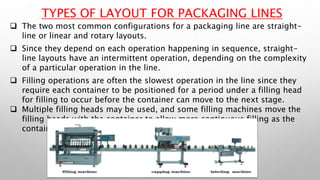
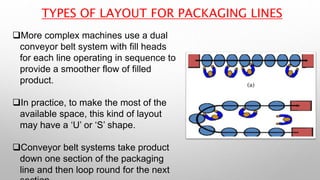
This document outlines the operation of a packaging line, detailing the steps involved in combining a product with its packaging, including key activities like filling, sealing, and labelling. It discusses the types of layouts (straight-line and rotary) and the importance of machine capability and conveyor alignment in maintaining efficiency. Various types of packaging materials are also described, emphasizing their roles in protection and marketing.