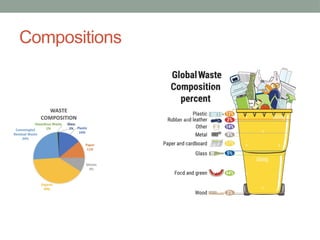
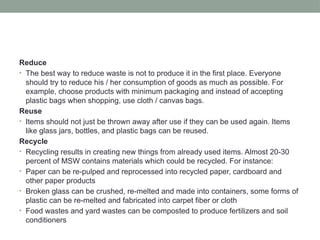
The document discusses solid waste management, focusing on various waste disposal methods and the environmental issues caused by improper waste handling. It highlights the composition of municipal solid waste in Pakistan, major problems related to waste management, and the health hazards associated with it. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of the '3 R's'—reduce, reuse, recycle—as effective strategies to address the solid waste problem.