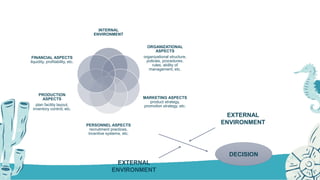
The document discusses decision making in management. It begins by outlining the objectives of understanding decision making and examines the steps in the decision making process. It then defines decision making as identifying and choosing alternative courses of action to solve problems. The key steps in the decision making process are: 1) diagnosing the problem, 2) analyzing the internal and external environment, 3) developing viable alternatives, 4) evaluating alternatives, 5) making a choice, 6) implementing the decision, and 7) evaluating and adapting the decision results using feedback. The document also discusses qualitative and quantitative approaches to decision making and provides examples of quantitative techniques.