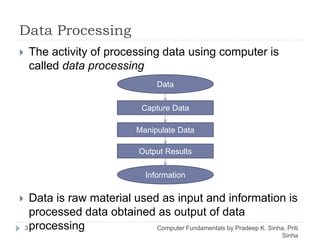
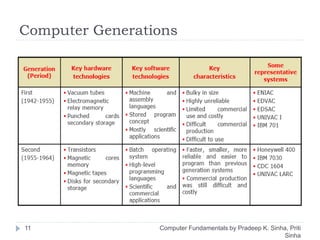
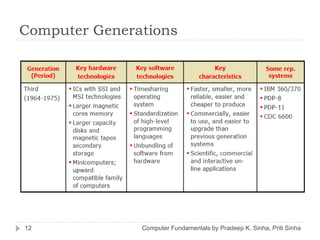
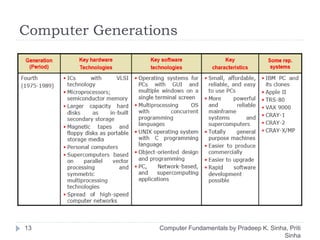
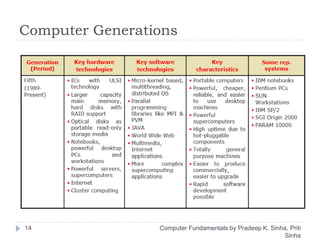
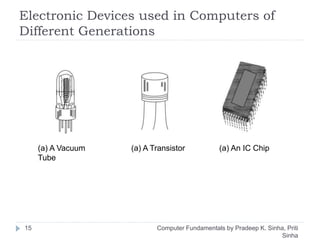
The document discusses the history and evolution of computers over multiple generations. It provides definitions of key terms like computer, data processing, and characteristics of computers such as automatic operation, speed, accuracy and more. Early computers mentioned include the Mark I Computer from 1937, the Atanasoff Berry Computer from 1939 and ENIAC from 1943. Generations of computers are defined with increasing capabilities from vacuum tubes in first generation to integrated circuits by the fourth generation providing faster and smaller devices.