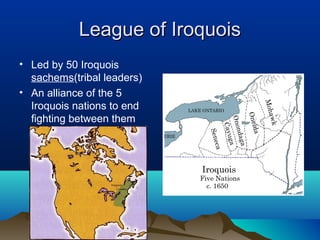
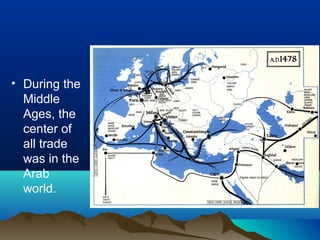
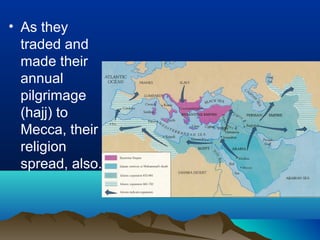
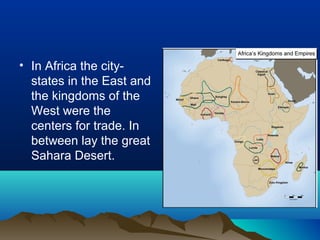
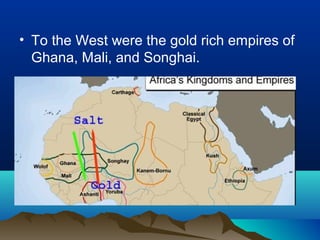
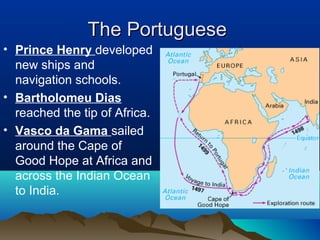
Native cultures across North America shared some common traits, such as a deep respect for nature and belief in maintaining balance. They were also diverse, with different environments and livelihoods. For example, the Anasazi built houses out of adobe in the dry Southwest, while the Iroquois formed a political alliance in the woodlands of New York. Trade networks also connected cultures across Africa, Asia, the Middle East and Europe during this time period. The rise of Islam spread religion and language along trade routes like the Silk Road. In Europe, Greeks developed democracy while the Roman Empire spread through law and a common Latin language. The Crusades and later explorers like da Gama opened new trade opportunities between Europe and Asia