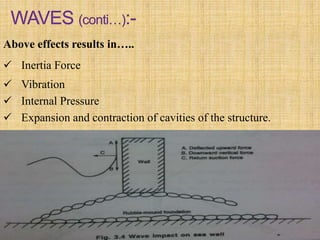
This document discusses various oceanographic concepts including wind, waves, tides, and currents. It defines wind as the horizontal movement of air due to differences in air pressure. Waves are generated by the transfer of energy from wind blowing over water. Tides are the rise and fall of ocean waters caused by the gravitational forces of the sun and moon. Currents refer to the horizontal movement of water which can be caused by factors such as tides, wind, and temperature differences. The document provides details on the characteristics and types of each of these concepts.