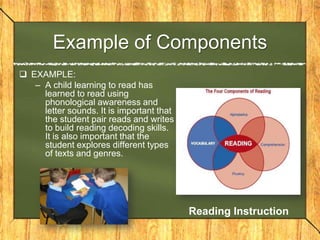
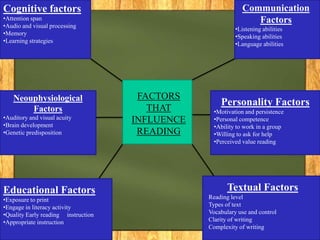
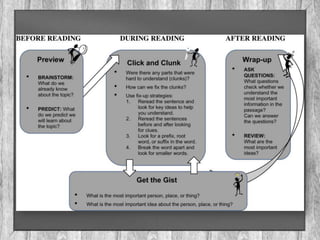
This document contains a summary of a presentation on current trends in reading and reading instruction. It discusses the goal of reading instruction as providing students with skills, strategies and knowledge to read fluently and comprehend text. It covers topics like phonological awareness, phonics instruction, word identification strategies, comprehension strategies, assessing struggling readers, and providing intensive instruction. Effective strategies discussed include establishing an environment to promote reading, using assessments to monitor progress, and obtaining early intervention when needed. The document also discusses factors that influence reading and strategies for teaching older readers.