Embed presentation
Download to read offline


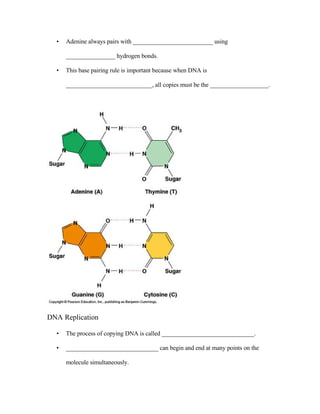

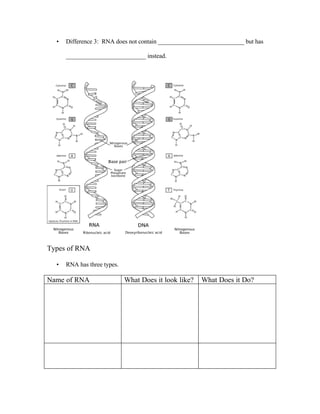





The document provides information on the structure and function of DNA and the process of protein synthesis. It discusses how DNA is made up of nucleotides containing nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphates. It also describes the double helix structure of DNA and how base pairing allows for DNA replication. The process of transcription is explained, where DNA is copied into mRNA which is then translated by ribosomes to synthesize proteins according to the genetic code. Mutations can potentially cause errors in protein synthesis leading to diseases.








