This document outlines the key topics in Chapter 5 of the textbook for the MCE 440 - Vibrations course taught by Eng. Omar Al-Ostah. The chapter discusses 2 degree of freedom (DOF) systems, including:
1) Developing the equations of motion for a 2 DOF spring-mass-damper system using Newton's second law applied to each mass.
2) Expressing the equations of motion in matrix form using the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices.
3) Analyzing the frequency response and complex frequency response of a damped 2 DOF system under harmonic forcing.
4) Working through an example problem of a plate supporting a pump.




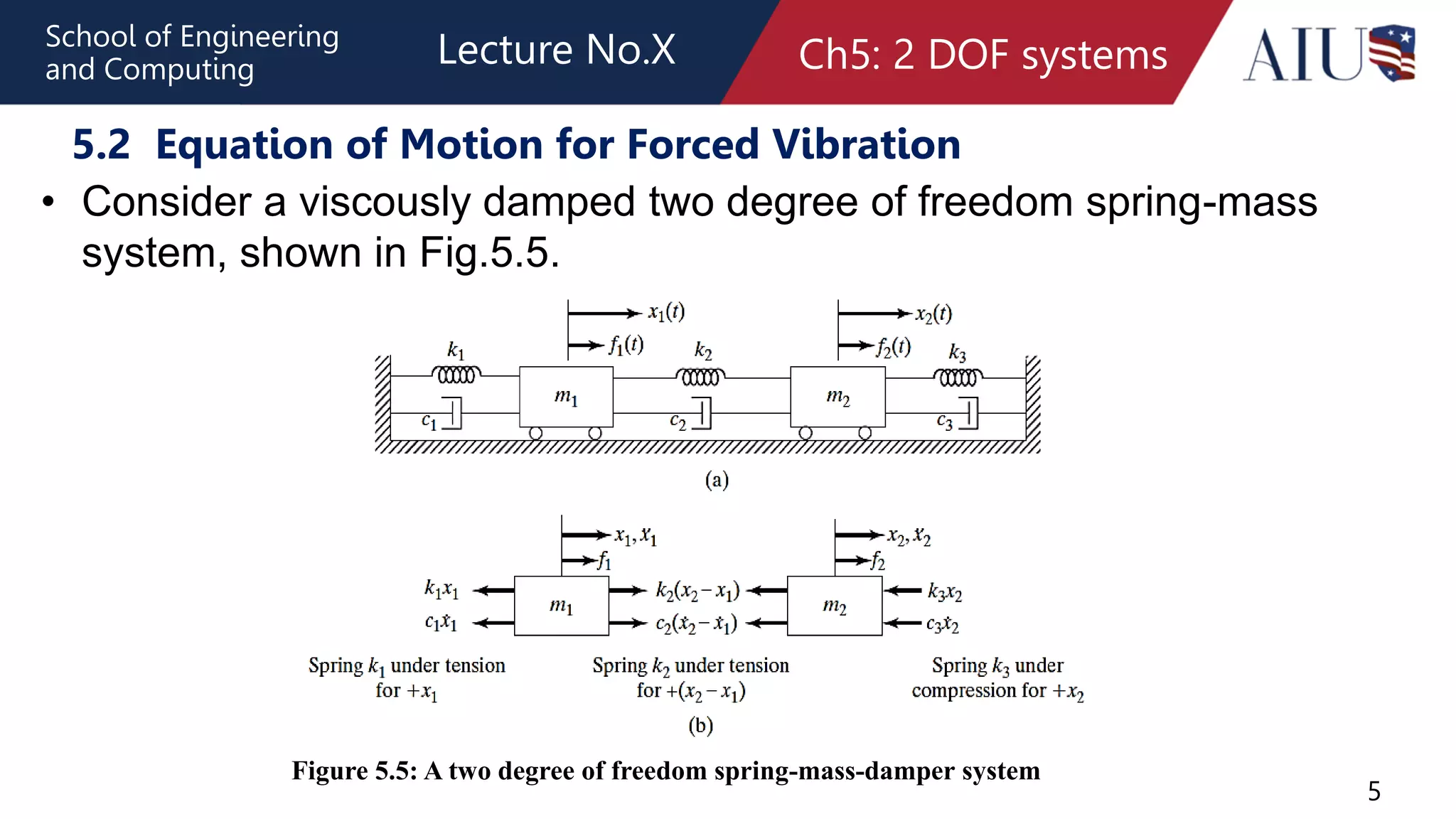
![6
Lecture No.X
School of Engineering
and Computing Ch5: 2 DOF systems
5.2 Equation of Motion for Forced Vibration
The application of Newton’s second law of motion to each of the
masses gives the equations of motion:
)
2
.
5
(
)
(
)
(
)
1
.
5
(
)
(
)
(
2
2
3
2
1
2
2
3
2
1
2
2
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
F
x
k
k
x
k
x
c
c
x
c
x
m
F
x
k
x
k
k
x
c
x
c
c
x
m
)
3
.
5
(
)
(
)
(
]
[
)
(
]
[
)
(
]
[ t
F
t
x
k
t
x
c
t
x
m
Both equations can be written in matrix form as
where [m], [c], and [k] are called the mass, damping, and stiffness
matrices, respectively, and are given by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5twodegreeoffreedomsystemsall-230719233104-23d1064e/75/Chapter5-two-degree-of-freedom-systems_All-pptx-6-2048.jpg)









