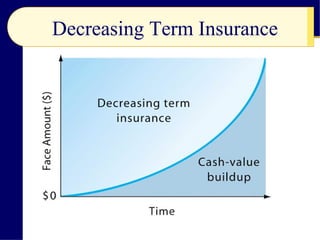
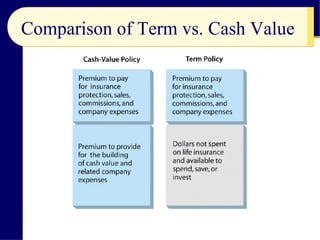
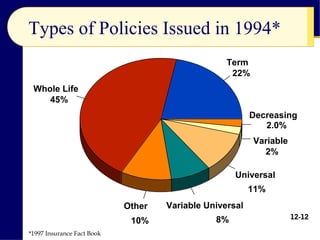
The document discusses life insurance planning, including the purposes of life insurance, calculating insurance needs, and different types of policies. It covers term life insurance, whole life insurance, and other policy types. Key points include determining insurance needs based on income and dependents, comparing costs and returns of policies, and choosing beneficiaries and settlement options. The document provides an overview of important considerations for life insurance planning.