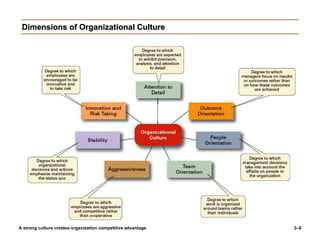
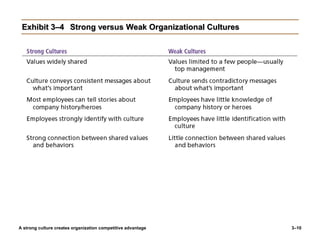
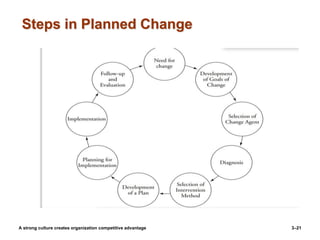
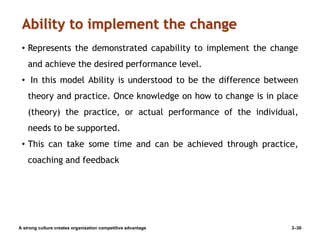
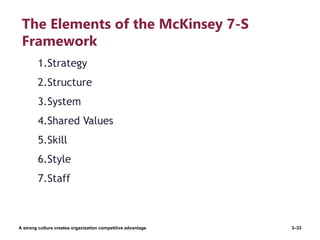
The document discusses organizational culture and change management. It defines organizational culture and describes its components. Strong cultures that have clearly defined and widely shared values can provide competitive advantages by increasing employee commitment and performance. The document also examines different types of organizational cultures and dimensions of culture. It then discusses managing cultural change, including reasons for change, planned and unplanned change, and models for managing change such as Lewin's three-stage model of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing as well as the ADKAR model of creating Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement of change. The McKinsey 7S model also provides a