Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times



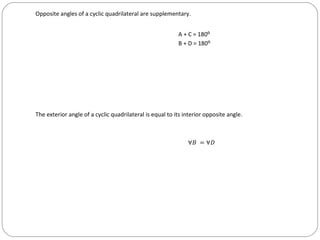

The document discusses properties of circles and angles related to circles. It defines the diameter as the axis of symmetry and explains that a radius perpendicular to a chord divides it into two equal parts. It also states that angles subtended by the same or equal length arcs are equal both at the circumference and at the center, and that the angle at the center is twice the angle at the circumference for the same arc. Additionally, it says that for a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles are supplementary and an exterior angle equals the interior opposite angle.



