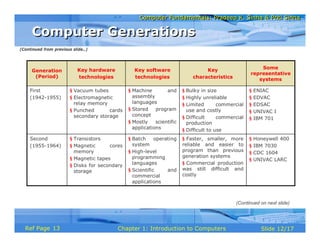
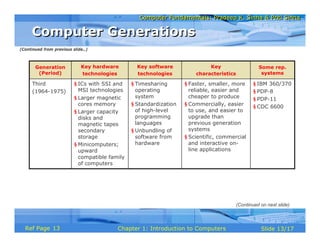
The document provides an introduction to computers, covering their definition, data processing, and important characteristics such as speed, accuracy, and versatility. It details the evolution of computers from early mechanical devices to modern digital systems across five generations, highlighting key advancements and technologies in each period. The text also emphasizes the significant figures and milestones in computer history.