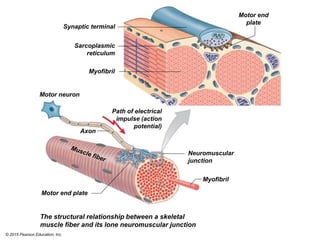
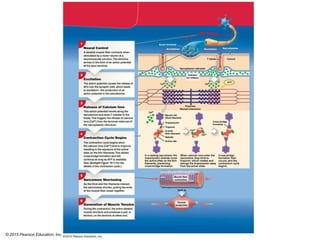
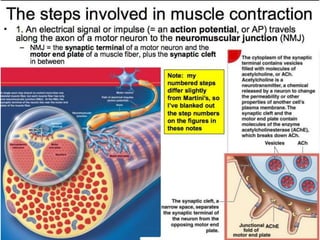
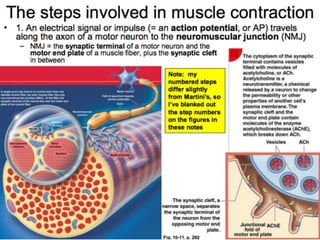
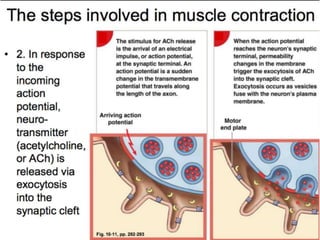
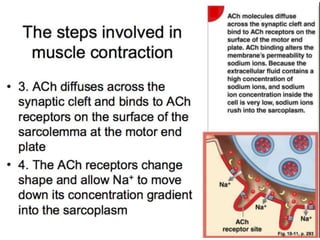
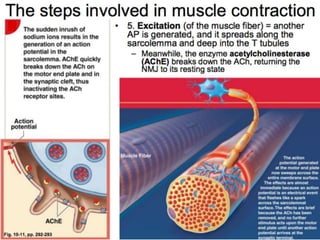
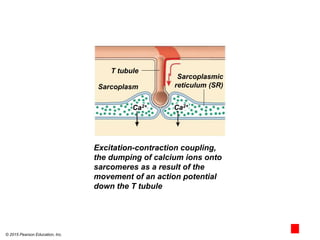
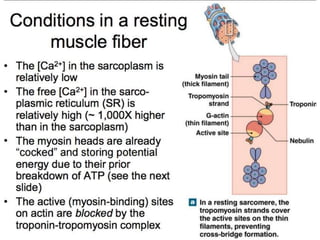
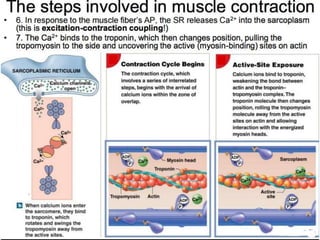
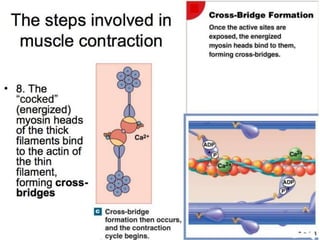
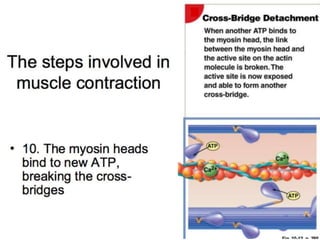
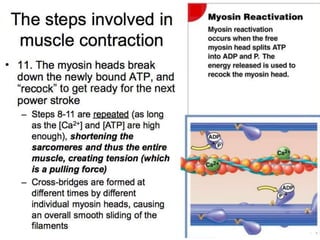
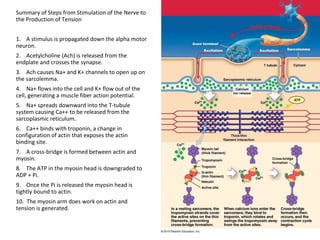
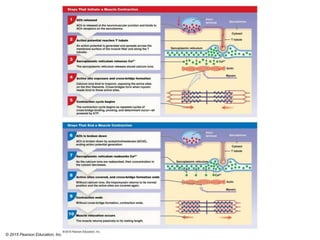
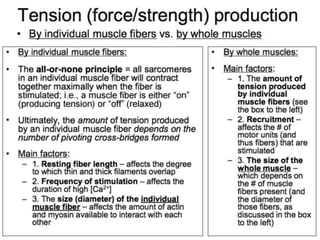
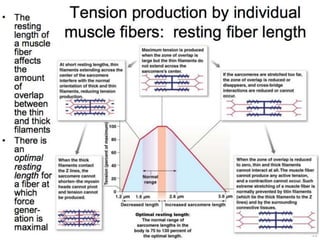
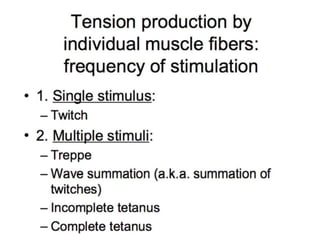
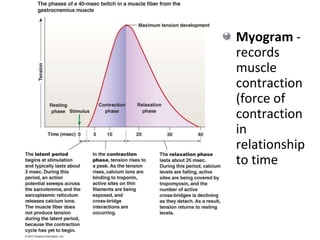
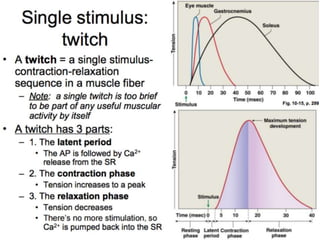
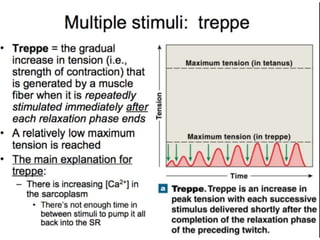
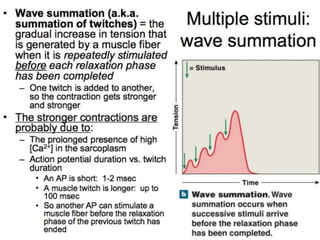
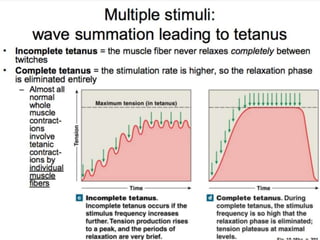
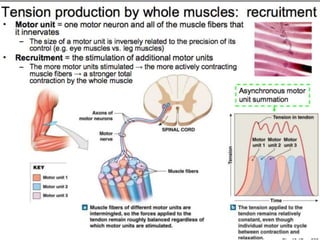
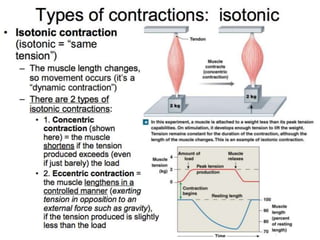
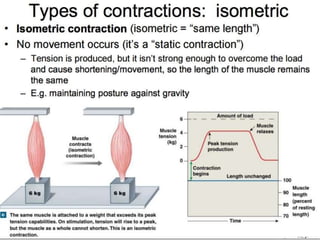
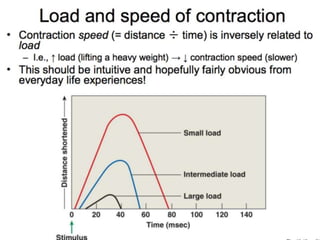
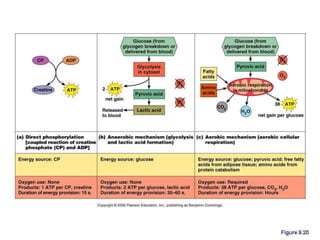
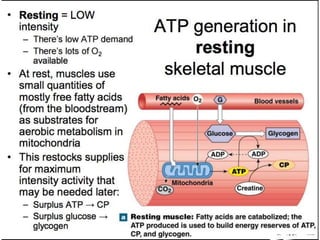
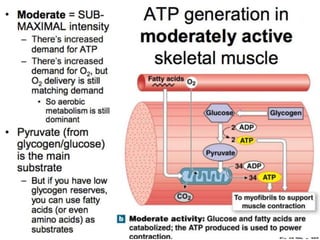
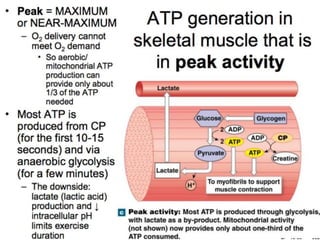
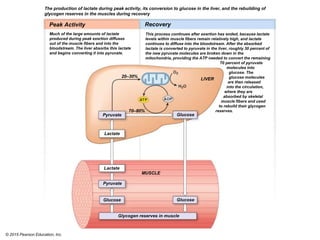
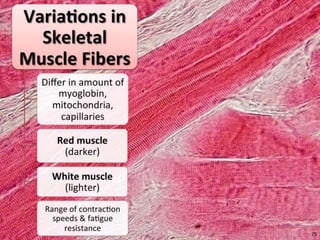
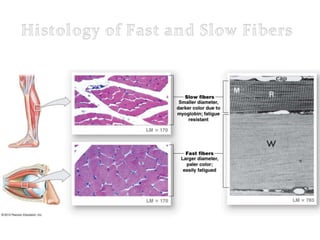
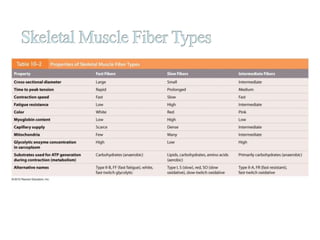
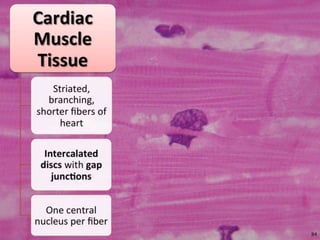
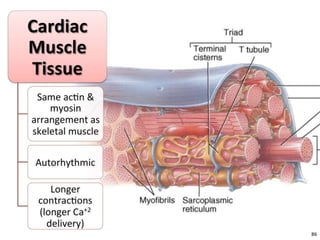
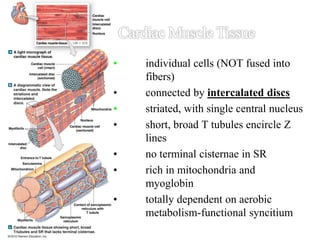
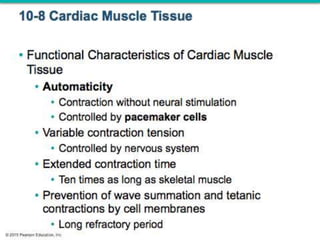
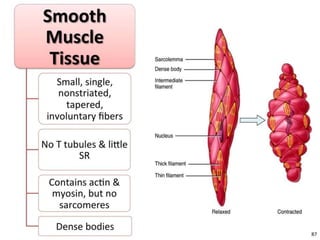
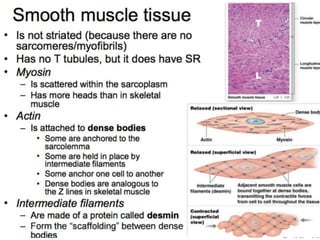
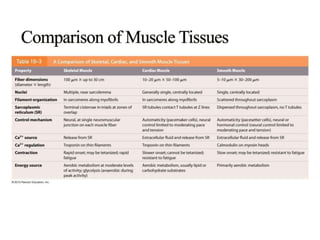
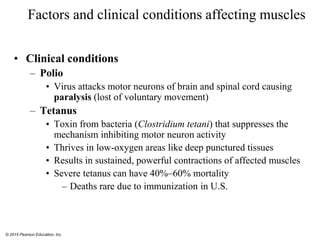
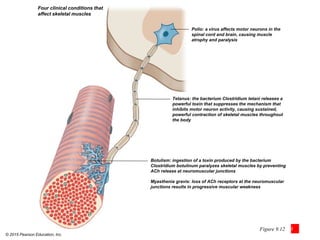
The document discusses skeletal muscle contraction and the neuromuscular junction. It describes how a motor neuron impulse stimulates a muscle fiber, causing the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. This triggers an action potential in the muscle fiber membrane and the subsequent release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, activating muscle contraction. It also summarizes the steps involved in muscle tension generation and lists several clinical conditions that can affect skeletal muscle function such as polio, tetanus, botulism, and myasthenia gravis.