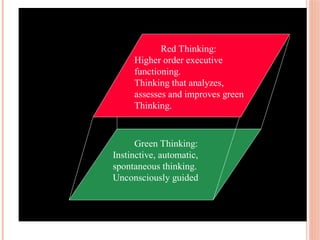
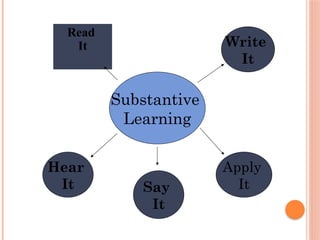
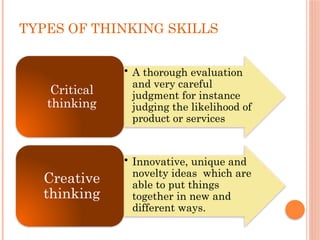
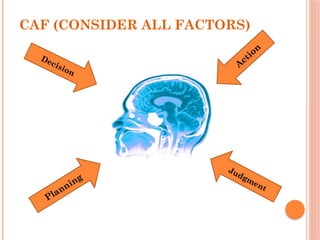
The document discusses thinking skills, emphasizing the importance of both creative and critical thinking in learning and problem-solving. It defines thinking skills and introduces metacognitive strategies to improve cognitive processes, including critical thinking's self-assessment and reflection. Additionally, it outlines various types of thinking skills and tools to aid in decision-making and planning.