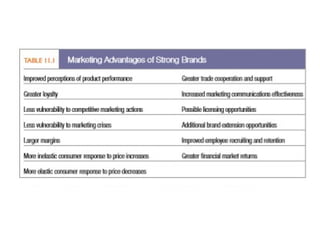
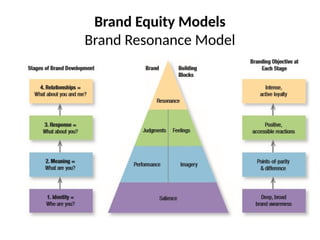
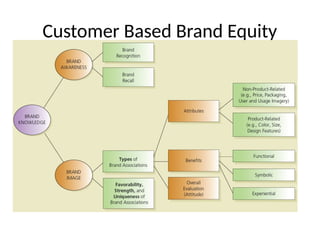
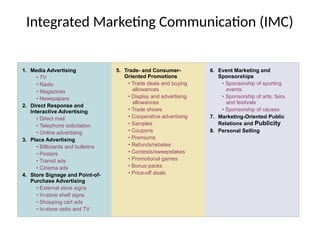
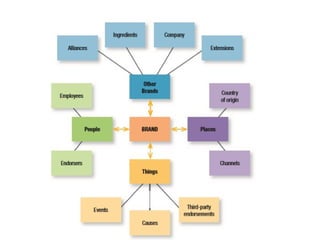
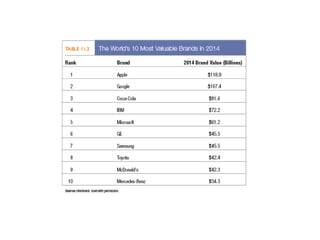
The document discusses the significance of brand equity as a valuable intangible asset for firms, defined as the added value associated with a brand. It highlights how brands help consumers identify products, reduce risks, and signal quality, while also providing firms with competitive advantages and financial returns. The document outlines the elements of strong brand equity, models of consumer response, and strategies for building brand equity through various marketing communications and promotional activities.