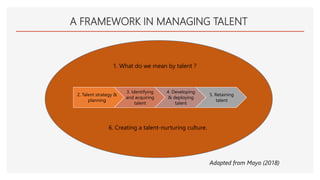
The document discusses the importance of HR analytics for talent management. It begins by defining talent and talent management, explaining that talent management is a continuous process of sourcing, hiring, developing, retaining and promoting employees. It then discusses how HR analytics can help with various aspects of talent management, including talent strategy and planning, identifying and acquiring talent, developing and deploying talent, and retaining talent. Some key implications of HR analytics for talent management are that it will make the HR function more strategic and data-driven, require better quality HR data, impact the tools used, and change long-held beliefs by analyzing outcomes.