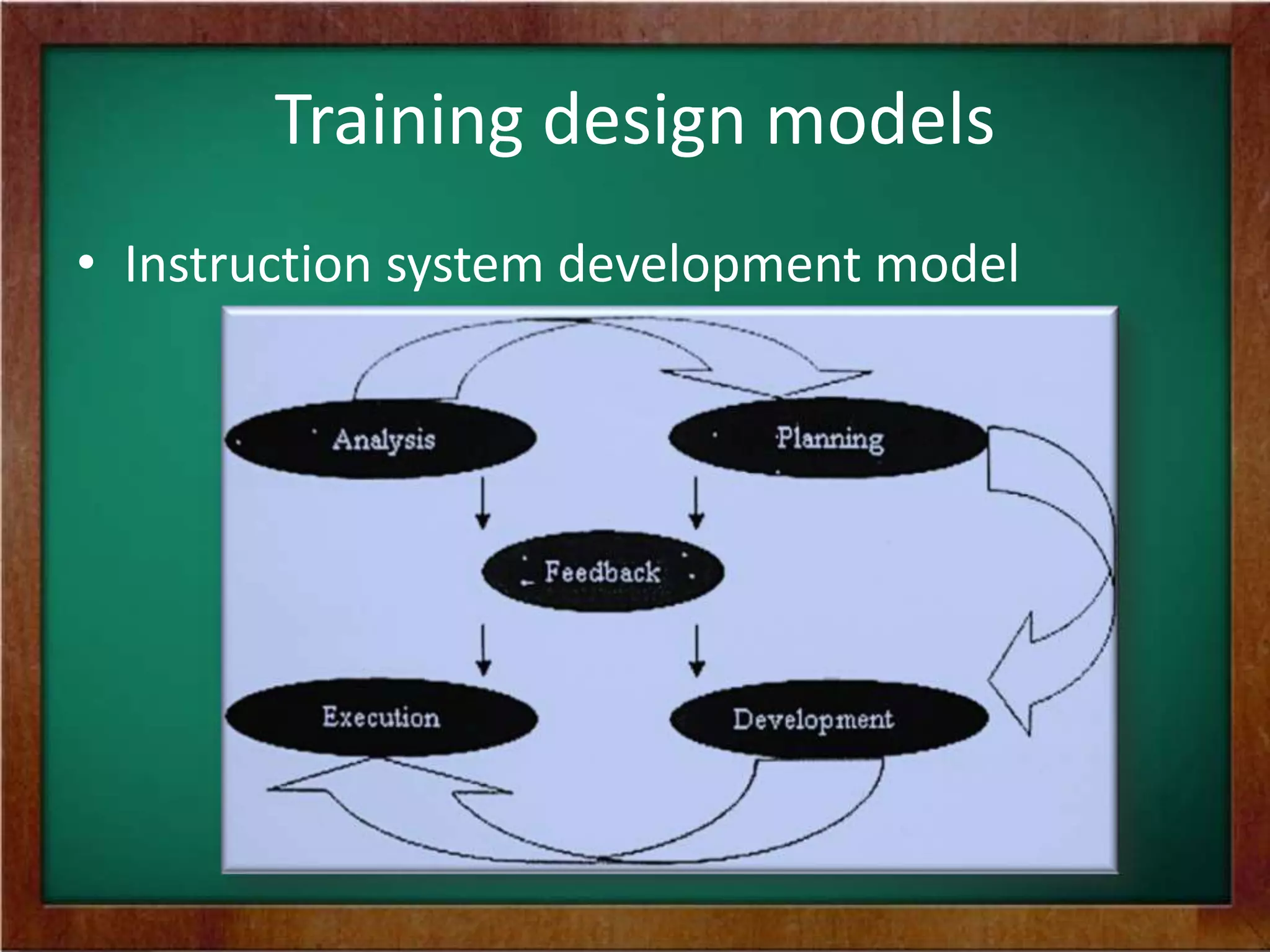
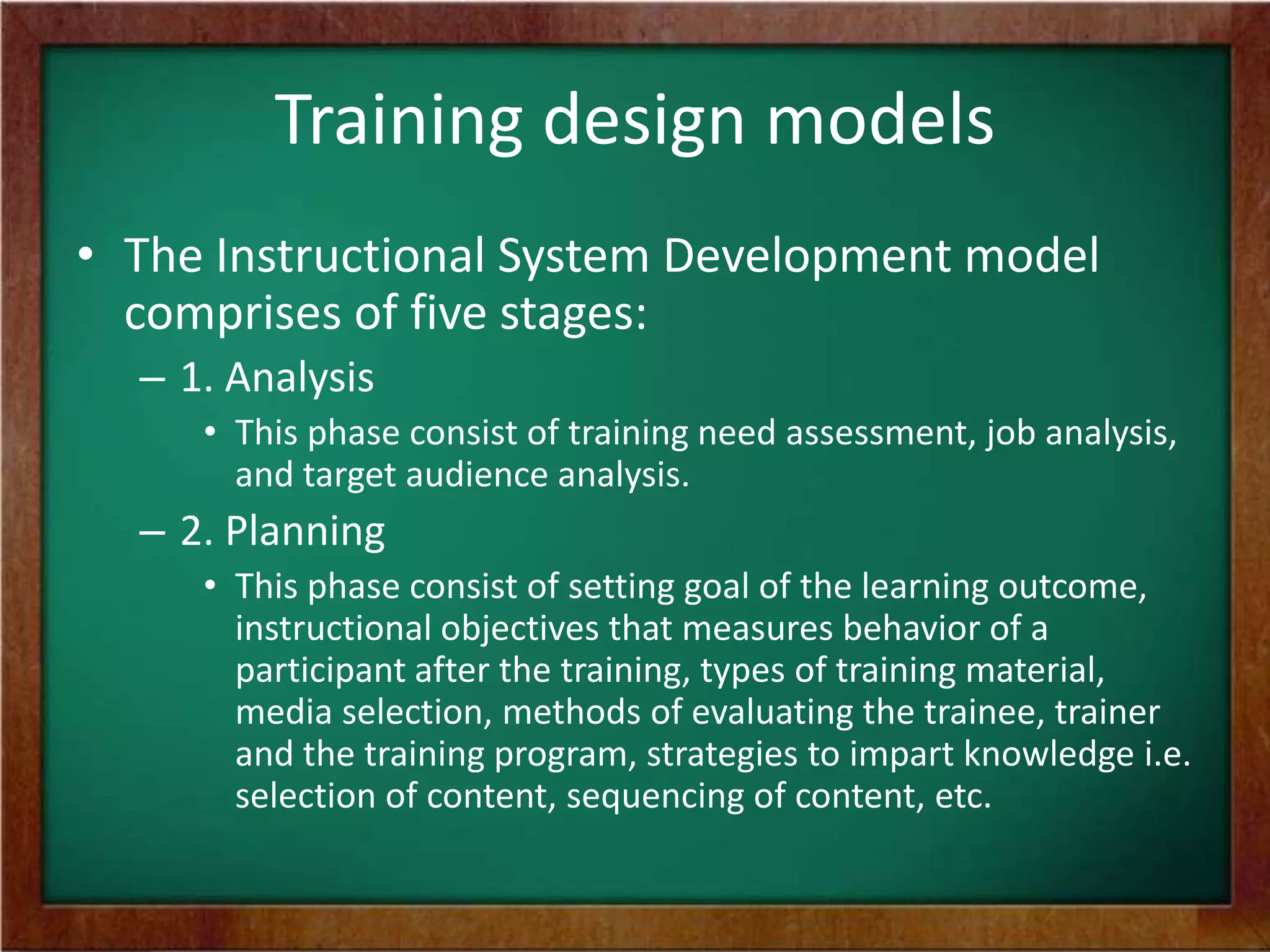
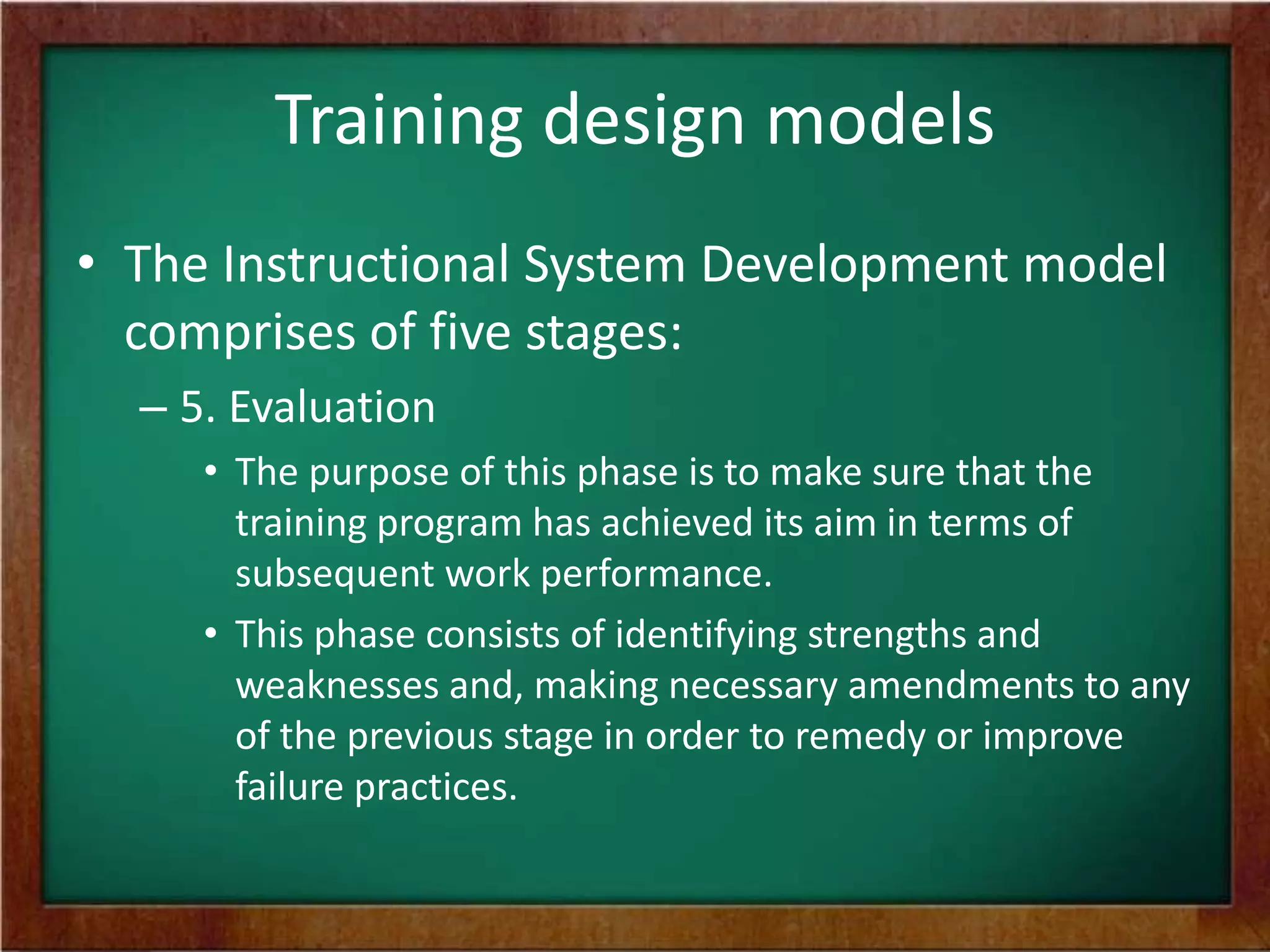
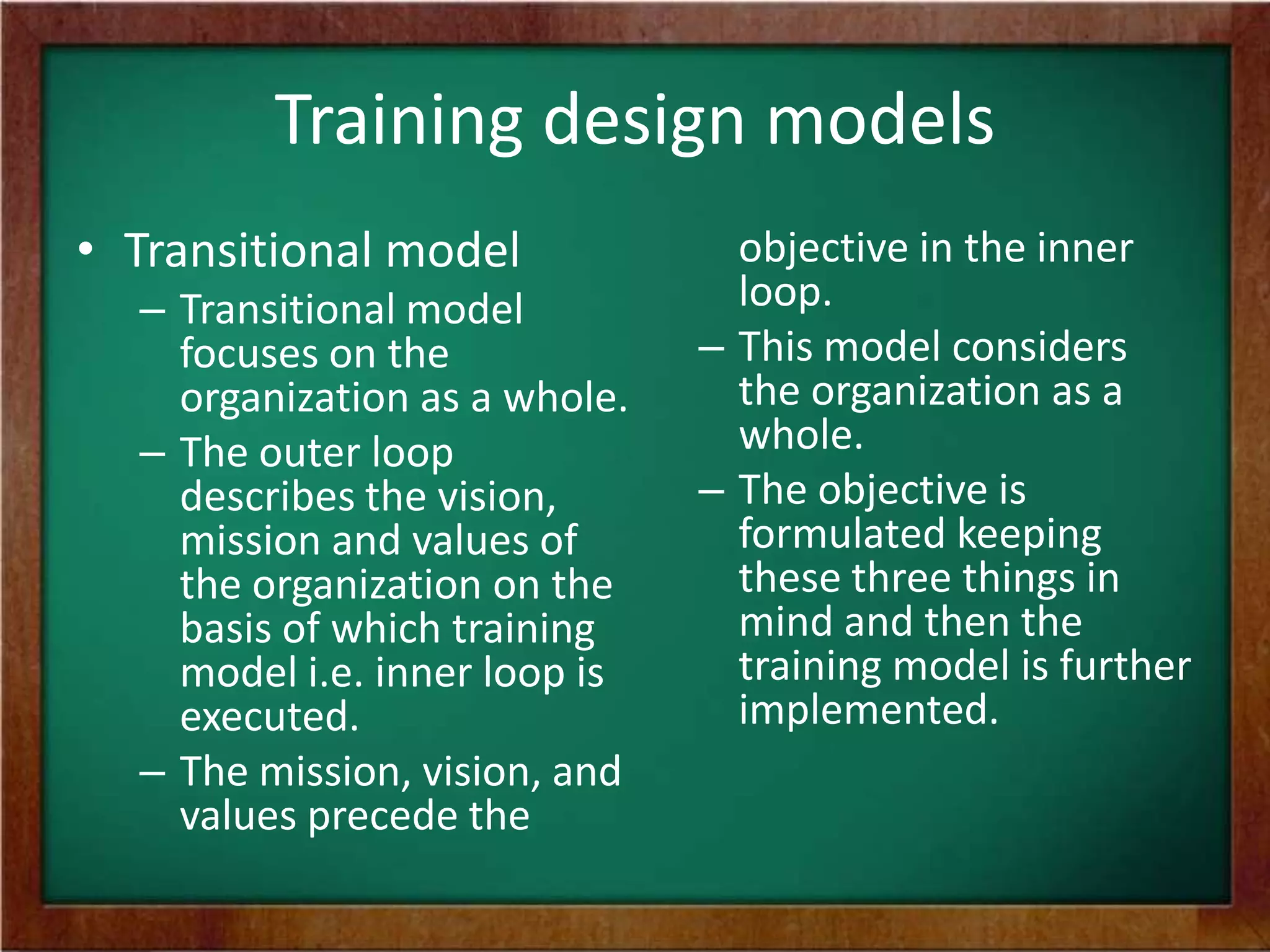
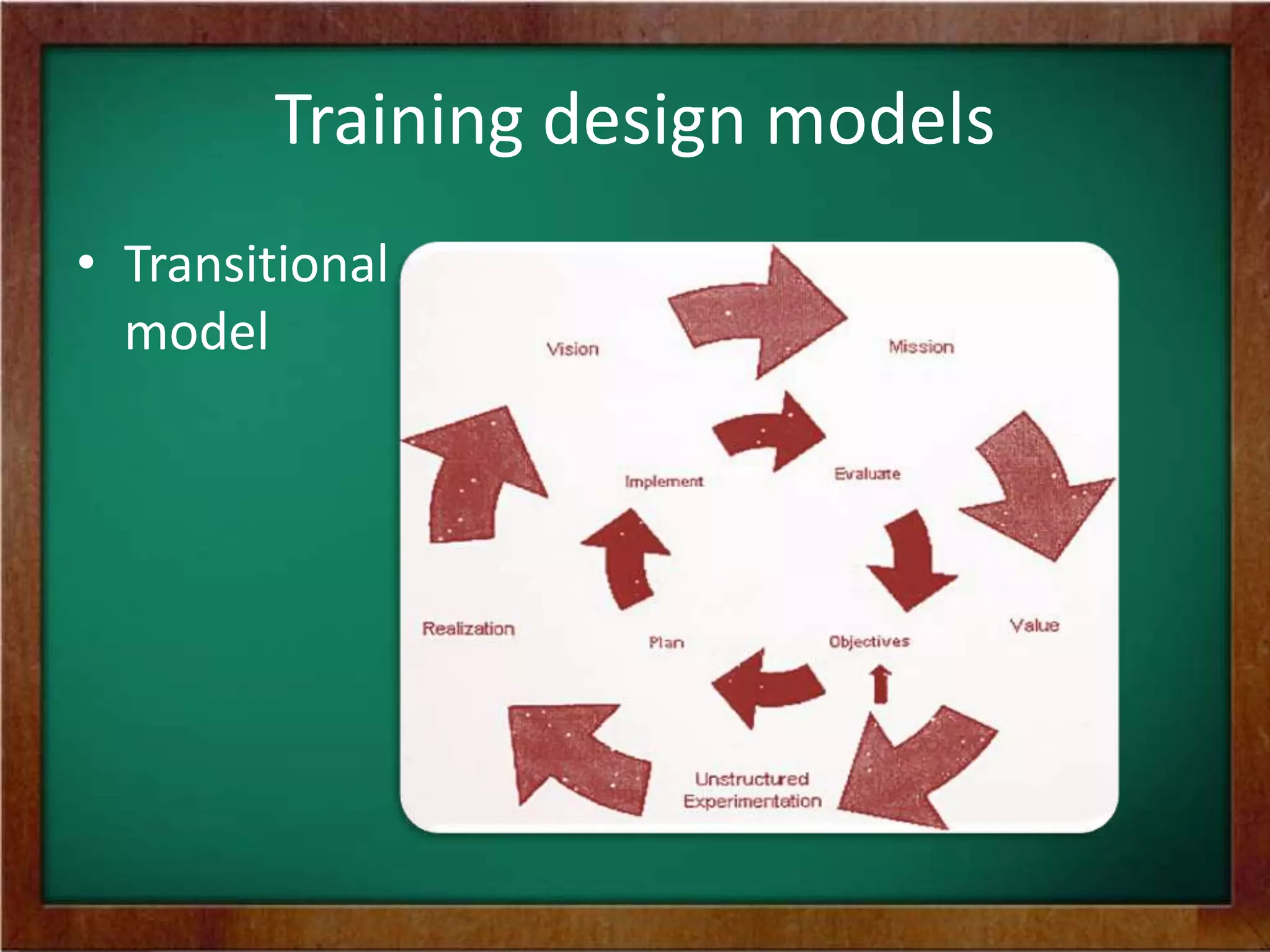
The document discusses the process of designing training programs. It begins by defining training design and its significance as a planning process that involves analyzing training needs, defining outcomes, and developing a plan to achieve those outcomes. It then outlines two common models for training design: the instructional systems development model, which is a five-stage process, and the transitional model, which focuses on aligning training with organizational vision, mission, and values. Key factors to consider in training design include trainee characteristics, resources, and motivational dynamics. The process of design involves identifying objectives, content, methods, activities, and evaluation criteria, as well as planning follow-up activities.