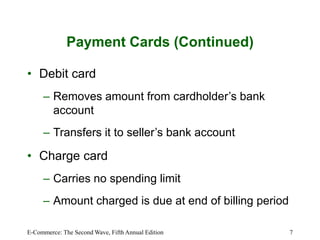
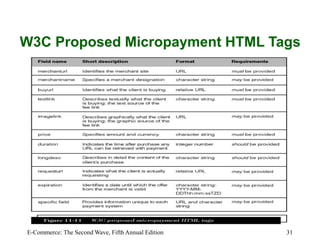
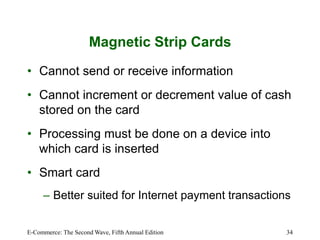
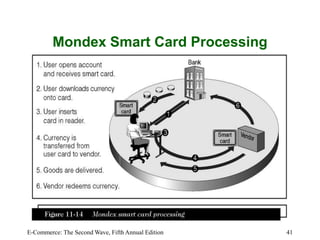
This chapter discusses online payment systems, including payment cards, electronic cash, electronic wallets, and stored-value cards. It covers how payment cards work for online transactions and the roles of different parties in processing payments. Electronic cash aims to facilitate micropayments but has faced challenges regarding security, anonymity and adoption. Electronic wallets and smart cards can store payment details to streamline online checkout.