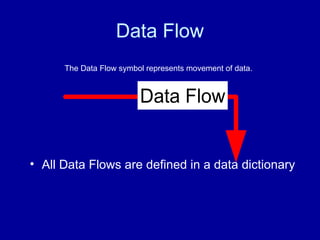
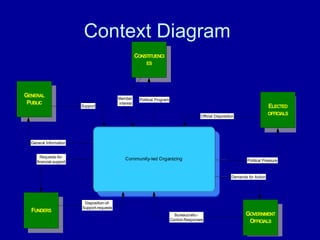
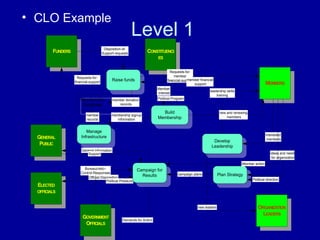
A data flow diagram (DFD) maps out the flow of information for any process or system. It uses defined symbols like rectangles, circles and arrows, plus short text labels, to show data inputs, outputs, storage points and the routes between each destination.