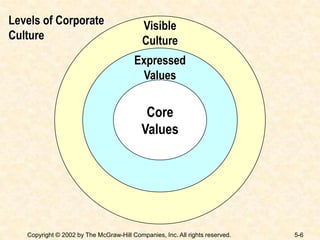
This document discusses organizational culture and change. It describes how organizational culture helps management achieve objectives through shared values, assumptions and norms. Cultural symbols, rituals, stories and heroes are used to sustain culture. There are different types of cultures that fit different personalities. The document also discusses forces that drive organizational change, models of change like Lewin's three-step model, and tactics managers can use to implement and deal with resistance to change.