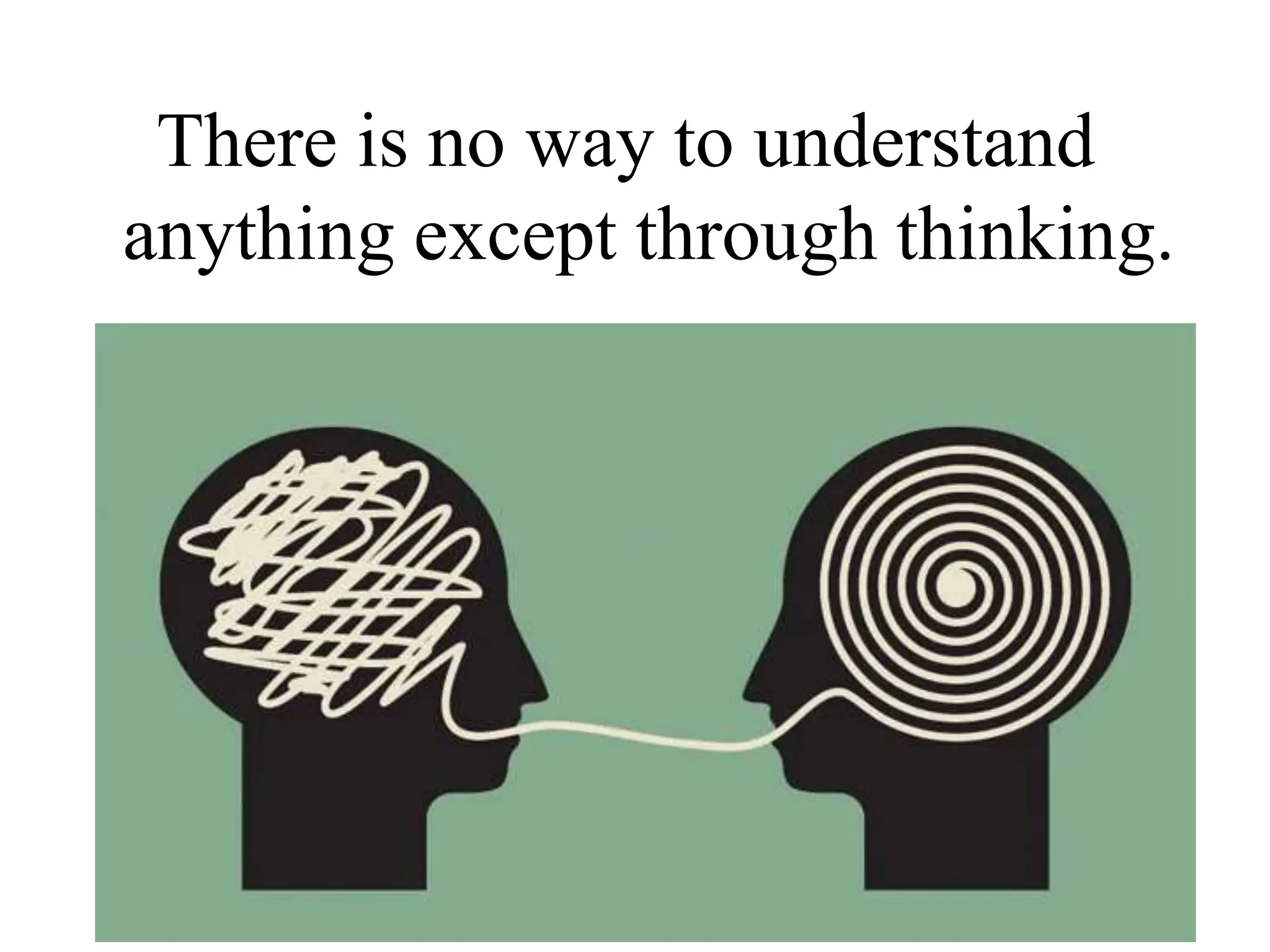
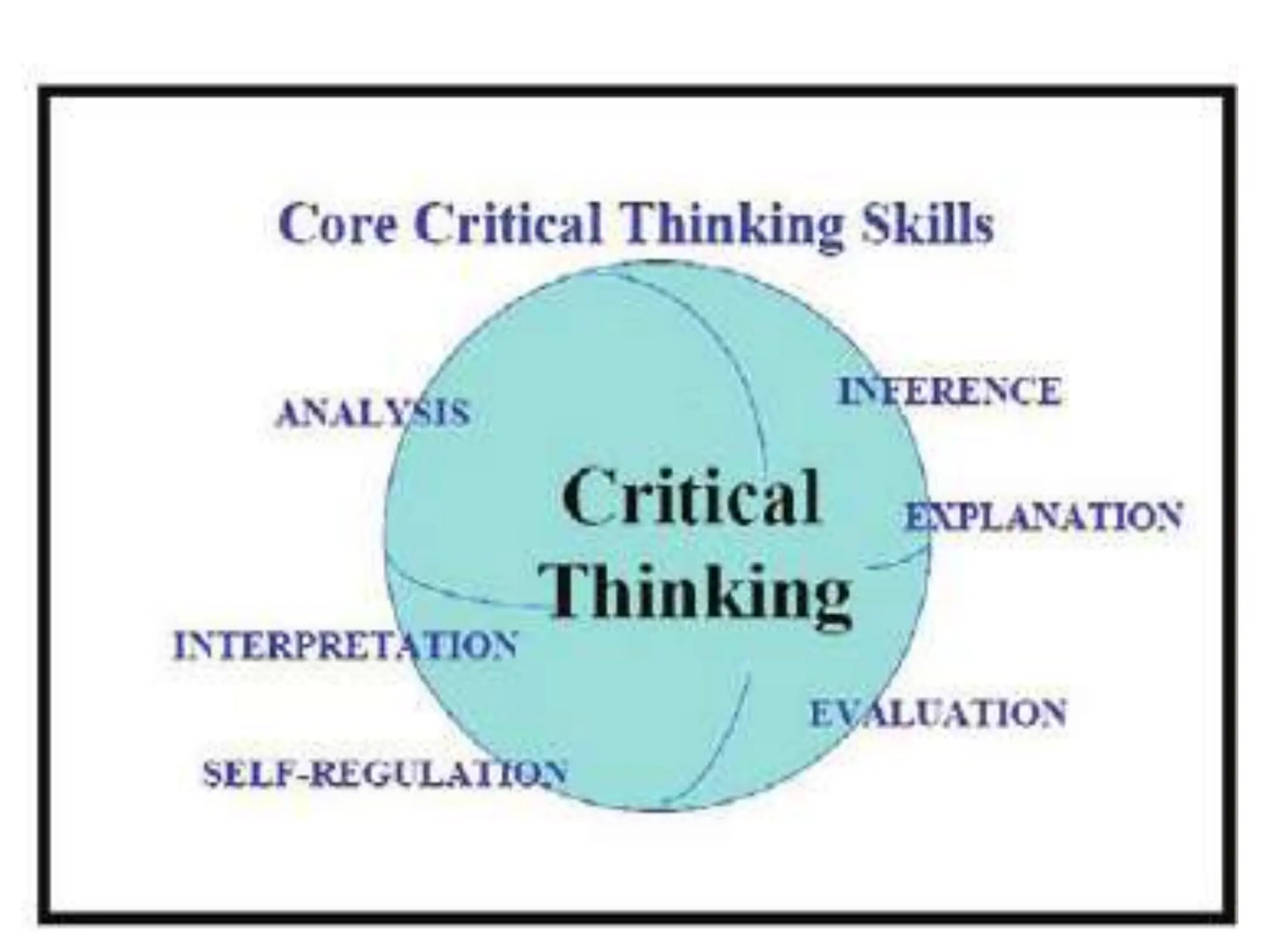
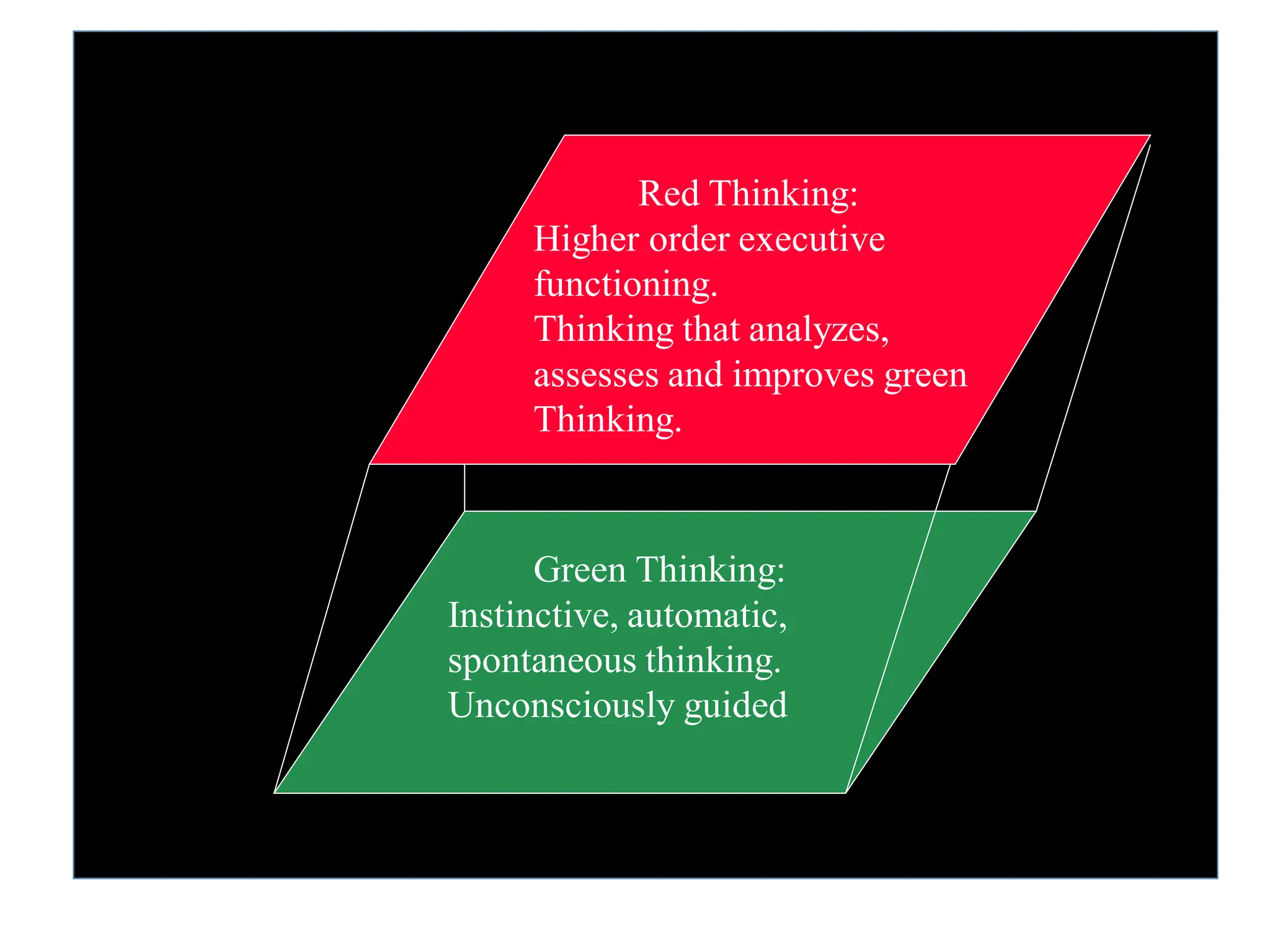
The document introduces critical thinking, emphasizing its importance in teaching and learning, and discusses the distinction between 'red thinking' (self-assessing, disciplined thought) and 'green thinking' (impulsive, unchecked thought). It highlights the role of critical thinking in understanding and analyzing human behavior and cognition, urging individuals to reflect on their own thinking processes. The text includes activities to evaluate and improve personal thinking quality and encourages self-assessment across various aspects of life.