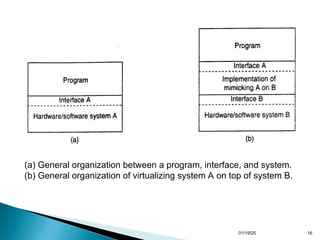
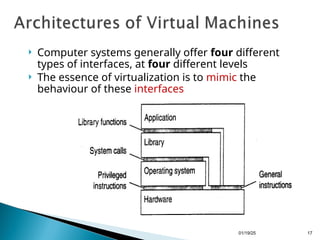
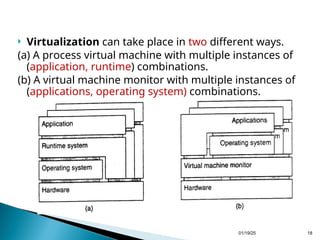
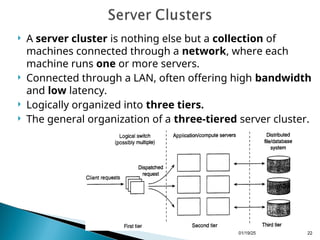
Chapter 3 discusses processes and threads within distributed systems, highlighting their roles in execution, scheduling, and code migration for scalability. It emphasizes the significance of multithreading in achieving high performance and resource virtualization, while explaining server-client interactions and the need for distribution transparency. Additionally, it outlines the design of multithreaded servers and the structure of server clusters, underscoring the complexities of process migration.