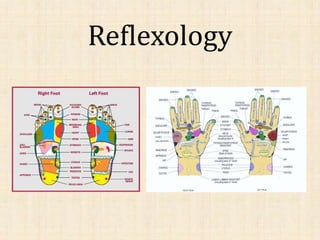
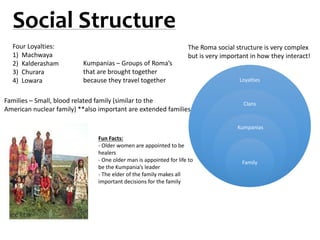
The document discusses health beliefs and practices of the Roma (Gypsy) culture. It describes their social structure as being based on clans and families, with elders holding important roles. Roma attribute health and illness to ideas of purity and fortune. Traditional healers treat Roma illnesses, while mainstream doctors treat those brought by non-Romas. Rituals and herbal remedies are used. High rates of smoking, obesity and infectious diseases pose risks. Providing separate clean/unclean items and building trust are important for health promotion in this ethnocentric culture.