate cannot bind. This also slows down the reaction rate.
- 4. Allosteric Regulation-= regulation by changing the structure of a molecule (allosteric = Greek for “different structure”). Such enzymes have two or more polypeptide chains each with its own active site. This enzyme also has two conformations-one with a functional active site and the other with a nonfunctional active site. This enzyme also has a place for the binding of an activator and an inhibitor. The activator will stabilize the conformation with the functional active site and the inhibitor will stabilize the inactive form of the enzyme.
- 5. Feedback inhibition- Usually enzymes work in biochemical pathways in which there are a series of intermediate chemical reactions that occur in order to get from point A (reactants) to point B (products). It is not unusual for an end product to act as an inhibitor to shut down the pathway when there is sufficient product present.
- 6. Cooperativity- This occurs when there are two or more sub-units to an enzyme, each with its own active site. When one substrate binds with one active site, the enzyme changes conformation so that the binding of other substrates are easier to achieve.