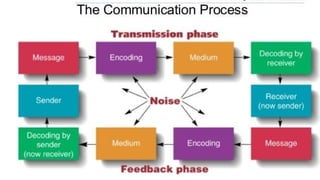
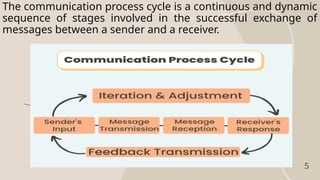
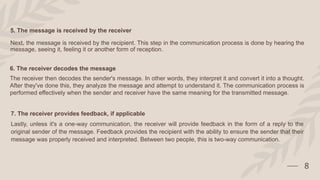
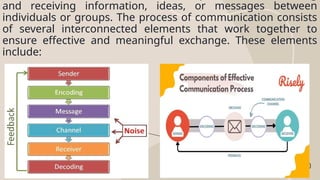
The document outlines the communication process, detailing its cyclical nature and essential components like sender, message, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. It describes the seven steps involved in effective communication, emphasizing the importance of clarity, active listening, and understanding the audience. Additionally, it provides tips for improving communication skills to enhance the overall exchange of information.