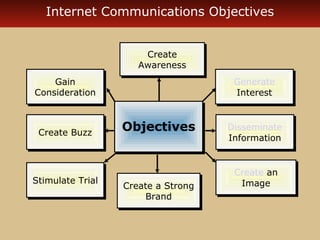
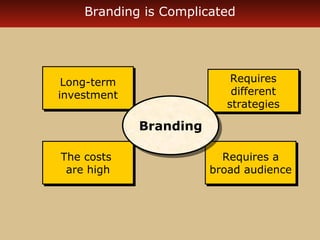
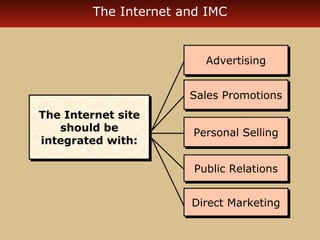
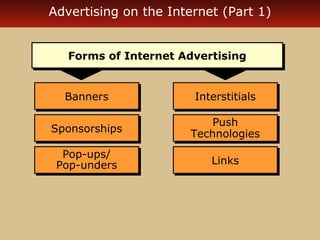
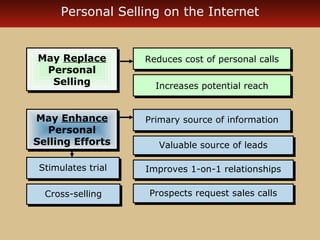
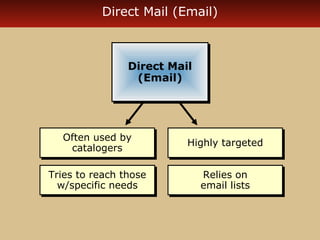
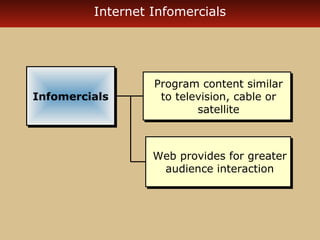
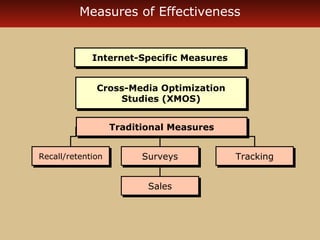
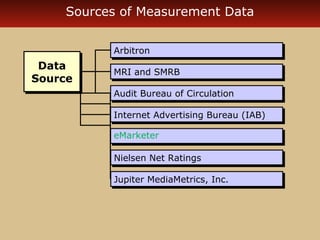
Internet advertising grew rapidly between 1999-2006, reaching $10 billion in 2005 and $16.9 billion in 2006. Various forms of internet advertising include banners, sponsorships, pop-ups, push technologies, and links. The internet can be integrated with advertising, sales promotions, personal selling, public relations, and direct marketing as part of an interactive marketing communications program. Both consumers and businesses have seen fast growth in e-commerce purchases over the internet.