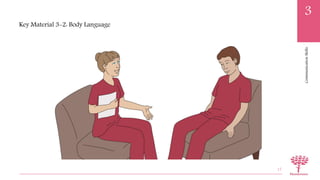
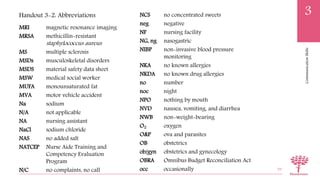
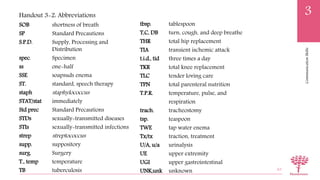
This document defines important medical terminology used in communication, including prefixes, roots, and suffixes. It explains that medical terms are made up of word parts including roots, which provide the basic meaning, prefixes which come before the root, and suffixes which are added to the end. Examples of each part are provided, as well as how they are combined to form medical terms. The document also lists common medical prefixes, roots, and suffixes and their meanings to help understand terminology.